Overview
- The DeepMind team has built a Generative Query Network (GQN) that has the ability to imagine objects from different angles, just like humans
- This AI system can re-create 3D objects based on a few 2D images, without having the full overall picture
- The GQN can also generate new scenes based on these 2D images
Introduction
As the effort to build more and more complex models and machines continues, it is becoming increasingly expensive to find not only the resources to build such machines, but to collect, annotate and label the training data. Because as you know, without having properly labeled data, the model might as well not exist!
Often to train these complex models, we had to manually tag and annotate the images to be used by the algorithm. A group of researchers claim to have found a solution to improvise this time taking process. Google’s DeepMind research team has created an algorithm that can create 3D objects based on a few 2D snapshots. In other words, the AI algorithm is able to use the 2D images to understand or “imagine” how the object looks like from various angles (which are not seen in the image).
The team of researchers have published a research paper explaining how the algorithm works. The system, called Generative Query Network or GQN, can think and imagine like humans. It can render 3D objects without having to be trained on what the various angles of the object look like.

As mentioned by the team, the AI system has two parts:
- Representation network: This is used to convert the sample images into a code the computer can understand. Thus the representation network describes the scene in the form of a code to the computer
- Generation network: It uses the code to create the other angles of the object which are not visible in the initial images
The GQN has the ability to learn about the shape, size and color of the object independently and can then combine all these features to form an accurate 3D model. Furthermore, the researchers were able to use this algorithm to develop new scenes without having to explicitly train the system as to what object should go where.
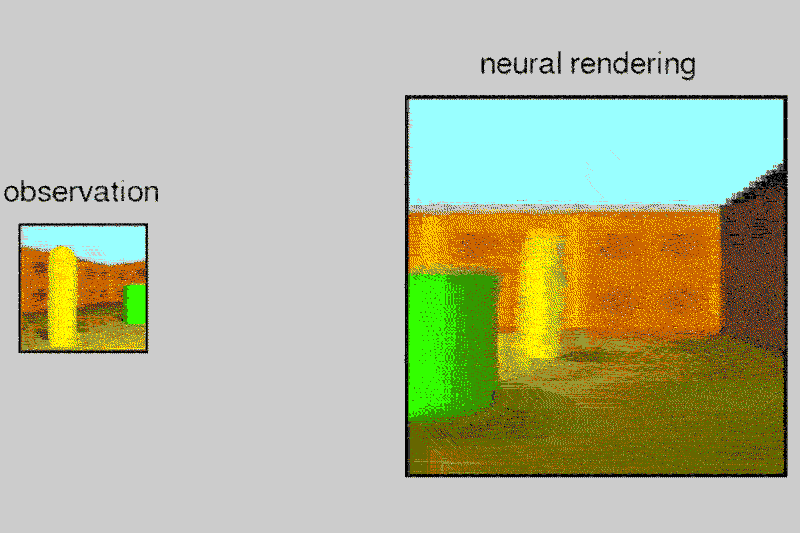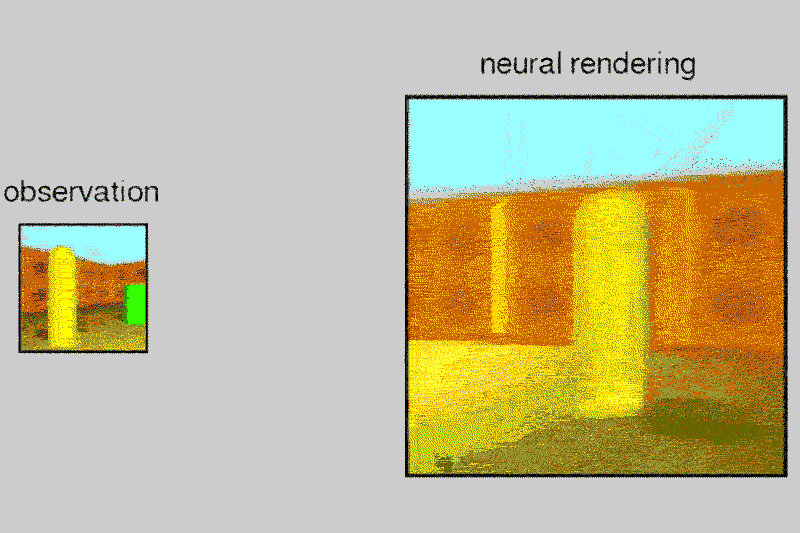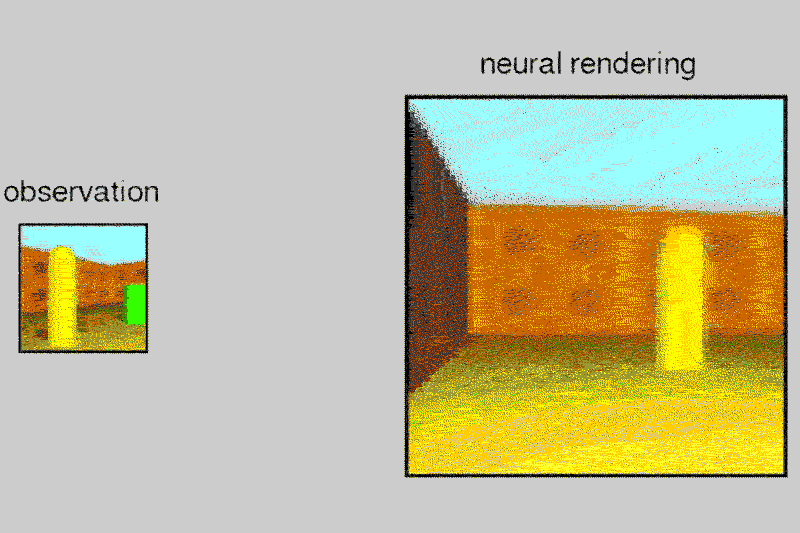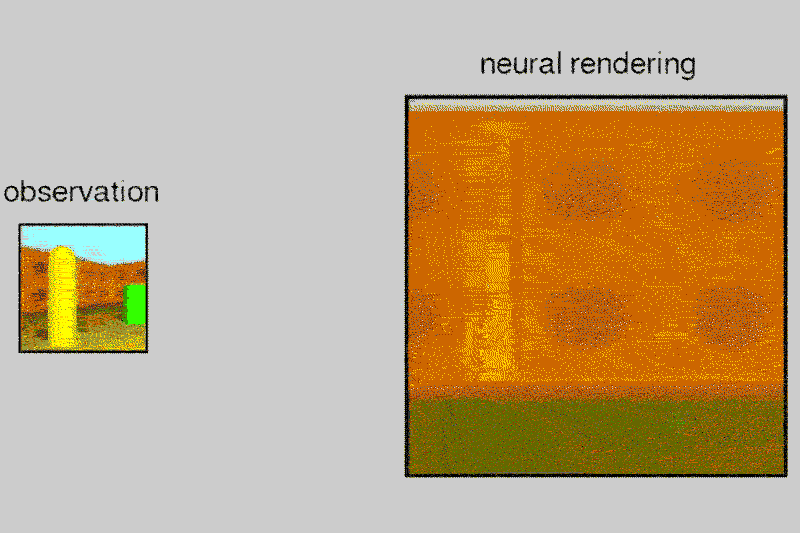
The tests were conducted in a virtual room and the results have been shared by the team in the above mentioned research paper. The algorithm has been tested only on objects so far and is not yet developed enough to work with human faces.
You can read about this algorithm in more detail on DeepMind’s blog post.
Our take on this
Another computer vision algorithm! Annotating and labeling data is a major time staking and often expensive exercise so this is another welcome addition. While still in its nascent stages (DeepMind admit as much in the blog), the potential applications are HUGE. GQN is not limited to tagging and annotating images, it can further be used by autonomous robots to have a better understanding of their surroundings.
What else can you think of where we can apply this algorithm? Let me know your thoughts on this in the comments section below!
Subscribe to AVBytes here to get regular data science, machine learning and AI updates in your inbox!







