Introduction
“What’s the difference between supervised learning and unsupervised learning?”
This is an all too common question among beginners and newcomers in machine learning. The answer to this lies at the core of understanding the essence of machine learning algorithms. Without a clear distinction between these supervised learning and unsupervised learning, your journey simply cannot progress.
This is actually among the first things you should learn when you’re embarking on your machine learning journey. We cannot simply jump into the model building phase if we don’t understand where algorithms like linear regression, logistic regression, clustering, neural networks, etc. fall under.

If we don’t know what the objective of the machine learning algorithm is, we will fail in our endeavor to build an accurate model. This is where the idea of supervised learning and unsupervised learning comes in.
In this article, I will discuss these two concepts using examples and also answer the big question – how to decide when to use supervised learning or unsupervised learning?
If you prefer learning in video form, the below video explains 10 machine learning algorithms in a very easy-to-understand manner:
I have mentioned a few excellent resources below that are ideal to check out as a beginner in machine learning:
Let’s begin by taking a look at Supervised Learning.
What is Supervised Learning?
In supervised learning, the computer is taught by example. It learns from past data and applies the learning to present data to predict future events. In this case, both input and desired output data provide help to the prediction of future events.
For accurate predictions, the input data is labeled or tagged as the right answer.
Supervised Machine Learning Categorisation
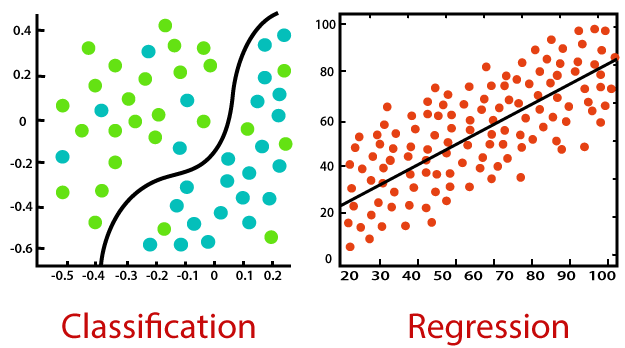
It is important to remember that all supervised learning algorithms are essentially complex algorithms, categorized as either classification or regression models.
1) Classification Models – Classification models are used for problems where the output variable can be categorized, such as “Yes” or “No”, or “Pass” or “Fail.” Classification Models are used to predict the category of the data. Real-life examples include spam detection, sentiment analysis, scorecard prediction of exams, etc.
2) Regression Models – Regression models are used for problems where the output variable is a real value such as a unique number, dollars, salary, weight or pressure, for example. It is most often used to predict numerical values based on previous data observations. Some of the more familiar regression algorithms include linear regression, logistic regression, polynomial regression, and ridge regression.
There are some very practical applications of supervised learning algorithms in real life, including:
- Text categorization
- Face Detection
- Signature recognition
- Customer discovery
- Spam detection
- Weather forecasting
- Predicting housing prices based on the prevailing market price
- Stock price predictions, among others
What is Unsupervised Learning?
Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, is the method that trains machines to use data that is neither classified nor labeled. It means no training data can be provided and the machine is made to learn by itself. The machine must be able to classify the data without any prior information about the data.
The idea is to expose the machines to large volumes of varying data and allow it to learn from that data to provide insights that were previously unknown and to identify hidden patterns. As such, there aren’t necessarily defined outcomes from unsupervised learning algorithms. Rather, it determines what is different or interesting from the given dataset.
The machine needs to be programmed to learn by itself. The computer needs to understand and provide insights from both structured and unstructured data. Here’s an accurate illustration of unsupervised learning:
Unsupervised Machine Learning Categorization
1) Clustering is one of the most common unsupervised learning methods. The method of clustering involves organizing unlabelled data into similar groups called clusters. Thus, a cluster is a collection of similar data items. The primary goal here is to find similarities in the data points and group similar data points into a cluster.
2) Anomaly detection is the method of identifying rare items, events or observations which differ significantly from the majority of the data. We generally look for anomalies or outliers in data because they are suspicious. Anomaly detection is often utilized in bank fraud and medical error detection.
Applications of Unsupervised Learning Algorithms
Some practical applications of unsupervised learning algorithms include:
- Fraud detection
- Malware detection
- Identification of human errors during data entry
- Conducting accurate basket analysis, etc.
When Should you Choose Supervised Learning vs. Unsupervised Learning?
In manufacturing, a large number of factors affect which machine learning approach is best for any given task. And, since every machine learning problem is different, deciding on which technique to use is a complex process.
In general, a good strategy for honing in on the right machine learning approach is to:
- Evaluate the data. Is it labeled/unlabelled? Is there available expert knowledge to support additional labeling? This will help to determine whether a supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised or reinforced learning approach should be used
- Define the goal. Is the problem recurring, defined one? Or, will the algorithm be expected to predict new problems?
- Review available algorithms that may suit the problem with regards to dimensionality (number of features, attributes or characteristics). Candidate algorithms should be suited to the overall volume of data and its structure
- Study successful applications of the algorithm type on similar problems
End Notes
Supervised learning and unsupervised learning are key concepts in the field of machine learning. A proper understanding of the basics is very important before you jump into the pool of different machine learning algorithms.
Unlock the Secrets of Supervised and Unsupervised Learning: Enroll in our comprehensive ‘Machine Learning Fundamentals’ course and master the core concepts to propel your data science journey!
As a next step, go ahead and check out the below article that covers the popular and core machine learning algorithms: