Agent creation has become easier than ever but have you ever thought – how can we make them more powerful than they already are? I recently thought of one possible way – what if they had realtime information about specific categories like finance and movies. That would be really cool, right? While exploring this option, I found RapidAPI a hub of APIs that can give access to AI agents to realtime information with a simple API call. I then decided to make a few agents that can make use of these APIs to make better role-playing agents.
In this article, I share the entire process for the same, so you can easily follow it and replicate the results for your own use. Let us start with some basic information –
Table of contents
What is RapidAPI?
RapidAPI is actually the older name and has recently become Nokia API Hub after acquisition. It has a catalog of APIs where we can use or publish APIs. It covers varied categories from Cybersecurity, Movies, Communication and more. You can explore more about RapidAPI here.
How to Use the APIs from RapidAPI?
1. First sign-in/sign-up to RapidAPI here
2. Go to a developer authorisation page and create an authorization of type ‘RapidAPI’ by click on the ‘Add Authorization’ on the right-top.
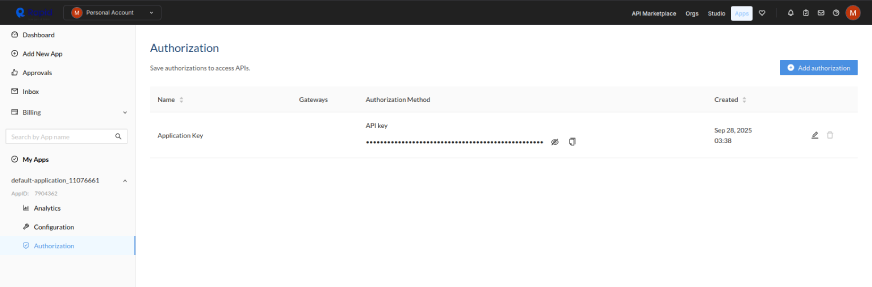
3. Go back to the home page to discover APIs and click on any API you like. For instance, I clicked on a cryptocurrency news API here.
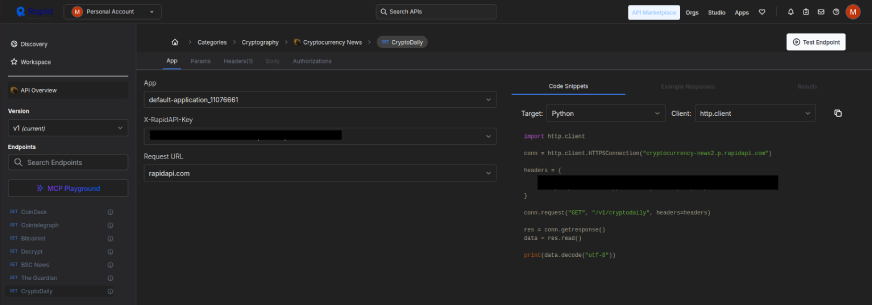
4. You would see a page like this, also the API key is already present in the test code. Just ensure that the target is set to ‘python’:
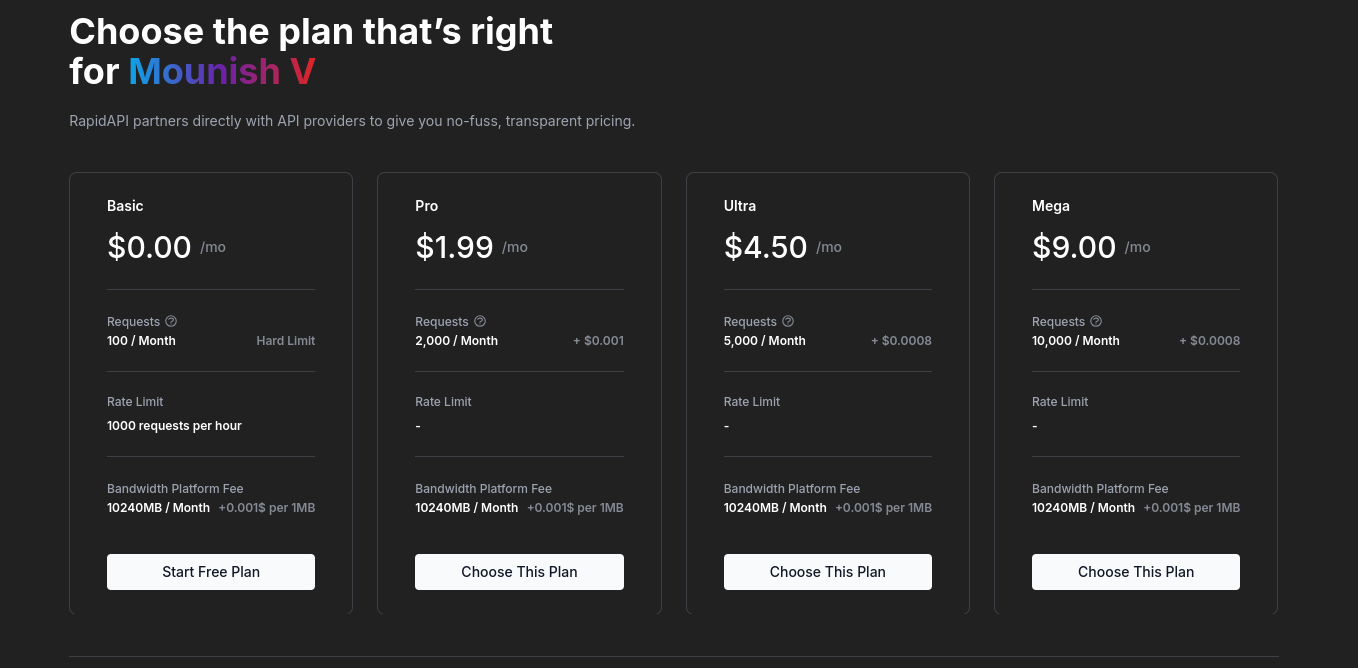
5. Now click on ‘Subscribe to test’ on the right-top and select the free-tier for now. And then click on subscribe after clicking ‘Start Free Plan’.
6. Now you can use the test-endpoint button on the right-top and test code will be executed and you can get the response.
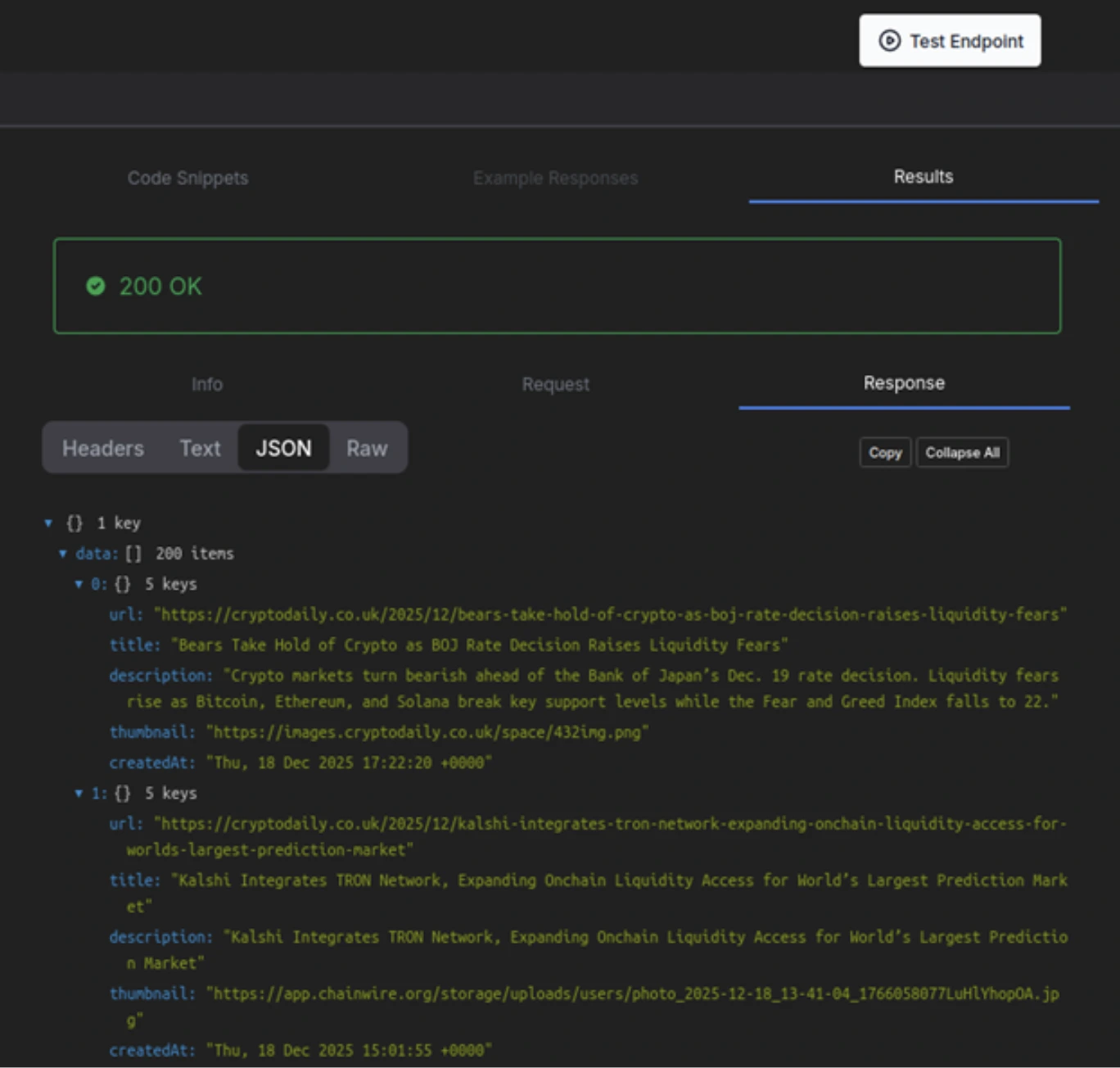
Note: Most of the APIs have a generous free-tier and can be used up-to the mentioned monthly limits.
Making Agents integrated with RapidAPI
In this section we’ll be making agents using the ‘create_agent’ function from langchain.agents and the agents will be powered by OpenAI, specifically the ‘gpt-5-mini’. Feel free to experiment with different models, model-providers or agent frameworks.
Prerequisite
To avoid repetition, we will use the same set of imports and initialize the APIs to use it for multiple agents. And make sure to subscribe to the APIs in the links if you want to test along with me. Also I’ll be using Google Colab for the demo.
Subscribe to these APIs
- https://rapidapi.com/letscrape-6bRBa3QguO5/api/real-time-news-data/playground
- https://rapidapi.com/sparior/api/yahoo-finance15/playground
- https://rapidapi.com/apidojo/api/zoopla/playground
- https://rapidapi.com/rapidapi-org1-rapidapi-org-default/api/imdb236/playground
Configure your Google Colab Notebook
Add your OpenAI API and RapidAPI as ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’ and ‘RAPIDAPI_KEY’ in the secrets section on the left, and don’t forget to turn on the notebook access.
Installations
!pip install langchain langchain_core langchain_openai -q Imports
from google.colab import userdata
import os
import http.client
import json
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.agents import create_agentAPI Keys
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'] = userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
RAPIDAPI_KEY = userdata.get('RAPIDAPI_KEY') Building a News Agent
@tool
def search_news(query: str, limit: int = 10) -> str:
"""Search for real-time news articles based on a query. Returns latest news articles."""
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("real-time-news-data.p.rapidapi.com")
headers = {
"x-rapidapi-key": RAPIDAPI_KEY,
"x-rapidapi-host": "real-time-news-data.p.rapidapi.com",
}
conn.request(
"GET",
f"/search?query={query}&limit={limit}&time_published=anytime&country=US&lang=en",
headers=headers,
)
res = conn.getresponse()
data = res.read()
result = json.loads(data.decode("utf-8"))
return json.dumps(result, indent=2)
news_agent = create_agent(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-5-mini"),
tools=[search_news],
)Note that we’re using the API provided by RapidAPI as a tool and passing the tool to the agent. The Agent will take help from the tool whenever it feels a tool call is necessary.
# Test the agent
result = news_agent.invoke({
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Search for latest news about Messi"}]
})
print(result["messages"][-1].content)Result

Great! We have made our first agent and it’s looking good. You can experiment with new prompts if you like.
Note: Our agent works mostly on when asked something using only one word (example: “Sports”,”Forest”..etc). This is because the tool accepts only a single string and not a sentence, to fix this we can configure our agent’s system prompt.
Stock Agent
Let’s create a Stock Agent that uses Yahoo’s API to fetch the stock details using a stock ticker symbol of any particular stock.
Code
@tool
def get_stock_history(symbol: str, interval: str = "1m", limit: int = 640) -> str:
"""Get historical stock price data for a symbol."""
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("yahoo-finance15.p.rapidapi.com")
headers = {
"x-rapidapi-key": RAPIDAPI_KEY,
"x-rapidapi-host": "yahoo-finance15.p.rapidapi.com",
}
path = (
f"/api/v2/markets/stock/history?"
f"symbol={symbol}&interval={interval}&limit={limit}"
)
conn.request("GET", path, headers=headers)
res = conn.getresponse()
data = res.read()
result = json.loads(data.decode("utf-8"))
return json.dumps(result, indent=2)
stock_agent = create_agent(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-5-mini"),
tools=[get_stock_history],
)
# Example call
result = stock_agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Get the last intraday price history for AAPL"}]}
)
print(result["messages"][-1].content)
Result
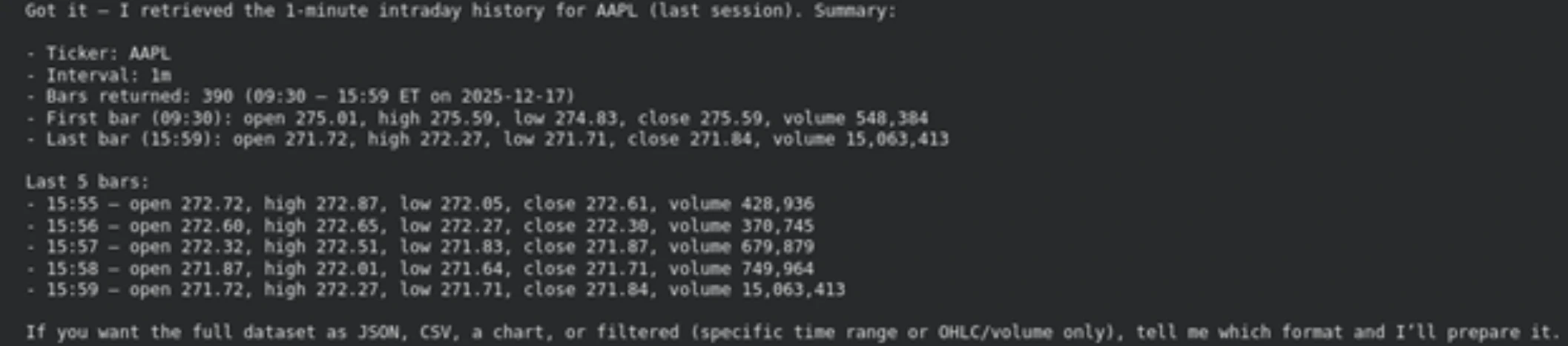
Great, we successfully retrieved the output for AAPL (Apple Inc.), and the information is completely real time.
Properties Agent
The goal here is to create an agent using an API that searches properties for sale/rent, the one we are using from Zoopla searches the properties specifically in the UK.
Code
@tool
def search_properties(
location_value: str,
location_identifier: str = "city",
page: int = 1,
) -> str:
"""
Search for residential properties.
Args:
location_value: The name of the location
(e.g., 'London', 'Manchester', 'E1 6AN').
location_identifier: The category of the location.
- Use 'city' for major cities (default).
- Use 'postal_code' if the user provides a postcode (e.g., 'W1').
- Use 'area' for smaller neighborhoods.
"""
# URL encoding to prevent InvalidURL errors
safe_val = location_value.replace(" ", "%20").replace(",", "%2C")
safe_id = location_identifier.replace(" ", "%20")
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("zoopla.p.rapidapi.com")
headers = {
"x-rapidapi-key": RAPIDAPI_KEY,
"x-rapidapi-host": "zoopla.p.rapidapi.com",
}
path = (
f"/properties/v2/list?locationValue={safe_val}"
f"&locationIdentifier={safe_id}"
f"&category=residential&furnishedState=Any"
f"&sortOrder=newest_listings&page={page}"
)
conn.request("GET", path, headers=headers)
res = conn.getresponse()
data = res.read()
result = json.loads(data.decode("utf-8"))
return json.dumps(result, indent=2)
property_agent = create_agent(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-5-mini"),
tools=[search_properties],
system_prompt=(
"You are a real-estate expert. When a user asks for a location, "
"infer the 'location_identifier' yourself, usually 'city' or "
"'postal_code'. Do not ask the user for technical identifiers; "
"call the tool immediately."
),
)
result = property_agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Search for properties in London, England"}]}
)
print(result["messages"][-1].content)
Result
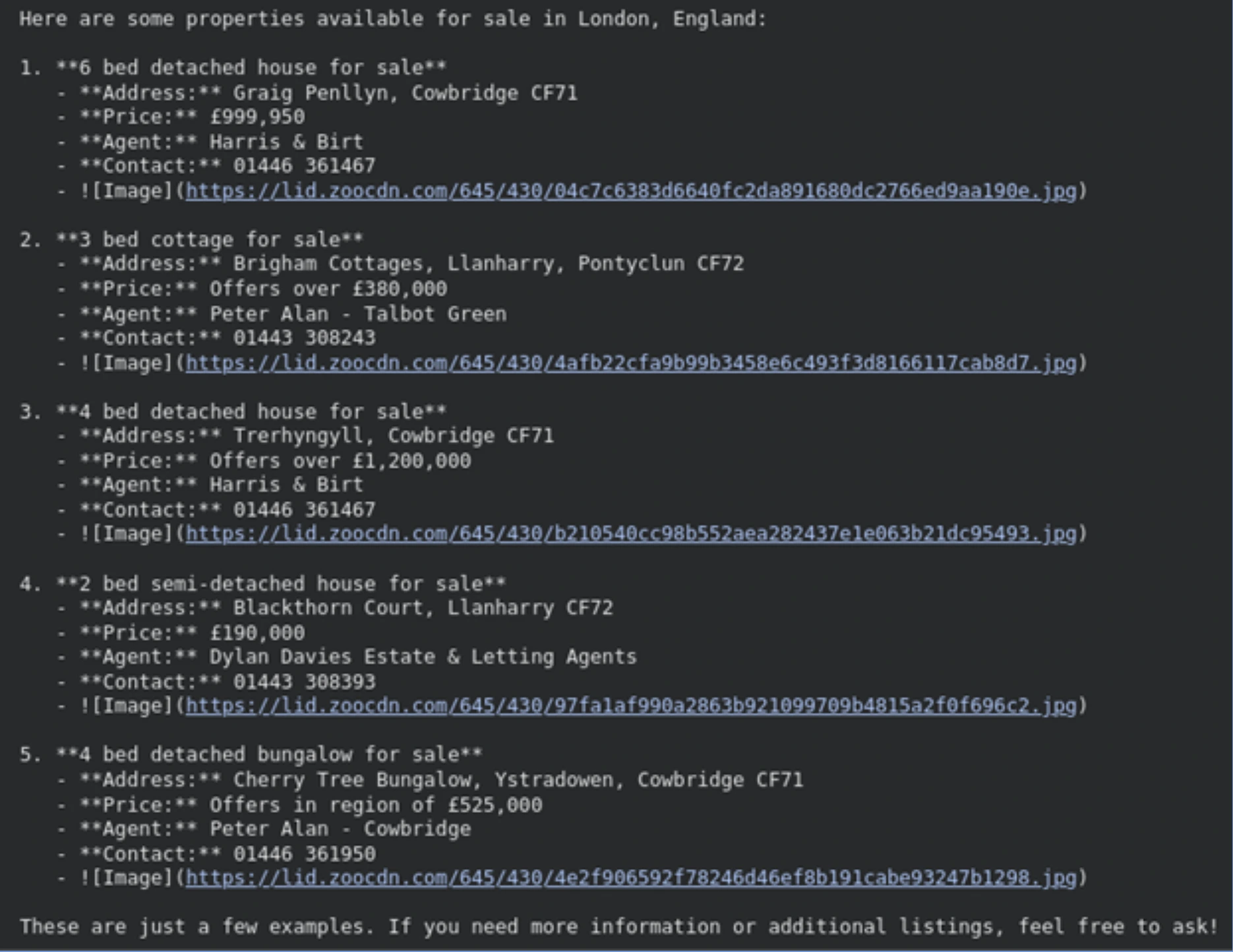
Movie Recommender Agent
This agent will have access to both IMDB’s top rated and worst rated API’s as tools and we will configure the system prompt to pick which tool to use based on the prompt.
@tool
def get_top_rated_movies() -> str:
"""
Fetch the list of top-rated English movies on IMDb.
Use this when the user wants a recommendation or a "good" movie.
"""
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("imdb236.p.rapidapi.com")
headers = {
"x-rapidapi-key": RAPIDAPI_KEY,
"x-rapidapi-host": "imdb236.p.rapidapi.com",
}
conn.request("GET", "/api/imdb/top-rated-english-movies", headers=headers)
res = conn.getresponse()
# Decode and return raw JSON for the agent to process
return res.read().decode("utf-8")
@tool
def get_lowest_rated_movies() -> str:
"""
Fetch the list of lowest-rated movies on IMDb.
Use this when the user asks for "bad" movies or movies to avoid.
"""
conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("imdb236.p.rapidapi.com")
headers = {
"x-rapidapi-key": RAPIDAPI_KEY,
"x-rapidapi-host": "imdb236.p.rapidapi.com",
}
conn.request("GET", "/api/imdb/lowest-rated-movies", headers=headers)
res = conn.getresponse()
return res.read().decode("utf-8")
movie_agent = create_agent(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-5-mini"),
tools=[get_top_rated_movies, get_lowest_rated_movies],
system_prompt=(
"You are an expert movie critic. Your goal is to help users find movies "
"based on quality. If a user asks for something 'good', 'recommended', "
"or 'classic', call get_top_rated_movies. If a user asks for something "
"'bad', 'terrible', or 'lowest rated', call get_lowest_rated_movies. "
"Both tools require no parameters. Summarize the results in a friendly "
"way in a single sentence."
),
)
# Example usage
result = movie_agent.invoke(
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "I'm in the mood for a really terrible movie, what's the worst out there?",
}
]
}
)
print(result["messages"][-1].content)Result
If you want truly awful, IMDb’s lowest-rated picks include Daniel der
Zauberer (Daniel the Wizard) and Smolensk — both hovering around a 1.2
average rating and perfect if you’re after a
“so-bad-it’s-fascinating” watch. Great! We have successfully created an agent which can access multiple tools and can suggest both highly rated or worst rated movies.
Conclusion
By integrating real time APIs with agents, we can move beyond static responses and build systems that feel truly intelligent. RapidAPI makes this integration simple and scalable across domains. Also it’s important that we pick the right tools and also tune the agent to work in harmony with the tool. For instance, many APIs can give an error while single quotes or spaces are present in the argument. Also RapidAPI offers MCP support across its APIs, which can be explored in the ongoing efforts of making better agents.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. An API allows different software systems to communicate by exchanging structured requests and responses over defined endpoints.
A. RapidAPI provides a unified platform to discover, test, subscribe to, and integrate thousands of real time APIs.
A. APIs give agents access to real time data, enabling dynamic responses instead of relying only on static model knowledge.
A. An effective agent uses clear prompts, well defined tools, proper input formatting, and error A. handling for reliable execution.


