Complete Machine Learning Guide to Parameter Tuning in Gradient Boosting (GBM) in Python
Overview
- Learn parameter tuning in gradient boosting algorithm using Python
- Understand how to adjust bias-variance trade-off in machine learning for gradient boosting
Introduction
If you have been using GBM as a ‘black box’ till now, maybe it’s time for you to open it and see, how it actually works!
This article is inspired by Owen Zhang’s (Chief Product Officer at DataRobot and Kaggle Rank 3) approach shared at NYC Data Science Academy. He delivered a~2 hours talk and I intend to condense it and present the most precious nuggets here.
Boosting algorithms play a crucial role in dealing with bias variance trade-off. Unlike bagging algorithms, which only controls for high variance in a model, boosting controls both the aspects (bias & variance), and is considered to be more effective. A sincere understanding of GBM here should give you much needed confidence to deal with such critical issues.
In this article, I’ll disclose the science behind using GBM using Python. And, most important, how you can tune its parameters and obtain incredible results.
If you are completely new to the world of Ensemble learning, you can enrol in this free course which covers all the techniques in a structured manner: Ensemble Learning and Ensemble Learning Techniques
Special Thanks: Personally, I would like to acknowledge the timeless support provided by Mr. Sudalai Rajkumar, currently AV Rank 2. This article wouldn’t be possible without his guidance. I am sure the whole community will benefit from the same.

Complete Guide to Parameter Tuning in Gradient Boosting (GBM) in Python
Table of Contents
- How Boosting Works?
- Understanding GBM Parameters
- Tuning Parameters (with Example)
1. How Boosting Works ?
Boosting is a sequential technique which works on the principle of ensemble. It combines a set of weak learners and delivers improved prediction accuracy. At any instant t, the model outcomes are weighed based on the outcomes of previous instant t-1. The outcomes predicted correctly are given a lower weight and the ones miss-classified are weighted higher. This technique is followed for a classification problem while a similar technique is used for regression.
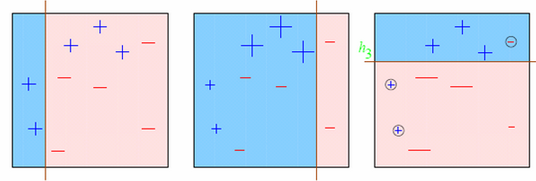
Let’s understand it visually:
Observations:
- Box 1: Output of First Weak Learner (From the left)
- Initially all points have same weight (denoted by their size).
- The decision boundary predicts 2 +ve and 5 -ve points correctly.
- Box 2: Output of Second Weak Learner
- The points classified correctly in box 1 are given a lower weight and vice versa.
- The model focuses on high weight points now and classifies them correctly. But, others are misclassified now.
Similar trend can be seen in box 3 as well. This continues for many iterations. In the end, all models are given a weight depending on their accuracy and a consolidated result is generated.
Did I whet your appetite? Good. Refer to these articles (focus on GBM right now):
- Learn Gradient Boosting Algorithm for better predictions (with codes in R)
- Quick Introduction to Boosting Algorithms in Machine Learning
- Getting smart with Machine Learning – AdaBoost and Gradient Boost
2. GBM Parameters
The overall parameters of this ensemble model can be divided into 3 categories:
- Tree-Specific Parameters: These affect each individual tree in the model.
- Boosting Parameters: These affect the boosting operation in the model.
- Miscellaneous Parameters: Other parameters for overall functioning.
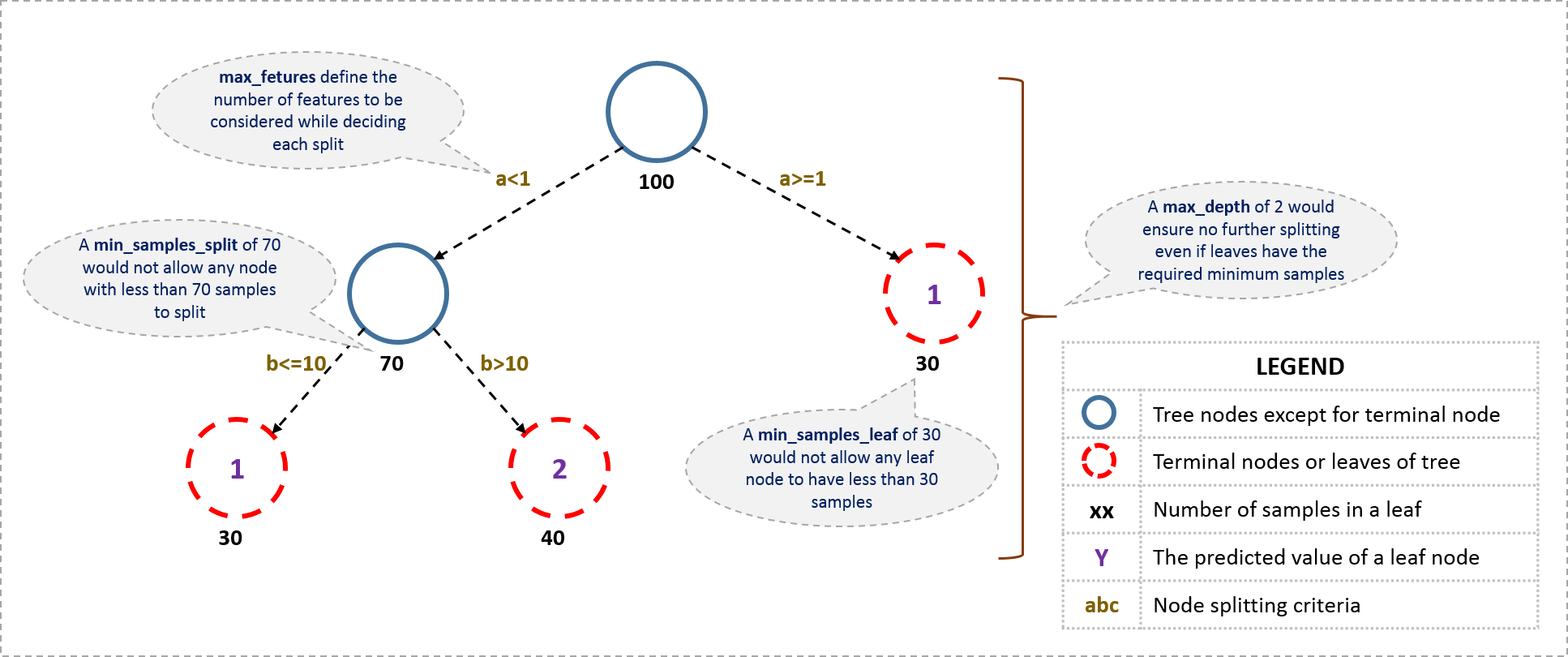
I’ll start with tree-specific parameters. First, lets look at the general structure of a decision tree:
The parameters used for defining a tree are further explained below. Note that I’m using scikit-learn (python) specific terminologies here which might be different in other software packages like R. But the idea remains the same.
- min_samples_split
- Defines the minimum number of samples (or observations) which are required in a node to be considered for splitting.
- Used to control over-fitting. Higher values prevent a model from learning relations which might be highly specific to the particular sample selected for a tree.
- Too high values can lead to under-fitting hence, it should be tuned using CV.
- min_samples_leaf
- Defines the minimum samples (or observations) required in a terminal node or leaf.
- Used to control over-fitting similar to min_samples_split.
- Generally lower values should be chosen for imbalanced class problems because the regions in which the minority class will be in majority will be very small.
- min_weight_fraction_leaf
- Similar to min_samples_leaf but defined as a fraction of the total number of observations instead of an integer.
- Only one of #2 and #3 should be defined.
- max_depth
- The maximum depth of a tree.
- Used to control over-fitting as higher depth will allow model to learn relations very specific to a particular sample.
- Should be tuned using CV.
- max_leaf_nodes
- The maximum number of terminal nodes or leaves in a tree.
- Can be defined in place of max_depth. Since binary trees are created, a depth of ‘n’ would produce a maximum of 2^n leaves.
- If this is defined, GBM will ignore max_depth.
- max_features
- The number of features to consider while searching for a best split. These will be randomly selected.
- As a thumb-rule, square root of the total number of features works great but we should check upto 30-40% of the total number of features.
- Higher values can lead to over-fitting but depends on case to case.
Before moving on to other parameters, lets see the overall pseudo-code of the GBM algorithm for 2 classes:
1. Initialize the outcome 2. Iterate from 1 to total number of trees 2.1 Update the weights for targets based on previous run (higher for the ones mis-classified) 2.2 Fit the model on selected subsample of data 2.3 Make predictions on the full set of observations 2.4 Update the output with current results taking into account the learning rate 3. Return the final output.
This is an extremely simplified (probably naive) explanation of GBM’s working. The parameters which we have considered so far will affect step 2.2, i.e. model building. Lets consider another set of parameters for managing boosting:
- learning_rate
- This determines the impact of each tree on the final outcome (step 2.4). GBM works by starting with an initial estimate which is updated using the output of each tree. The learning parameter controls the magnitude of this change in the estimates.
- Lower values are generally preferred as they make the model robust to the specific characteristics of tree and thus allowing it to generalize well.
- Lower values would require higher number of trees to model all the relations and will be computationally expensive.
- n_estimators
- The number of sequential trees to be modeled (step 2)
- Though GBM is fairly robust at higher number of trees but it can still overfit at a point. Hence, this should be tuned using CV for a particular learning rate.
- subsample
- The fraction of observations to be selected for each tree. Selection is done by random sampling.
- Values slightly less than 1 make the model robust by reducing the variance.
- Typical values ~0.8 generally work fine but can be fine-tuned further.
Apart from these, there are certain miscellaneous parameters which affect overall functionality:
- loss
- It refers to the loss function to be minimized in each split.
- It can have various values for classification and regression case. Generally the default values work fine. Other values should be chosen only if you understand their impact on the model.
- init
- This affects initialization of the output.
- This can be used if we have made another model whose outcome is to be used as the initial estimates for GBM.
- random_state
- The random number seed so that same random numbers are generated every time.
- This is important for parameter tuning. If we don’t fix the random number, then we’ll have different outcomes for subsequent runs on the same parameters and it becomes difficult to compare models.
- It can potentially result in overfitting to a particular random sample selected. We can try running models for different random samples, which is computationally expensive and generally not used.
- verbose
- The type of output to be printed when the model fits. The different values can be:
- 0: no output generated (default)
- 1: output generated for trees in certain intervals
- >1: output generated for all trees
- The type of output to be printed when the model fits. The different values can be:
- warm_start
- This parameter has an interesting application and can help a lot if used judicially.
- Using this, we can fit additional trees on previous fits of a model. It can save a lot of time and you should explore this option for advanced applications
- presort
- Select whether to presort data for faster splits.
- It makes the selection automatically by default but it can be changed if needed.
I know its a long list of parameters but I have simplified it for you in an excel file which you can download from my GitHub repository.
3. Parameter Tuning with Example
We will take the dataset from Data Hackathon 3.x AV hackathon. The details of the problem can be found on the competition page. You can download the data set from here. I have performed the following steps:
- City variable dropped because of too many categories
- DOB converted to Age | DOB dropped
- EMI_Loan_Submitted_Missing created which is 1 if EMI_Loan_Submitted was missing else 0 | Original variable EMI_Loan_Submitted dropped
- EmployerName dropped because of too many categories
- Existing_EMI imputed with 0 (median) since only 111 values were missing
- Interest_Rate_Missing created which is 1 if Interest_Rate was missing else 0 | Original variable Interest_Rate dropped
- Lead_Creation_Date dropped because made little intuitive impact on outcome
- Loan_Amount_Applied, Loan_Tenure_Applied imputed with median values
- Loan_Amount_Submitted_Missing created which is 1 if Loan_Amount_Submitted was missing else 0 | Original variable Loan_Amount_Submitted dropped
- Loan_Tenure_Submitted_Missing created which is 1 if Loan_Tenure_Submitted was missing else 0 | Original variable Loan_Tenure_Submitted dropped
- LoggedIn, Salary_Account dropped
- Processing_Fee_Missing created which is 1 if Processing_Fee was missing else 0 | Original variable Processing_Fee dropped
- Source – top 2 kept as is and all others combined into different category
- Numerical and One-Hot-Coding performed
For those who have the original data from competition, you can check out these steps from the data_preparation iPython notebook in the repository.
Lets start by importing the required libraries and loading the data:
Python Code:
Before proceeding further, lets define a function which will help us create GBM models and perform cross-validation.
def modelfit(alg, dtrain, predictors, performCV=True, printFeatureImportance=True, cv_folds=5):
#Fit the algorithm on the data
alg.fit(dtrain[predictors], dtrain['Disbursed'])
#Predict training set:
dtrain_predictions = alg.predict(dtrain[predictors])
dtrain_predprob = alg.predict_proba(dtrain[predictors])[:,1]
#Perform cross-validation:
if performCV:
cv_score = cross_validation.cross_val_score(alg, dtrain[predictors], dtrain['Disbursed'], cv=cv_folds, scoring='roc_auc')
#Print model report:
print "\nModel Report"
print "Accuracy : %.4g" % metrics.accuracy_score(dtrain['Disbursed'].values, dtrain_predictions)
print "AUC Score (Train): %f" % metrics.roc_auc_score(dtrain['Disbursed'], dtrain_predprob)
if performCV:
print "CV Score : Mean - %.7g | Std - %.7g | Min - %.7g | Max - %.7g" % (np.mean(cv_score),np.std(cv_score),np.min(cv_score),np.max(cv_score))
#Print Feature Importance:
if printFeatureImportance:
feat_imp = pd.Series(alg.feature_importances_, predictors).sort_values(ascending=False)
feat_imp.plot(kind='bar', title='Feature Importances')
plt.ylabel('Feature Importance Score')
The code is pretty self-explanatory. Please feel free to drop a note in the comments if you find any challenges in understanding any part of it.
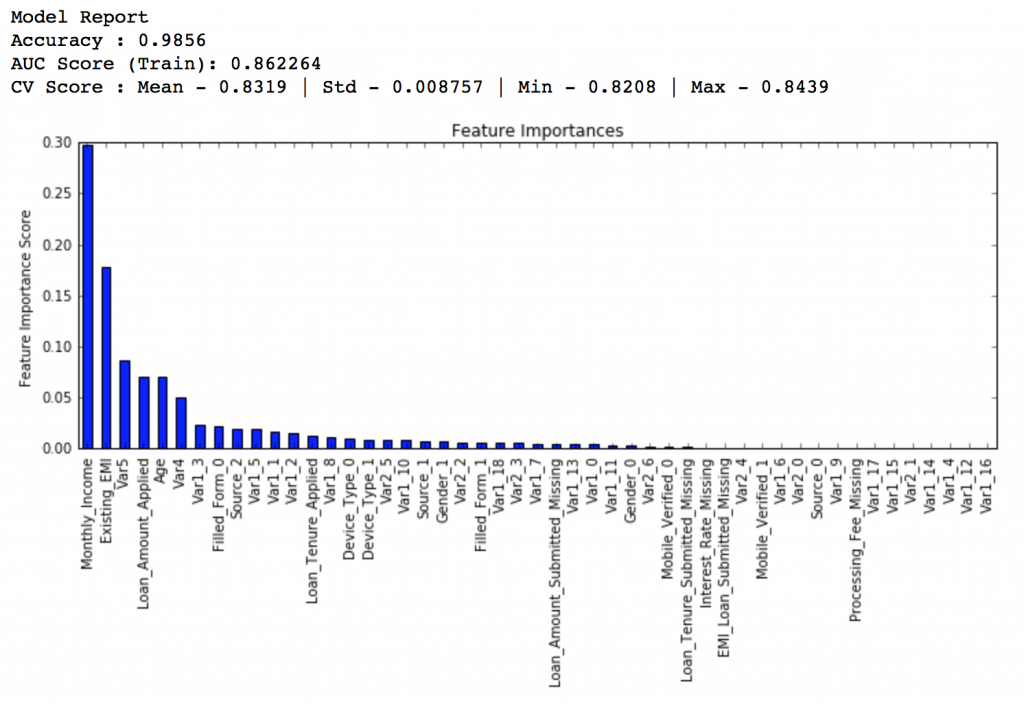
Lets start by creating a baseline model. In this case, the evaluation metric is AUC so using any constant value will give 0.5 as result. Typically, a good baseline can be a GBM model with default parameters, i.e. without any tuning. Lets find out what it gives:
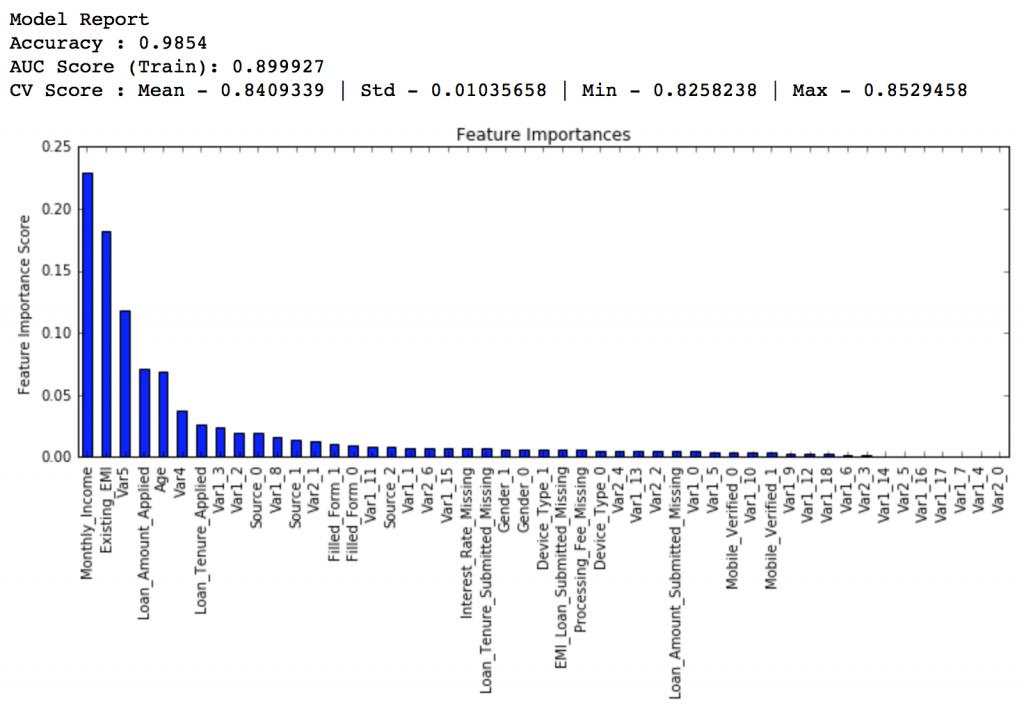
#Choose all predictors except target & IDcols predictors = [x for x in train.columns if x not in [target, IDcol]] gbm0 = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=10) modelfit(gbm0, train, predictors)
So, the mean CV score is 0.8319 and we should expect our model to do better than this.
General Approach for Parameter Tuning
As discussed earlier, there are two types of parameter to be tuned here – tree based and boosting parameters. There are no optimum values for learning rate as low values always work better, given that we train on sufficient number of trees.
Though, GBM is robust enough to not overfit with increasing trees, but a high number for a particular learning rate can lead to overfitting. But as we reduce the learning rate and increase trees, the computation becomes expensive and would take a long time to run on standard personal computers.
Keeping all this in mind, we can take the following approach:
- Choose a relatively high learning rate. Generally the default value of 0.1 works but somewhere between 0.05 to 0.2 should work for different problems
- Determine the optimum number of trees for this learning rate. This should range around 40-70. Remember to choose a value on which your system can work fairly fast. This is because it will be used for testing various scenarios and determining the tree parameters.
- Tune tree-specific parameters for decided learning rate and number of trees. Note that we can choose different parameters to define a tree and I’ll take up an example here.
- Lower the learning rate and increase the estimators proportionally to get more robust models.
Fix learning rate and number of estimators for tuning tree-based parameters
In order to decide on boosting parameters, we need to set some initial values of other parameters. Lets take the following values:
- min_samples_split = 500 : This should be ~0.5-1% of total values. Since this is imbalanced class problem, we’ll take a small value from the range.
- min_samples_leaf = 50 : Can be selected based on intuition. This is just used for preventing overfitting and again a small value because of imbalanced classes.
- max_depth = 8 : Should be chosen (5-8) based on the number of observations and predictors. This has 87K rows and 49 columns so lets take 8 here.
- max_features = ‘sqrt’ : Its a general thumb-rule to start with square root.
- subsample = 0.8 : This is a commonly used used start value
Please note that all the above are just initial estimates and will be tuned later. Lets take the default learning rate of 0.1 here and check the optimum number of trees for that. For this purpose, we can do a grid search and test out values from 20 to 80 in steps of 10.
#Choose all predictors except target & IDcols
predictors = [x for x in train.columns if x not in [target, IDcol]]
param_test1 = {'n_estimators':range(20,81,10)}
gsearch1 = GridSearchCV(estimator = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.1, min_samples_split=500,min_samples_leaf=50,max_depth=8,max_features='sqrt',subsample=0.8,random_state=10),
param_grid = param_test1, scoring='roc_auc',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch1.fit(train[predictors],train[target])
The output can be checked using following command:
gsearch1.grid_scores_, gsearch1.best_params_, gsearch1.best_score_
As you can see that here we got 60 as the optimal estimators for 0.1 learning rate. Note that 60 is a reasonable value and can be used as it is. But it might not be the same in all cases. Other situations:
- If the value is around 20, you might want to try lowering the learning rate to 0.05 and re-run grid search
- If the values are too high ~100, tuning the other parameters will take long time and you can try a higher learning rate
Tuning tree-specific parameters
Now lets move onto tuning the tree parameters. I plan to do this in following stages:
- Tune max_depth and num_samples_split
- Tune min_samples_leaf
- Tune max_features
The order of tuning variables should be decided carefully. You should take the variables with a higher impact on outcome first. For instance, max_depth and min_samples_split have a significant impact and we’re tuning those first.
Important Note: I’ll be doing some heavy-duty grid searched in this section which can take 15-30 mins or even more time to run depending on your system. You can vary the number of values you are testing based on what your system can handle.
To start with, I’ll test max_depth values of 5 to 15 in steps of 2 and min_samples_split from 200 to 1000 in steps of 200. These are just based on my intuition. You can set wider ranges as well and then perform multiple iterations for smaller ranges.
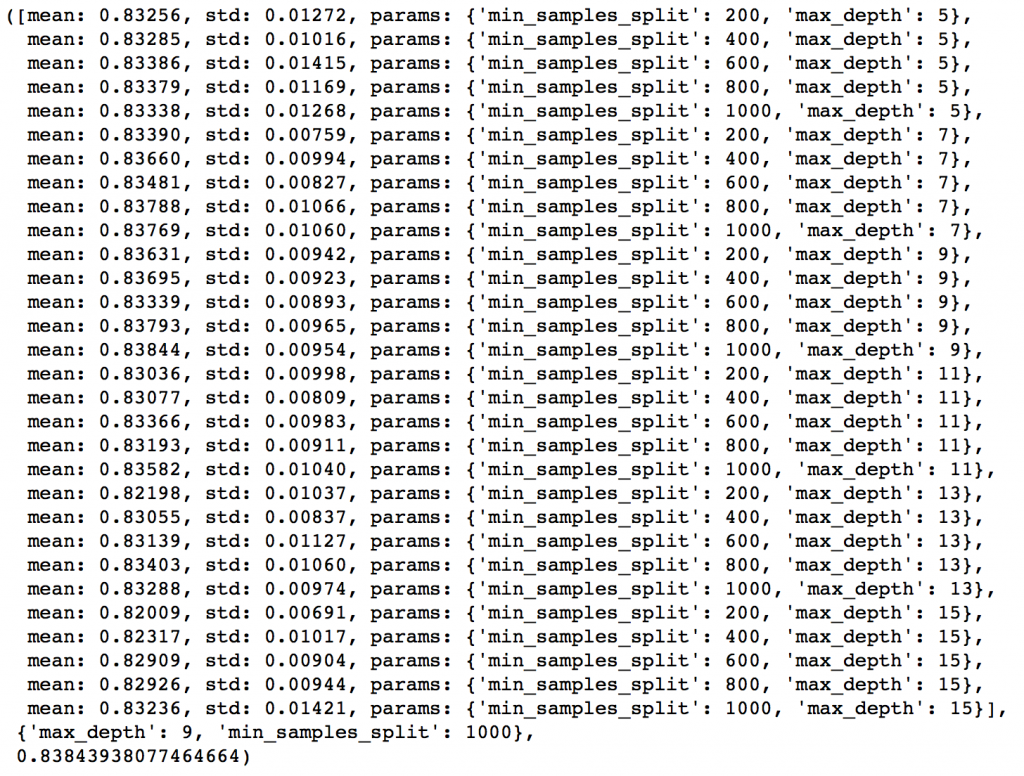
param_test2 = {'max_depth':range(5,16,2), 'min_samples_split':range(200,1001,200)}
gsearch2 = GridSearchCV(estimator = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=60, max_features='sqrt', subsample=0.8, random_state=10),
param_grid = param_test2, scoring='roc_auc',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch2.fit(train[predictors],train[target])
gsearch2.grid_scores_, gsearch2.best_params_, gsearch2.best_score_
Here, we have run 30 combinations and the ideal values are 9 for max_depth and 1000 for min_samples_split. Note that, 1000 is an extreme value which we tested. There is a fare chance that the optimum value lies above that. So we should check for some higher values as well.
Here, I’ll take the max_depth of 9 as optimum and not try different values for higher min_samples_split. It might not be the best idea always but here if you observe the output closely, max_depth of 9 works better in most of the cases. Also, we can test for 5 values of min_samples_leaf, from 30 to 70 in steps of 10, along with higher min_samples_split.
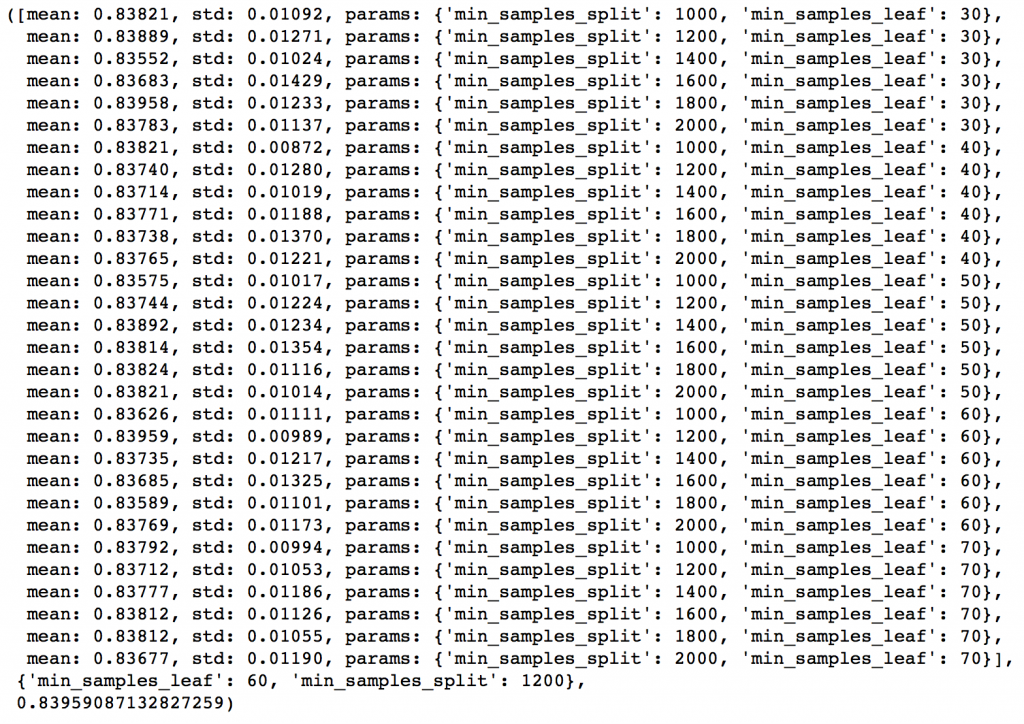
param_test3 = {'min_samples_split':range(1000,2100,200), 'min_samples_leaf':range(30,71,10)}
gsearch3 = GridSearchCV(estimator = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=60,max_depth=9,max_features='sqrt', subsample=0.8, random_state=10),
param_grid = param_test3, scoring='roc_auc',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch3.fit(train[predictors],train[target])
gsearch3.grid_scores_, gsearch3.best_params_, gsearch3.best_score_
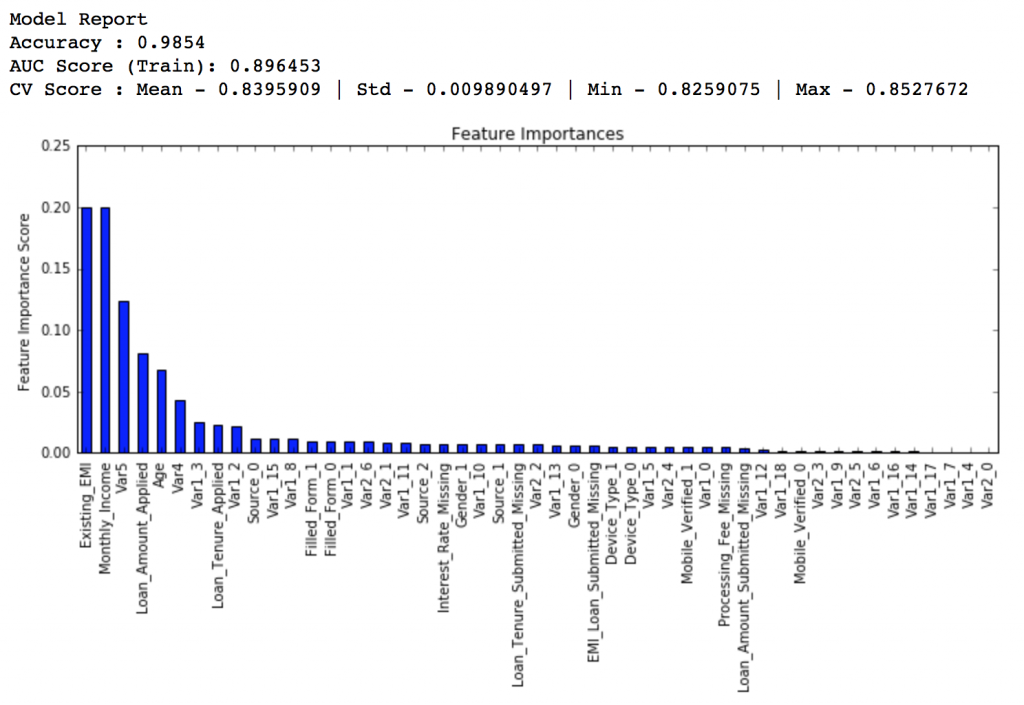
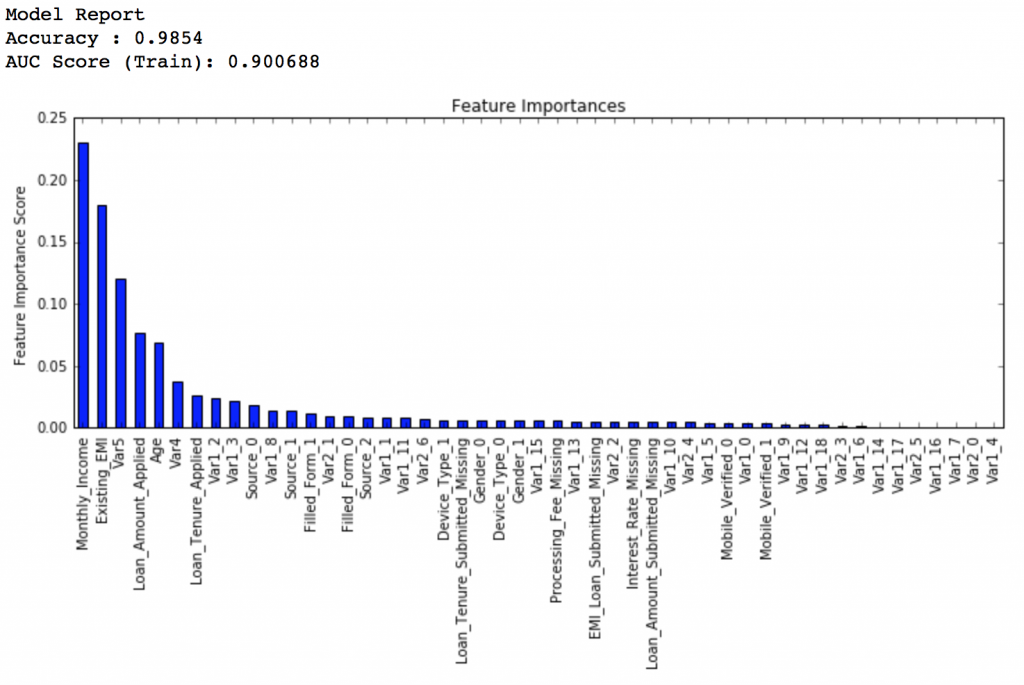
Here we get the optimum values as 1200 for min_samples_split and 60 for min_samples_leaf. Also, we can see the CV score increasing to 0.8396 now. Let’s fit the model again on this and have a look at the feature importance.
modelfit(gsearch3.best_estimator_, train, predictors)
If you compare the feature importance of this model with the baseline model, you’ll find that now we are able to derive value from many more variables. Also, earlier it placed too much importance on some variables but now it has been fairly distributed.
Now lets tune the last tree-parameters, i.e. max_features by trying 7 values from 7 to 19 in steps of 2.
param_test4 = {'max_features':range(7,20,2)}
gsearch4 = GridSearchCV(estimator = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=60,max_depth=9, min_samples_split=1200, min_samples_leaf=60, subsample=0.8, random_state=10),
param_grid = param_test4, scoring='roc_auc',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
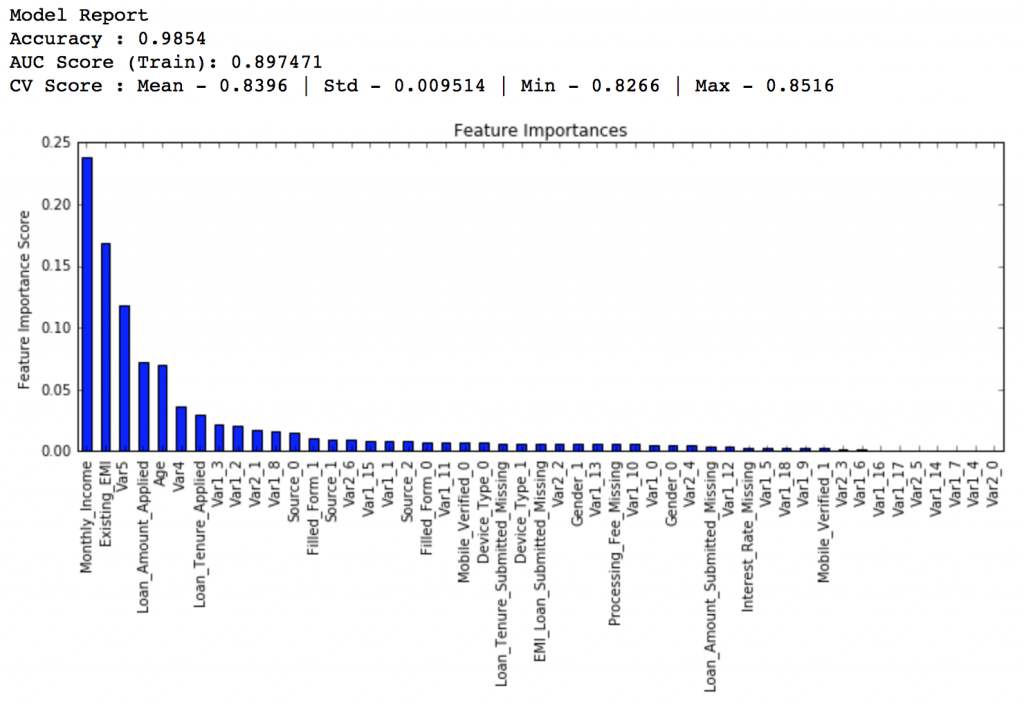
gsearch4.fit(train[predictors],train[target])
gsearch4.grid_scores_, gsearch4.best_params_, gsearch4.best_score_
Here, we find that optimum value is 7, which is also the square root. So our initial value was the best. You might be anxious to check for lower values and you should if you like. I’ll stay with 7 for now. With this we have the final tree-parameters as:
- min_samples_split: 1200
- min_samples_leaf: 60
- max_depth: 9
- max_features: 7
Tuning subsample and making models with lower learning rate
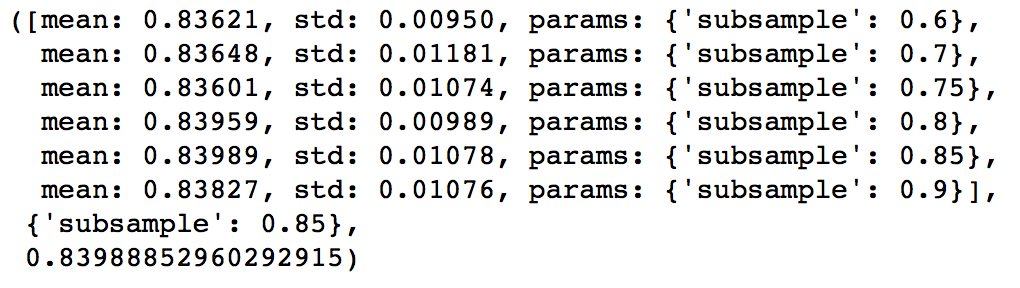
The next step would be try different subsample values. Lets take values 0.6,0.7,0.75,0.8,0.85,0.9.
param_test5 = {'subsample':[0.6,0.7,0.75,0.8,0.85,0.9]}
gsearch5 = GridSearchCV(estimator = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=60,max_depth=9,min_samples_split=1200, min_samples_leaf=60, subsample=0.8, random_state=10,max_features=7),
param_grid = param_test5, scoring='roc_auc',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch5.fit(train[predictors],train[target])
gsearch5.grid_scores_, gsearch5.best_params_, gsearch5.best_score_
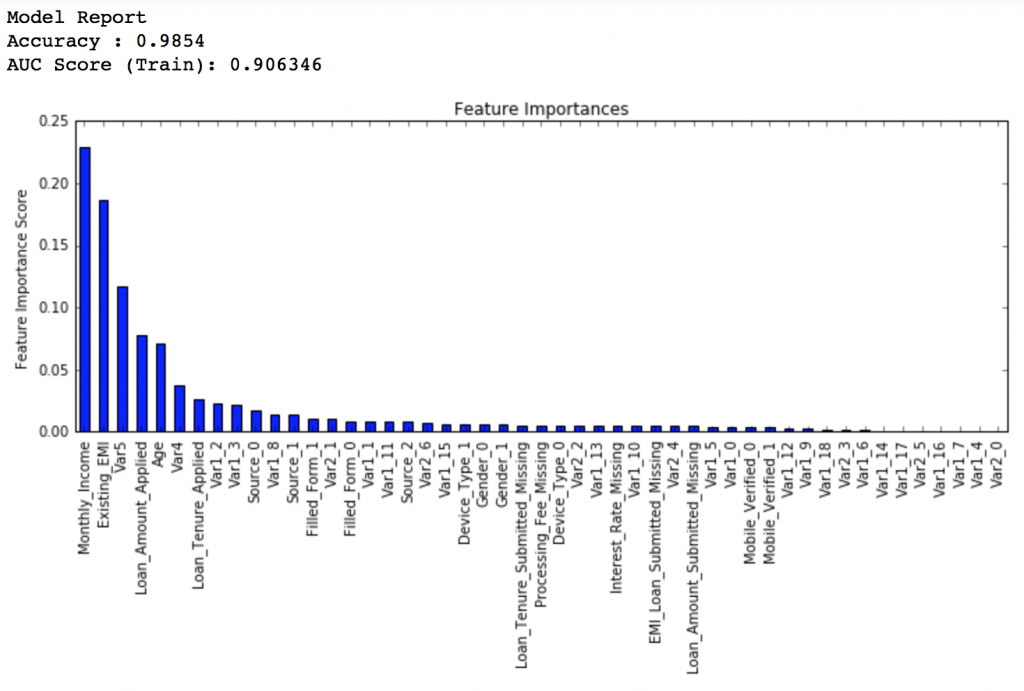
Here, we found 0.85 as the optimum value. Finally, we have all the parameters needed. Now, we need to lower the learning rate and increase the number of estimators proportionally. Note that these trees might not be the most optimum values but a good benchmark.
As trees increase, it will become increasingly computationally expensive to perform CV and find the optimum values. For you to get some idea of the model performance, I have included the private leaderboard scores for each. Since the data is not open, you won’t be able to replicate that but it’ll good for understanding.
Lets decrease the learning rate to half, i.e. 0.05 with twice (120) the number of trees.
predictors = [x for x in train.columns if x not in [target, IDcol]] gbm_tuned_1 = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.05, n_estimators=120,max_depth=9, min_samples_split=1200,min_samples_leaf=60, subsample=0.85, random_state=10, max_features=7) modelfit(gbm_tuned_1, train, predictors)
Private LB Score: 0.844139
Now lets reduce to one-tenth of the original value, i.e. 0.01 for 600 trees.
predictors = [x for x in train.columns if x not in [target, IDcol]] gbm_tuned_2 = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.01, n_estimators=600,max_depth=9, min_samples_split=1200,min_samples_leaf=60, subsample=0.85, random_state=10, max_features=7) modelfit(gbm_tuned_2, train, predictors)
Private LB Score: 0.848145
Lets decrease to one-twentieth of the original value, i.e. 0.005 for 1200 trees.
predictors = [x for x in train.columns if x not in [target, IDcol]] gbm_tuned_3 = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.005, n_estimators=1200,max_depth=9, min_samples_split=1200, min_samples_leaf=60, subsample=0.85, random_state=10, max_features=7, warm_start=True) modelfit(gbm_tuned_3, train, predictors, performCV=False)
Private LB Score: 0.848112
Here we see that the score reduced very slightly. So lets run for 1500 trees.
predictors = [x for x in train.columns if x not in [target, IDcol]] gbm_tuned_4 = GradientBoostingClassifier(learning_rate=0.005, n_estimators=1500,max_depth=9, min_samples_split=1200, min_samples_leaf=60, subsample=0.85, random_state=10, max_features=7, warm_start=True) modelfit(gbm_tuned_4, train, predictors, performCV=False)
Private LB Score: 0.848747
Therefore, now you can clearly see that this is a very important step as private LB scored improved from ~0.844 to ~0.849 which is a significant jump.
Another hack that can be used here is the ‘warm_start’ parameter of GBM. You can use it to increase the number of estimators in small steps and test different values without having to run from starting always. You can also download the iPython notebook with all these model codes from my GitHub account.
If you like this article and want to read a similar post for XGBoost, check this out – Complete Guide to Parameter Tuning in XGBoost
End Notes
This article was based on developing a GBM ensemble learning model end-to-end. We started with an introduction to boosting which was followed by detailed discussion on the various parameters involved. The parameters were divided into 3 categories namely the tree-specific, boosting and miscellaneous parameters depending on their impact on the model.
Finally, we discussed the general approach towards tackling a problem with GBM and also worked out the AV Data Hackathon 3.x problem through that approach.
I hope you found this useful and now you feel more confident to apply GBM in solving a data science problem. You can try this out in out upcoming signature hackathon Date Your Data.
Did you like this article? Would you like to share some other hacks which you implement while making GBM models? Please feel free to drop a note in the comments below and I’ll be glad to discuss.










Great Article!! Can you do this for SVM,XGBoost, deep learning and neural networks.
Absolutely!! I plan to do an entire series if people like the first ones. XGBoost is definitely coming up next week.. There are a few others along with SVM and Deep Learning in my mind. But I haven't thought about a specific order yet.. Feel free to push in more suggestions.. It'll be easier for me to decide :) Also, it'll be great if you can share this article with others in your network. The more people read these, higher will be the preference we can set on articles of this kind!!
Wow great article, pretty much detailed and easy to understand. Am a great fan of articles posted on this site. Keep up the good work !
Thanks Jignesh :)
absolutely fantastic article. Loved the step by step approach. Would love to read more of these on SVM, deep learning. Also, it would be fantastic to have R code.
glad you liked it.. stay tuned for more!!
Guys, The article for XGBoost is out - http://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2016/03/complete-guide-parameter-tuning-xgboost-with-codes-python/ I've also updated the same towards the end of this article. Enjoy and share your feedback! Cheers, Aarshay
Great example! One question; Where do you define 'dtrain'? I see it as an argument for the function.
Hi Don, Thanks for reaching out. So dtrain is a function argument and copies the passed value into dtrain. To explain further, a function is defined using following: def modelfit(alg, dtrain, predictors, performCV=True, printFeatureImportance=True, cv_folds=5): This tells that modelfit is a function which takes arguments as alg, dtrain, predictors and so on.. I need not define these arguments explicitly. When I call a function using: modelfit(gbm_tuned_4, train, predictors, performCV=False) The passed values get mapped to arguments. In this case: alg = gbm_tuned_4 dtrain =train predictors = predictors, and so on.. One this to note is that for some arguments I have defined a default value, like "performCV=True, printFeatureImportance=True, cv_folds=5". So you need not pass these always in a function. If not passed, the default values are taken. Cheers, Aarshay
Hi Aarshay, The article is simply superb. I have the following doubts.. Please clarify : 1. what is the difference between pylab and pyplot module in matplotlib library? (I searched in google and found certain results that pylab should not be used any further) can you please give some additional details what is the difference and which is preferred. 2. modelfit(gbm0,train,predictors,printOOB=False) is written by you at a specific place. modelfit does not accept 'printOOB' parameter. Can you please explain what is the use of this parameter?
Thanks Praveen! Regarding your concerns. 1. I didn't thought about this earlier but a quick search tells me that pyplot is the recommended option as you rightly mentioned. You can get some more intuition from this comment which I found online: "The pyplot interface is generally preferred for non-interactive plotting (i.e., scripting). The pylab interface is convenient for interactive calculations and plotting, as it minimizes typing. Note that this is what you get if you use the ipython shell with the -pylab option, which imports everything from pylab and makes plotting fully interactive." 2. I was using this earlier but I removed it later. I've updated the code with this removed. It was being used earlier to plot the OOB (out-of-bag) improvement curve. GBM returns OOB improvement scores which can be plotted to check how well the model is fitting. But later I found that the estimates provided are biased and many people recommend it should not be used. So I removed that plot from my codes.
That was amazing content, thanks for your efforts. What's your Kaggle account, if you don't mind sharing?
Thanks Jay.. Here is my kaggle account - https://www.kaggle.com/aarshayjain Even I am pretty new at Kaggle. This was my first serious participation..
Great article. Thank you so much for sharing. May I ask you some questions? 1.. You tuned the parameters with an order, first n_estimate and leraning_rate, then keep these parameters as the constants when you tuned other tree related parameters. Does the order really matter? I think it matters. But how did you figure out this order and what kinds of theories did you based on? 2. In sklearn, there is a tool called GridSearchCV. If we don't consider the cost of computing, we put every parameter together as a dict{ }, can we get a final, optimized set of parameters? I doubt it. What is your opinion? 3. Is your tuning method suitable for other datasets and other problems? Your response is highly appreciated. Thank you so much for your great work.
Amazing article! There is one small issue - in section Tuning tree-specific parameters the first stage called "Tune max_depth and num_samples_split", I guess it should be "min_samples_split"
And one more thing: "Here, I’ll take the max_depth of 9 as optimum and not try different values for higher min_samples_split" should be "Here, I’ll take the max_depth of 9 as optimum and NOW try different values for higher min_samples_split"
Great article. Thanks for sharing. One question: How do you adjust steps for parameter tuning? For instance you set 10 as step size for n_estimators paramater and found out that 60 has the highest CV accuracy. What if 55 provides significantly(!) better prediction accuracy and we missed it. Which approach should we follow to adjust step size? For example, should we try every number for integer parameter if computationally possible (10-20 hours maybe)? Thanks.
Hi, Please can you rename your variables in terms of X and y? Let X = training data(matrix) and y = target(a vector). I assume dtrain[predictors] = X and dtrain['Disbursed'] = y. In this section: #Print Feature Importance: if printFeatureImportance: feat_imp = pd.Series(alg.feature_importances_, predictors).sort_values(ascending=False) What is predictors? I know these questions sound basic but I'd really appreciate some help
Hey Aarshay, You said "The evaluation metric is AUC so using any constant value will give 0.5 as result. Typically, a good baseline can be a GBM model with default parameters," That's exactly what I encountered. I always got roc_auc_score of 0.5 even if I changed the parameters like n_estimators. I failed to get a baseline like 0.8 with default parameters. Part of my code is as follow. grd = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=10) grd.fit(X_train, y_train) score = roc_auc_score(y_test, grd.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1]) print (score) Do you think there's any problem? How can I get a higher auc score? Thanks a lot! Btw, I used different dataset with you.
Great article! My question is regarding to the max_depth: "Should be chosen (5-8) based on the number of observations and predictors. This has 87K rows and 49 columns so lets take 8 here." I want to know how 8 is calculated given 87K rows and 49 columns?
"If the value is around 20, you might want to try lowering the learning rate to 0.05 and re-run grid search" Can you please explain why you said so? if n-estimators is less, why would we decrease the learning rate?
hi, Thanks for it. Can you do this for R? I mean parameter tunig for GBM using R libraries please
Great Article
Hi. Great explanation. Just wanted to know while computing roc auc score why do you use dtrain_predprob instead of dtrain_predictions? Why not use the actual predictions while computing the roc-auc score?
I think you need to convert the String columns to int or float type first. I get this error when using the default code provided here: --------------------------------------------------------------------------- ValueError Traceback (most recent call last) in () 2 predictors = [x for x in train.columns if x not in [target, IDcol]] 3 gbm0 = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=10) ----> 4 modelfit(gbm0, train, predictors) in modelfit(alg, dtrain, predictors, performCV, printFeatureImportance, cv_folds) 1 def modelfit(alg, dtrain, predictors, performCV=True, printFeatureImportance=True, cv_folds=5): 2 #fit the algorithm on the data ----> 3 alg.fit(dtrain[predictors], dtrain['Disbursed']) 4 #predict on the training set 5 dtrain_predictions = alg.predict(dtrain[predictors]) ~\AppData\Local\Continuum\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\sklearn\ensemble\gradient_boosting.py in fit(self, X, y, sample_weight, monitor) 977 978 # Check input --> 979 X, y = check_X_y(X, y, accept_sparse=['csr', 'csc', 'coo'], dtype=DTYPE) 980 n_samples, self.n_features_ = X.shape 981 if sample_weight is None: ~\AppData\Local\Continuum\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\validation.py in check_X_y(X, y, accept_sparse, dtype, order, copy, force_all_finite, ensure_2d, allow_nd, multi_output, ensure_min_samples, ensure_min_features, y_numeric, warn_on_dtype, estimator) 571 X = check_array(X, accept_sparse, dtype, order, copy, force_all_finite, 572 ensure_2d, allow_nd, ensure_min_samples, --> 573 ensure_min_features, warn_on_dtype, estimator) 574 if multi_output: 575 y = check_array(y, 'csr', force_all_finite=True, ensure_2d=False, ~\AppData\Local\Continuum\Anaconda3\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\validation.py in check_array(array, accept_sparse, dtype, order, copy, force_all_finite, ensure_2d, allow_nd, ensure_min_samples, ensure_min_features, warn_on_dtype, estimator) 431 force_all_finite) 432 else: --> 433 array = np.array(array, dtype=dtype, order=order, copy=copy) 434 435 if ensure_2d: ValueError: could not convert string to float: 'S122'
Hi Raj, Yes you need to convert string column to float.
Thank you for this amazing article. I have two questions. first, can we tune these hyperparameters using GPU ? because this is very time-consuming. The second one is when I implement this method on the costarica_poverty dataset the accuracy does not reduce by increasing the n-estimators (like what happened for you on 70 and 80 estimators) which is not good. and also after setting max_depth, num_samples_split and and min_samples_leaf I get accuracy = 1 and AUC score = 1. I would be very thank full if you show me a way to handle this.
thanks a lot for the article. I have two questions. first, can we tune these hyperparameters using GPU ? because this is very time-consuming. The second one is when I implement this method on the costarica_poverty dataset the accuracy does not reduce by increasing the n-estimators (like what happened for you on 70 and 80 estimators) which is not good. and also after setting max_depth, num_samples_split and and min_samples_leaf I get accuracy = 1 and AUC score = 1. I would be very thank full if you show me a way to handle this.