Marketing Analytics: Essentials of Cross-Selling and Upselling (with a case study)
Introduction
Cross selling and Upselling is one of the most widely discussed concept in marketing analytics. Every other day when you visit a supermarket, restaurant to purchase something, this concept comes into live action. This concept is being taught in every marketing class across the world, thereby students are expected to know of it.
You may be curiously wondering why we have selected this topic of “Cross-Sell”? Well, the answer to this is very obvious. In our experience (spawning several decades) of setting up and training teams, we have conducted hundreds of interviews. And guess what? For our standard interview question of “Elaborate on a project you have worked on from start to end”, the most frequent response has been a Cross-Sell Model! However, when a lot of people were quizzed around the basic concepts of cross-sell / up-sell, they were unable to provide satisfactory answers. They would know the code used, but were unable to explain this simple concept.
So, here we are discussing our version of this popular and important Cross-Sell story! In order to explain the end to end process, we have also provided a case study in the second half of the article. We hope that this article becomes a ready reference for any one interested in implementing cross-sell / up-sell in their organization.
Definition – Cross-Sell and Up-Sell
Cross-sell involves the sale of multiple products offered by a single product/service provider to a new or existing customer. Up-sell is selling higher value products/services to an existing customer.
For example:
- You plan to purchase a mobile phone within a price range of Rs. 30,000(~$500). However, you eventually end up purchasing a mobile phone of Rs.42,000 ($650) because the salesman presented various other phones with fantastic features and you got swayed away with them. (This is Up-Selling).
- You plan to purchase a mobile phone worth Rs. 30,000(~$500), but the salesman offered you a charming deal of buying mobile phone with exclusive JBL headphones for Rs.40,000 (~$634) only and you again got swayed away. (This is Cross-Selling).
Cross-selling is a core component of a customer centric relationship strategy and requires an integrated view of the customer. The success of a cross-sell program depends on enablers such as organizational commitment; well-defined business strategy; effective execution; regular monitoring; and effective targeting strategy. Cross-selling has proved to be a defining strategy for profitable growth across multiple sectors.
Benefits of Cross Selling
Cross Selling offers benefit to both the ends of marketing cycle i.e. customer and firm.
For the Firm
- Builds customer equity
- Differentiates from competition, enhances market position
- Promotes diversification and innovation
- Stimulates universe expansion and entry into new markets
- Balances growth between new and existing customers, low and high margin products and segments
- Enhance customer profitability
- Discourages customer attrition, improves customer loyalty
For the Customer
- Patronizes the brand
- Broadens choices of product and services
- Offers convenience through one-stop shopping, flexibility, consolidated bill and others
- Increases customer satisfaction
- Lowers price
- Encourages better customer service from relationship marketing
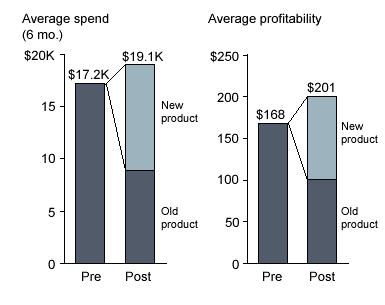
Bain, a top global consulting firm was given a project to increase the number of cross-selling relationships among existing customers and to increase spend of each customer targeted for a leading Bank. Bain’s analysis identified profitable customers for cross-selling and determined that, on average, cross-selling the new product would increase individual customer spend and profitability significantly.
Source: Bain
Industry Exemplars
E-commerce: The long term strength of Amazon is its ability to recognize customers one-on-one and effectively cross-sell across categories based on targeted recommendations. The decision engine is “collaborative filtering”, which recommends items deemed to be similar to the items that the “user or a similar like minded consumer” liked in the past based on expanded view of customers’ purchase history and behaviours.
Retail: Segmentation based cross-sell and product diversification is the key enabler for Tesco to reach top supermarket status in Britain. Targeting is based on differentiated profiles using segmentation and effective data usage of loyalty program, demographics and lifestyle attributes.
Financial Services: Cross-sell is a core strategy for revenue growth for Wells Fargo, which has the highest cross-sell ratio in the industry at 6 products per household. The bank is an adopter of a successful bundling strategy backed by strong analytics support and effective tracking of cross-sell initiatives.
Cross-sell Offer Strategy
Bundling the sale of products or services together as a combined offering using demand for the primary product to sell the secondary product. An example is a package / combo deal. This combined product or offer is at a discount so that it is more attractive to buy the bundle than products standalone. For example – Selling a combo meal for McDonalds is a good example of bundled sale.
Sequential cross-sell involves selling different products or services at different points of the customer’s tenure with the firm. A good example of this is life-stage marketing, i.e. if a customer has bought a printer from you 6 months back, it might be time to check if he needs a cartridge.
Varying strategies tailored to different segment level profiles constitute an integral component of a customer centric approach to cross-selling.
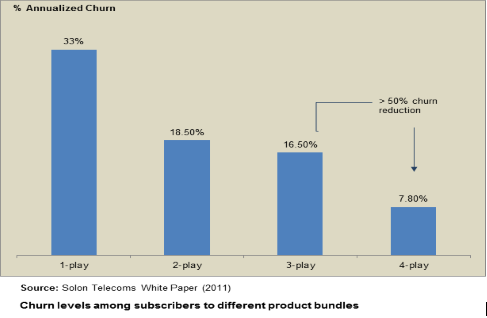
The impact of bundling can be powerful. It normally leads to higher engagement and longer life cycle of the cusotmer. The following figure for a mobile service provider in Europe shows that subscribers opting for a 4-play bundle (4 services) have a quarter of the churn rate as compared to 1-play subscribers.
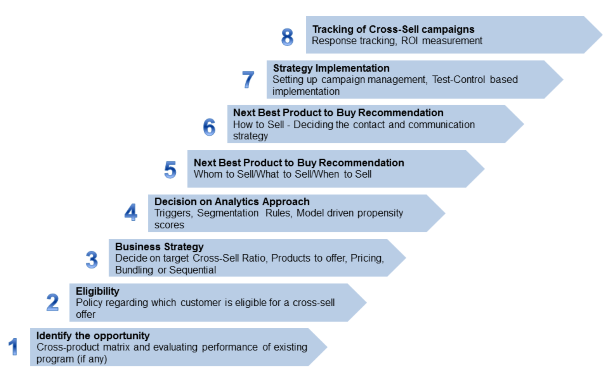
Cross-Sell Process
The cross-sell process is outlined step by step in the following figure. Step 1, 4 and 5 will be elaborated upon subsequently.
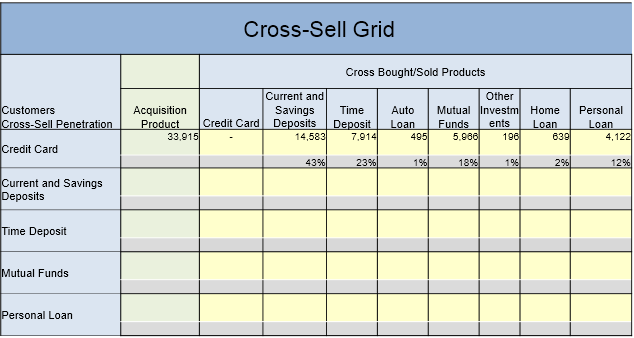
Cross-sell grid for identification of opportunities
A cross-sell grid is a mapping of products held by customers and which is segmented by product group. The grid is created based on a unique customer identification key. The product on the vertical axis usually refers to the first relationship of the customer with the bank.
Here is an example below. In this grid, a good percentage (43 % = 14,583/33,915)) of credit card customers hold current and savings deposit products. We can conclude that this specific cross-sell program is a successful one. However, a bigger push for unsecured and secured loans is required as the penetration of these loans among credit card customers is relatively low. Clearly this segment is an untapped opportunity.
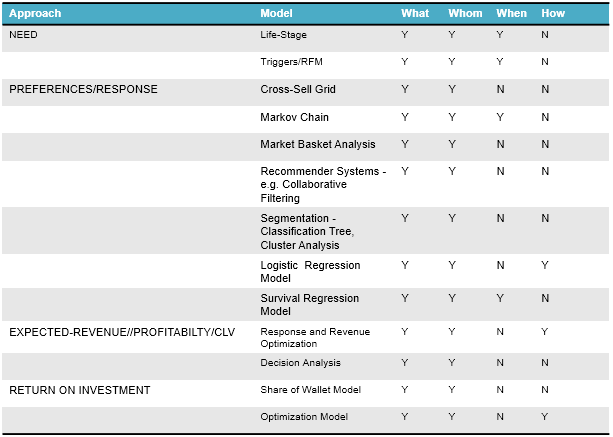
Next Best Product to Recommend Model Framework
Next Best Product to Recommend Models are the foundation of cross-sell targeting analytics. These encompass triggers, segmentation, regression models and optimization.
The models provide answers to the following questions
- What – choice of product
- Whom – selection of customers
- When – timing
- How – contact strategy
Further, inter-purchase time (or time elapsed between purchases) is also modeled in the retail industry.
Next, we will discuss a case study using segmentation and logistic regression model.
Bank Case Study: Next Best Product Recommendation Model
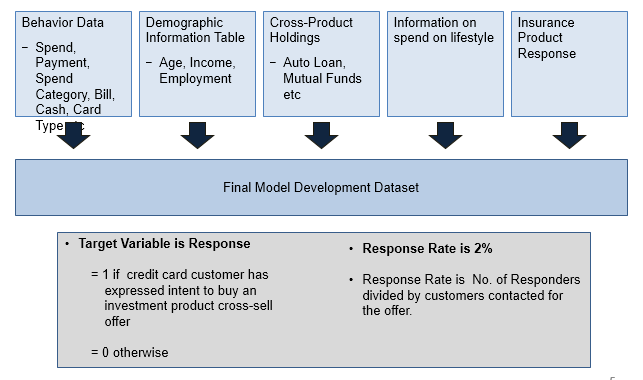
1. Objective: The objective for the Bank is to improve the efficiency of “Investment to Credit Card” cross-sell program based on focused targeting. Investment is also called a liability product in the banking industry.
- Till date, the monthly cross-sell campaign file is based on a random pull of 100,000 customers from an eligible base of 200,000 credit card customers. The historical campaign response rates has been around 2%, that is, 2% of those contacted have expressed interest in the Investment cross-sell offer.
- Structured campaigns have been conducted for this type of program and therefore campaign level data is available
- An analytical approach to enable focused targeting is based on Segmentation and a Response Model
- This Response Model will be used to identify customers most likely to take Investment products based on their past transactions and demographic behaviour.
- The Response Model will be used to determine the target population to be cross-sold the product as well as the contact strategy. In this case, “what product” is an Investment product.
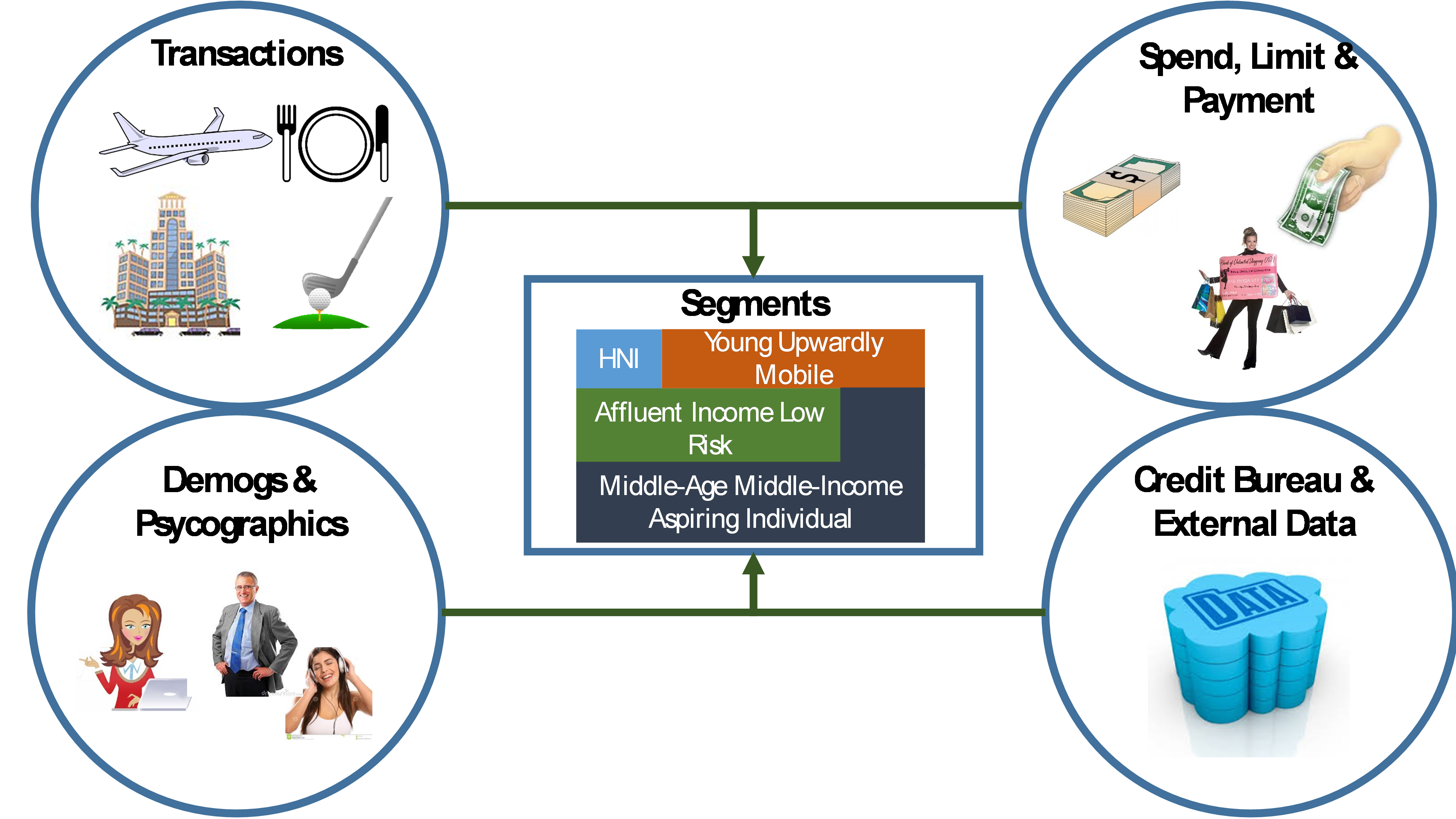
2. Segmentation: For customized one- to- one marketing programs as each segment may have different needs and preferences. The Response Model will be developed for the Segment “Affluent Income Low Risk”.
3. Data Preparation: Data Preparation for Response Model using Credit Card Customer Information and Historical Campaign Files
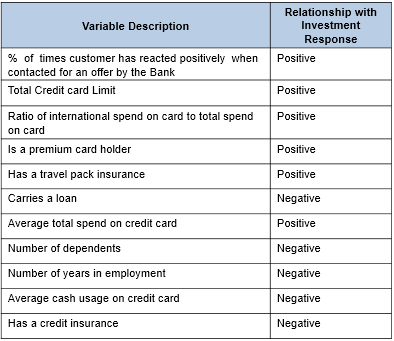
4. Response Model: The following table shows the variables description and relationship to cross-sell response / propensity in descending order of importance using Logistic Regression
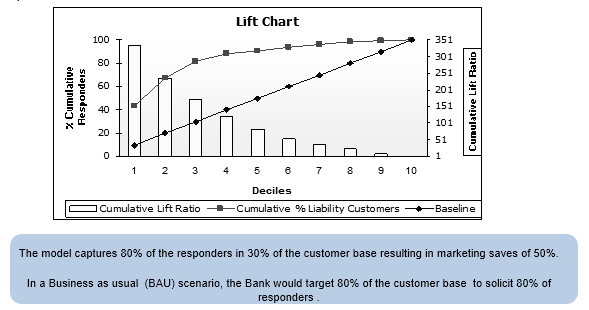
5. Model Performance: The model rank orders based on a decile distribution split. It also demonstrates good performance throughout the score range based on cumulative lift ratio.
Note: Rank Order implies that the response rate increases monotonically with increasing response score (for a model where higher response score indicates a higher expected response rate).
Cumulative lift ratio is the cumulative response rate (by decile) divided by the sample response rate. Higher this lift ratio, better is the model discrimination power in distinguishing the responders from the non-responders.
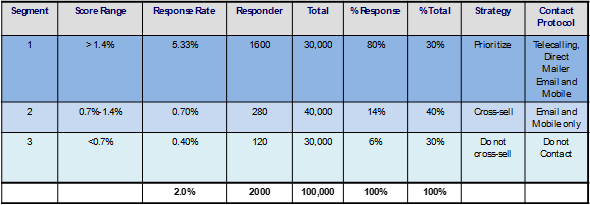
6. Implementation: Based on the response model, a cut-off of the score can be decided. Customers exceeding the cut-off should be considered for marketing. A suggested strategy could be:
- Segment 1 has a response rate which is about 2x the current campaign response rate.
- Campaign file selection of 100,000 using a cross-sell model would involve the targeting of all customers in Segment 1 and some high score customers in Segment 2 from the eligible customer base of 200,000.
- Response Rate is expected to more than double (from the current 2%) given the model based targeting and contact strategy and based on real life experience of industry practitioners like us!
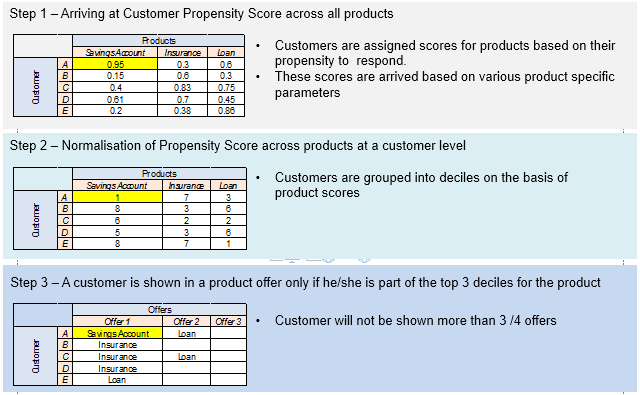
7. Product Prioritization for Multi-Product Cross-Sell Marketing: The decision logic to determine “which product” and “product priority” from a Bank’s basket of products is outlined.
End Notes
By now, we hope you’ve understood the usefulness of this concept in marketing analytics. The case study shared in this article is intended to give you a practical insight on the use of this concept in analytics. Cross Selling and Up-selling is one of the most prominent strategy used across marketing strategy of any company.
Did you find this article useful ? How did your previous cross sell model perform? Share your views in the comments section below.
About the Authors
Sandhya Kuruganti and Hindol Basu are authors of a book on business analytics titled “Business Analytics: Applications to Consumer Marketing”, recently published by McGraw Hill and is available on Flipkart and Amazon India. They are seasoned analytics professionals with a collective industry experience of more than 30 years.



Good Read
Good One
Lucid and Informative.
Hi i want to start my career in data science with banking services so please tell me the way from where to start
Reading this awesome article again. I was preparing data for Cross-Sell modelling in a Personal Lending Use Case. In have data on customers who were campaigned every month and out of those which customers opted for the product. Say, in the month of January, 100 were campaigned and 5 of them opted or expressed interest in the Cross-Sell product. Now , in the month of February the 95 who did not opted for the product along with 15 new customers were campaigned again. My query is 95 customers appears in Jan and Feb both. I was thinking of considering 6 months of campaign data for training my binary classification model. What changes should I do in my data preparation step? If I take all the 6 months' stacked data, then one customer might appear more than once. Please suggest if I have an ambiguity in understanding of Cross-Sell Model. Thanks in advance.
The post provides good guidance on cross-selling and upselling, as well as being informative