This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Introduction
In this article, we are going to talk about a dynamo DB a No-SQL, and a very highly scalable database provided by Amazon AWS. DynamoDB is a scalable hosted NoSQL database service that offers low latency and key-value pair databases. It is also considered a replacement for MongoDB for various Enterprises. boto3 dynamod supports lesser programming languages compared to MongoDB and those are as follows: Java, JavaScript, Python, PHP, NET, etc.
Table of contents
Why DynamoDB?
There are various aspects in which DynamoDb is much superior to other No-SQL databases.
- It uses tabes to store the records. The core components are Items and attributes. While MongoDB contained a database and a database includes collections of documents.
- Also it is very easy to deploy since it’s a web service provided by AWS
- It is more secure since AWS provides it with security.
- DynamoDB is available free of cost(Free tier) one can store up to 25 GB.
Features of DynamoDB
These are the following features that make DynamoDb python popular in the field of No-SQL databases.
- It’s a serverless database. No need to worry about managing the resources.
- It stores the data redundantly across multiple availability zones in order to keep latency low and always uptime.
- It supports over 25 million requests per second.
- It encrypts all the data by default.
- Data Backup
Use Cases of DynamoDB
Many Big companies use boto3 dynamod for their tasks. ie Amazon, Amway, Netflix, Starlink, etc. Since DynamoDB python is provided by AWS and it also supports the encryption by default promising the security at its highest level.
DynamoDb is used for :
- Inventory Tracking
- Storing User Transactions
- Fraud Detection
- In Gaming Technologies etc.
Due to the low latency of DynamoDb python and the highly rich infrastructure given by AWS, DynamoDb is widely popular for handling NoSQL databases across various platforms.
Creating DynamoDB Table on AWS
Even if you have a free tier of AWS account, you can use it and store up to 25GB of data with low latency read and write.
- Search for DynamoDB and open it.
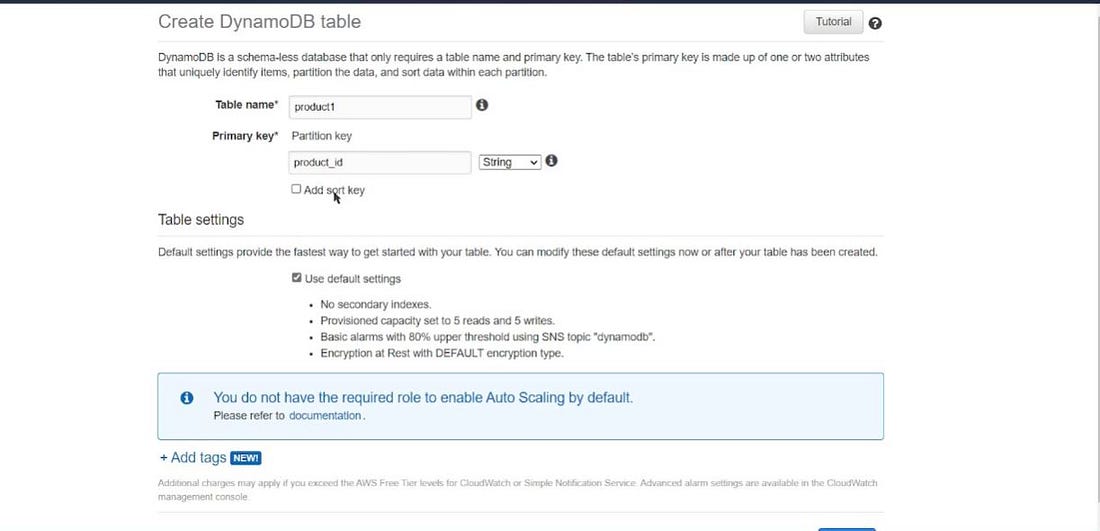
- Create a table by assigning a table name and a key name. We can also create a dynamo DB table using Python boto3 as well.
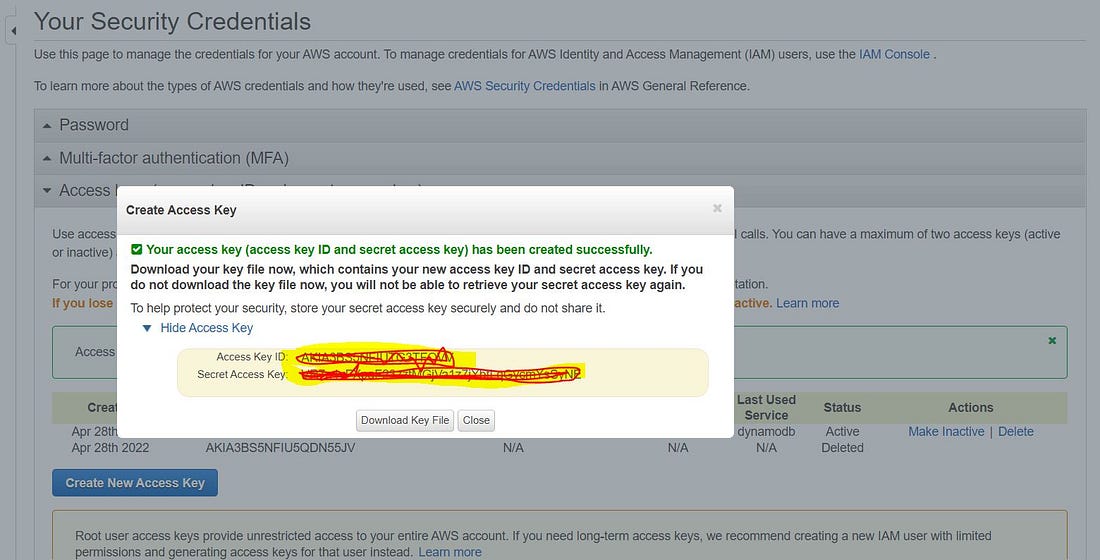
- Saving the service Credentials
In order to connect with our AWS resources, we need to have access to our access_key and its secret key.
Connecting AWS Resources with Python
Connecting AWS resources to the DynamoDb python environment requires a boto3 package.
Installing the Requirement
!pip install boto3
import boto3
import os
import requests
import tqdmCreating dynamoDb client
Creating a dynamo DB client is a connection instance that lets us connect with our dynamo DB service.
We need to specify region_name, aws_access_key_id, aws_secret_access_key in order to connect with our dynamoDb service.
dynamo_client = boto3.resource(service_name = 'dynamodb',region_name = 'us-east-1',
aws_access_key_id = 'AKIA3BS5NFXXXXXXX',
aws_secret_access_key = 'qfGTJL28HrqcbhKCM0t//xxx7gTGG4iNrv3/d94Lsp')List the services by a resource
dynamo_client.get_available_subresources()
[3]: [Table]Connecting with our Table
You can also list down all available tables in our dynamo DB service.
### getting the product table
product_table = dynamo_client.Table('product_table1')
product_table.table_statusthe table_status return [‘ACTIVE’] if the table has been successfully connected. If not try to check the region of services.
After having the successful connection now let’s populate some data
Populating the records
Now having a successful connection with our empty dynamo DB table it’s time to create some records using python.
product_table.put_item(Item = {'product_id':"AV004","Brand":"Lacoste","Price":7800,"Sale":"Online"})put_itemit is used to insert a record into our table.
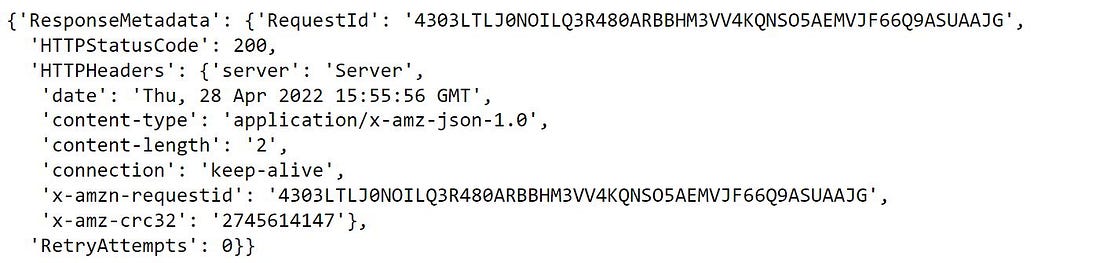
The output shows that the data has been successfully inserted. we can confirm this by exploring the dynamo DB items for the selected table from the AWS management console.
Writing a JSON file into our table
We can populate multiple records either by using an iterator or simply by using a batch writer.
the batch writer writes the records faster than writing using an iterator with the help of the method table.put_item.
import json
file = open('sample_products_data.json','r')
file = file.read()
data_file = json.loads(file)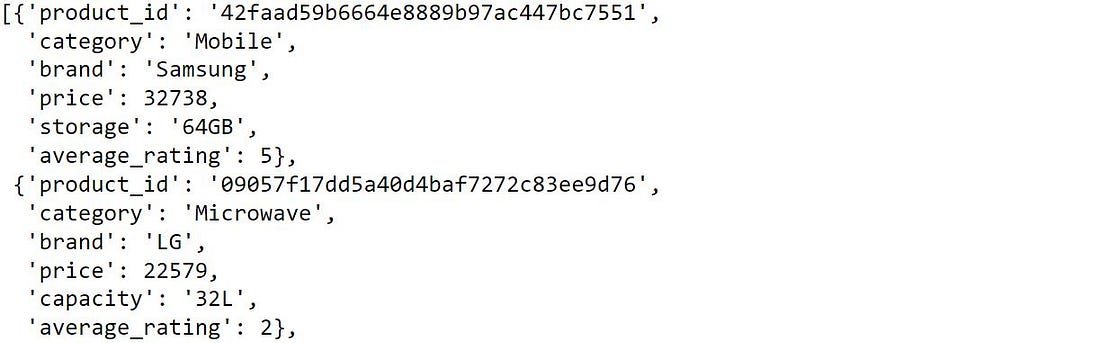
- Putting records using Iterators
Putting the put_item method in a loop writes multiple rows in our table but it’s a rather slow process. Batch writing is faster than loop writing.
for record in tqdm.tqdm(data_file[:50]):
product_table.put_item(Item = record)

- Bulk writing using the batch writer
Whenever we need to write a big number of records we write records in batches using the batch writer.
with product_table.batch_writer() as batch:
for record in tqdm.tqdm(data_file]):
batch.put_item(Item = record)
Reading Data from Dynamo DB
the method get_itemonly returns the matching record from the table. it needs keys to filter the records.
## if you know the key of the information you are looking for
product_table.get_item(Key = {'product_id':'AV002'})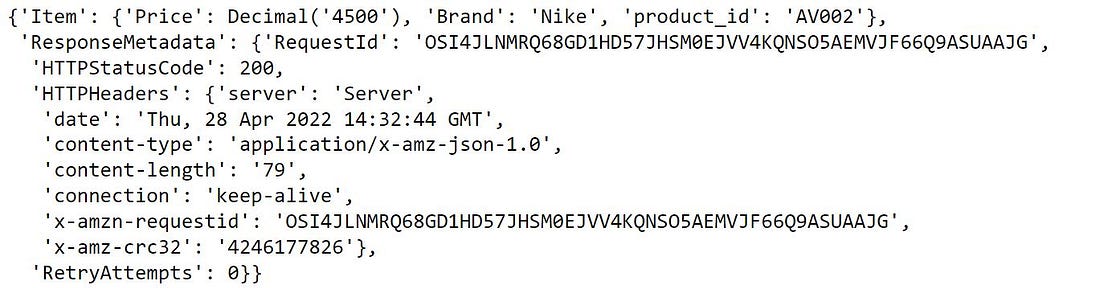
Get all Items aka Scan
scan method searches for all the records available in the table. It works similarly to the find_all method of MongoDB.
for item in product_table.scan()['Items']:
print(item['product_id'])
len(product_table.scan()['Items'])
Output: 115
Updating Records
Using the update_item method we can update any records. If you want to update multiple records we need to make use of a list of all the keys to identify the records that need to be updated.
product_table.update_item(Key = {'product_id':'AV002'},
UpdateExpression = 'set Price =:S',
ExpressionAttributeValues = {":S":2000})Deleting Records
Using the method delete_item we can delete a record or multiple records as well.
product_table.delete_item(Key = {'product_id':'AV002'})
Querying the Records
Querying the records with boto3 dynamod is done using the Scan function. we need to give conditions and it scans for every row.
We want to return all attributes of records where the average rating of products is equal to 4
from boto3.dynamodb.conditions import Attr
product_table.scan(Select = "ALL_ATTRIBUTES",
FilterExpression = Attr("average_rating").eq(4))
Applying Multiple Filters
We want to filter all the attributes where the average rating is equal to 4 and the category is ‘shoes’.
We can also apply these filters and aggregation from the DynamoDb console. You can explore this document for more information about querying the data.
### multiple filters
product_table.scan(Select = "ALL_ATTRIBUTES",
FilterExpression = Attr('average_rating').eq(4) & Attr('category').eq('Shoes'))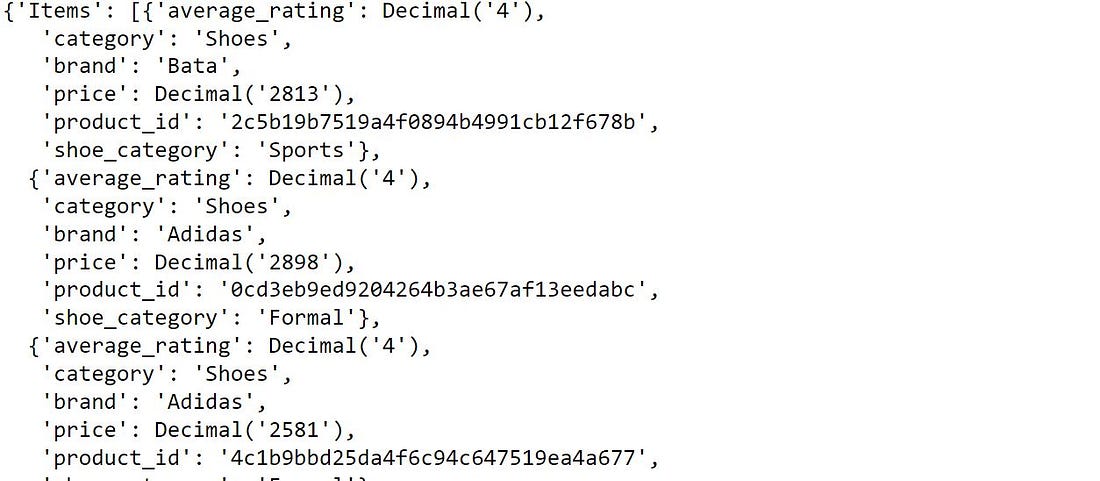
Conclusion
This article discussed creating Dynamo DB and accessing AWS resources in Python Using the boto3 package.
- In this article, we performed basic CRUD operations like creating, inserting, deleting, and updating the records in Dynamo DB
- We also talked about querying the data and aggregation
Well, this is not enough. Here are some external resources you must check out in order to extend your knowledge of boto3 dynamod. AWS is a highly scalable, low latency, and highly secure database provided by Amazon web services. It was launched back in 2012 after MongoDB. This is being used in various industries from retail to media companies. If you enjoyed reading this article or have got some questions regarding this article write me here.
Frequently Asked Questions
To connect to DynamoDB using Boto3 in Python, you use Boto3, which is like a toolkit for accessing Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources. With Boto3, you can connect to DynamoDB by writing Python code that specifies the service and provides necessary details like authentication.
Boto3 is a handy tool for working with AWS services like DynamoDB in Python. It helps you write code to manage AWS resources easily, making tasks like storing and retrieving data in DynamoDB simpler.
DynamoDB is a type of database provided by AWS. In Python, you can interact with DynamoDB using Boto3, allowing you to perform tasks like saving and getting data from DynamoDB tables using Python code.
The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.







