The ecosystem of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has taken off in the last couple of years. More and more open-source projects, aimed at helping developers build RAG applications, are now seen across the internet. And why not? RAG is an effective method to augment large language models (LLMs) with an external knowledge source. So we thought, why not share the best GitHub repositories for mastering RAG systems with our readers?
But before we do that, here is a little about RAG and its applications.
RAG pipelines operate in the following way:
- The system retrieves documents or data,
- Data that is informative or useful for the context of completing that user prompt, and
- The system feeds that context into an LLM to produce a response that is accurate and knowledgeable for that context.
As mentioned, we will explore different open-source RAG frameworks and their GitHub repositories here that enable users to easily build RAG systems. The aim is to help developers, students, and tech enthusiasts choose an RAG toolkit that suits their needs and make use of it.
Table of contents
Why You Should Master RAG Systems
Retrieval-Augmented Generation has quickly emerged as one of the most impactful innovations in the field of AI. As companies place more and more focus on implementing smarter systems with context awareness, mastering it is no longer optional. Companies are utilizing RAG pipelines for chatbots, knowledge assistants, and enterprise automation. This is to ensure that their AI models are utilizing real-time, domain-specific data, rather than relying solely on pre-trained knowledge.
In the age when RAG is being used to automate smarter chatbots, assistants, and enterprise tools, understanding it thoroughly can give you a great competitive edge. Knowing how to build and optimize RAG pipelines can open up countless doors in AI development, data engineering, and automation. This shall ultimately make you more marketable and future-proof your career.
In the quest for that mastery, here are the top GitHub repositories for RAG systems. But before that, a look at how these RAG frameworks actually help.
What Does the RAG Framework Do?
The Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework is an advanced AI architecture developed to improve the capabilities of LLMs by integrating external information into the response generation process. This makes the LLM responses more informed or temporally relevant than the data used when initially constructing the language model. The model can retrieve relevant documents or data from external databases or knowledge repositories (APIs). It can then use it to generate responses based on user inquiries rather than simply relying on the data from the originally trained model.
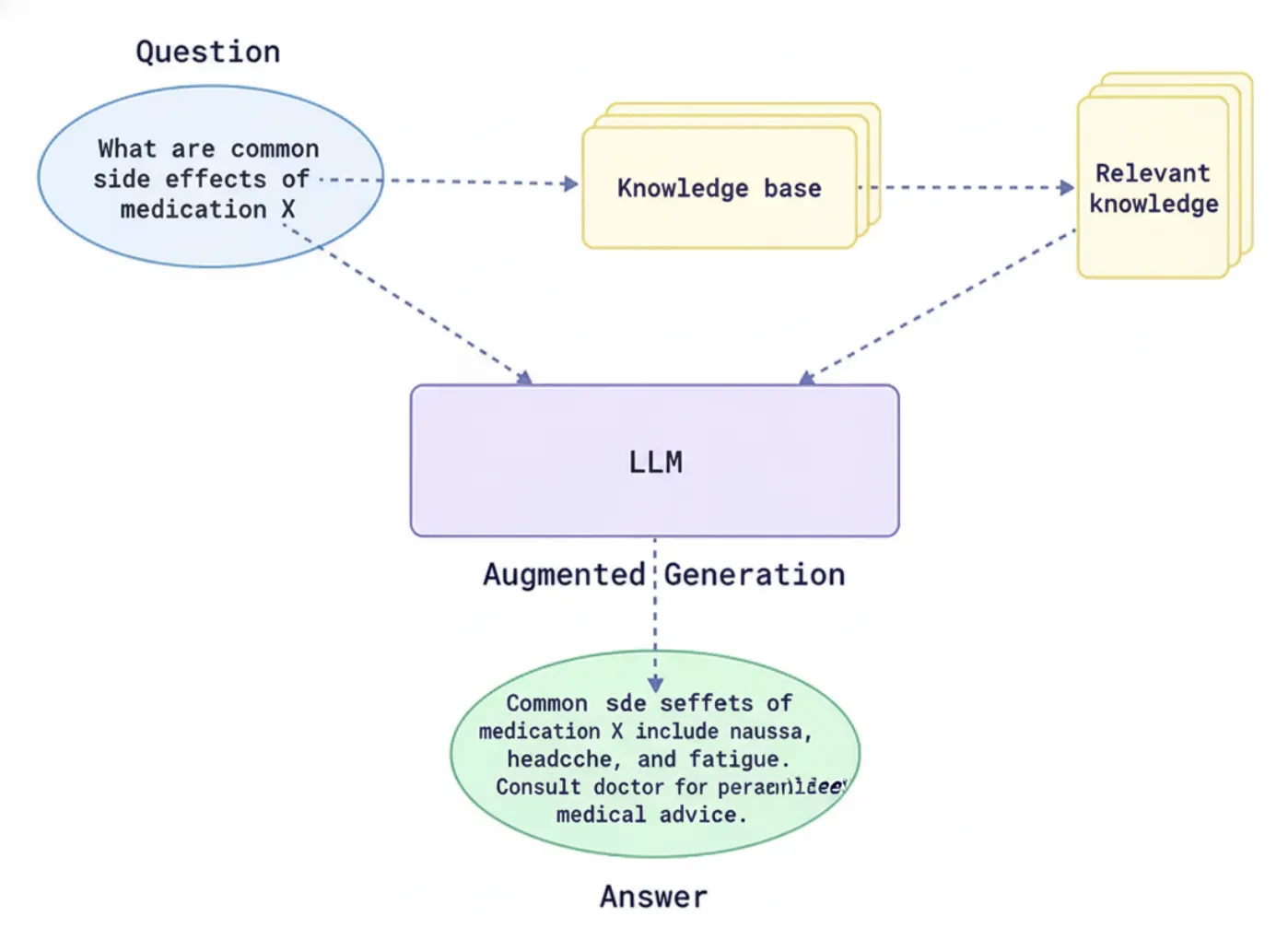
This enables the model to process questions and develop answers that are also correct, date-sensitive, or relevant to context. Meanwhile, they can also mitigate issues related to knowledge cut-off and hallucination, or incorrect responses to prompts. By connecting to both general and domain-specific knowledge sources, RAG enables an AI system to provide responsible, trustworthy responses.
You can read all about RAG systems here.
Applications of this are across use cases, like customer support, search, compliance, data analytics, and more. RAG systems also eliminate the need to frequently retrain the model or attempt to serve individual user responses through the model being trained.
Top Repositories to Master the RAG Systems
Now that we know how RAG systems help, let us explore the top GitHub repositories with detailed tutorials, code, and resources for mastering RAG systems. These GitHub repositories will help you master the tools, skills, frameworks, and theories necessary for working with RAG systems.
1. LangChain
LangChain is a complete LLM toolkit that enables developers to create sophisticated applications with features such as prompts, memories, agents, and data connectors. From loading documents to splitting text, embedding and retrieval, and generating outputs, LangChain provides modules for each step of a RAG pipeline.
LangChain (know all about it here) boasts a rich ecosystem of integrations with providers such as OpenAI, Hugging Face, Azure, and many others. It also supports several languages, including Python, JavaScript, and TypeScript. LangChain features a step-by-step procedure design, allowing you to mix and match tools, build agent workflows, and use built-in chains.
- LangChain’s core feature set includes a tool chaining system, rich prompt templates, and first-class support for agents and memory.
- LangChain is open-source (MIT license) with a huge community (70K+ GitHub stars)
- Components: Prompt templates, LLM wrappers, vectorstore connectors, agents (tools + reasoning), memories, etc.
- Integrations: LangChain supports many LLM providers (OpenAI, Azure, local LLMs), embedding models, and vector stores (FAISS, Pinecone, Chroma, etc.).
- Use Cases: Custom chatbots, document QA, multi-step workflows, RAG & agentic tasks.
Usage Example
LangChain’s high-level APIs make simple RAG pipelines concise. For example, here we use LangChain to answer a question using a small set of documents with OpenAI’s embeddings and LLM:
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
# Sample documents to index
docs = ["RAG stands for retrieval-augmented generation.", "It combines search and LLMs for better answers."]
# 1. Create embeddings and vector store
vectorstore = FAISS.from_texts(docs, OpenAIEmbeddings())
# 2. Build a QA chain (LLM + retriever)
qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=OpenAI(model_name="text-davinci-003"),
retriever=vectorstore.as_retriever()
)
# 3. Run the query
result = qa({"query": "What does RAG mean?"})
print(result["result"])This code takes the docs and loads them into a FAISS vector store using OpenAI embeds. It then uses RetrievalQA to grab the relevant context and generate an answer. LangChain abstracts away the retrieval and LLM call. (For additional instructions, please refer to the LangChain APIs and Tutorials.)
For more, check the Langchain’s GitHub repository here.
2. Haystack by deepset-ai
Haystack, by deepset, is an RAG framework designed for an enterprise that is built around composable pipelines. The main idea is to have a graph-like pipeline. The one in which you wire together nodes (i.e, components), such as retrievers, readers, and generators, into a directed graph. Haystack is designed for deployment in prod and offers many choices of backends Elasticsearch, OpenSearch, Milvus, Qdrant, and many more, for document storage and retrieval.
- It offers both keyword-based (BM25) and dense retrieval and makes it easy to plug in open-source readers (Transformers QA models) or generative answer generators.
- It is open-source (Apache 2.0) and very mature (10K+ stars).
- Architecture: Pipeline-centric and modular. Nodes can be plugged in and swapped accurately.
- Components include: Document stores (Elasticsearch, In-Memory, etc.), retrievers (BM25, Dense), readers (e.g., Hugging Face QA models), and generators (OpenAI, local LLMs).
- Ease of Scaling: Distributed setup (Elasticsearch clusters), GPU support, REST APIs, and Docker.
- Possible Use Cases include: RAG for search, document QA, recap applications, and monitoring user queries.
Usage Example
Below is a simplified example using Haystack’s modern API (v2) to create a small RAG pipeline:
from haystack.document_stores import InMemoryDocumentStore
from haystack.nodes import BM25Retriever, OpenAIAnswerGenerator
from haystack.pipelines import Pipeline
# 1. Prepare a document store
doc_store = InMemoryDocumentStore()
documents = [{"content": "RAG stands for retrieval-augmented generation."}]
doc_store.write_documents(documents)
# 2. Set up retriever and generator
retriever = BM25Retriever(document_store=doc_store)
generator = OpenAIAnswerGenerator(model_name="text-davinci-003")
# 3. Build the pipeline
pipe = Pipeline()
pipe.add_node(component=retriever, name="Retriever", inputs=[])
pipe.add_node(component=generator, name="Generator", inputs=["Retriever"])
# 4. Run the RAG query
result = pipe.run(query="What does RAG mean?")
print(result["answers"][0].answer)This code writes one doc into an in-memory store, uses BM25 to find relevant text, then asks the OpenAI model to answer. Haystack’s Pipeline orchestrates the flow. For more, check deepset repository here.
Also, check out how to buildan Agentic QA RAG system using Haystack here.
3. LlamaIndex
LlamaIndex, formerly known as GPT Index, is a data-centric RAG framework focused on indexing and querying your data for LLM use. Consider LlamaIndex as a set of tools used to build custom indexes over documents (vectors, keyword indexes, graphs) and then query them. LlamaIndex is a powerful way to connect different data sources like text files, APIs, and SQL to LLMs using index structures.
For example, you can create a vector index of all of your files, and then use a built-in query engine to answer any questions you may have, all using LlamaIndex. LlamaIndex supplies high-level APIs and low-level modules to be able to customize every part of the RAG process.
- LlamaIndex is open source (MIT License) with a growing community (45K+ stars)
- Data connectors: (For PDFs, docs, web content), multiple index types (vector store, tree, graph), and a query engine that enables you to navigate efficiently.
- Simply plug it into LangChain or other frameworks. LlamaIndex works with any LLM/embedding (OpenAI, Hugging Face, local LLMs).
- LlamaIndex allows you to build your RAG agents more easily by automatically creating the index and then fetching the context from the index.
Usage Example
LlamaIndex makes it very easy to create a searchable index from documents. For instance, using the core API:
from llama_index import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
# 1. Load documents (all files in the 'data' directory)
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data").load_data()
# 2. Build a vector store index from the docs
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
# 3. Create a query engine from the index
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
# 4. Run a query against the index
response = query_engine.query("What does RAG mean?")
print(response)This code will read files in the ./data directory, index them in memory, and then query the index. LlamaIndex returns the answer as a string. For more, check the Llamindex repository here.
Or, build a RAG pipeline using LlamaIndex. Here is how.
4. RAGFlow
RAGFlow is an RAG engine designed for enterprises from InfiniFlow to accommodate complex and large-scale data. It refers to the goal of “deep document understanding” in order to parse different formats such as PDFs, scanned documents, images, or tables, and summarize them into organized chunks.
RAGFlow features an integrated retrieval model with agent templates and visual tooling for debugging. Key elements are the advanced template-based chunking for the documents and the notion of grounded citations. It helps with reducing hallucinations because you can know which source texts support which answer.
- RAGFlow is open-source (Apache-2.0) with a strong community (65K stars).
- Highlights: parsing of deep documents (i.e., breaking down tables, images, and multi-policy documents), document chunking with template rules (custom rules for managing documents), and citations to show how to document provenance to answer questions.
- Workflow: RAGFlow is used as a service, which means you start a server (using Docker), and then index your documents, either through a UI or API. RAGFlow also has CLI tools and Python/REST APIs for building chatbots.
- Use Cases: Large enterprises dealing with heavy documents and useful use cases where code-based traceability and accuracy are a requisite.
Usage Example
import requests
api_url = "http://localhost:8000/api/v1/chats_openai/default/chat/completions"
api_key = "YOUR_RAGFLOW_API_KEY"
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}"}
data = {
"model": "gpt-4o-mini",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What is RAG?"}],
"stream": False
}
response = requests.post(api_url, headers=headers, json=data)
print(response.json()["choices"][0]["message"]["content"])This example illustrates the chat completion API of RAGFlow, which is compatible with OpenAI. It sends a chat message to the “default” assistant, and the assistant will use the indexed documents as a context. For more, check the repository.
5. txtai
txtai is an all-in-one AI framework that provides semantic search, embeddings, and RAG pipelines. It comes with an embeddable vector-searchable database, stemming from SQLite+FAISS, and utilities that allow you to orchestrate LLM calls. With txtai, once you have created an Embedding index using your text data, you should either join it to an LLM manually in the code or use the built-in RAG helper.
What I really like about txtai is its simplicity: it can run 100% locally (no cloud), it has a template built in for a RAG pipeline, and it even provides autogenerated FastAPI services. It is also open source (Apache 2.0), easy to prototype and deploy.
- Open-source (Apache-2.0, 7K+ stars) Python package.
- Capabilities: Semantic search index (vector DB), RAG pipeline, and FastAPI service generation.
- RAG support: txtai has a RAG class, taking in an Embeddings instance and an LLM, which automatically glues the retrieved context into LLM prompts for you.
- LLM flexibility: Use OpenAI, Hugging Face transformers, llama.cpp, or any model you want with your own LLM interface.
You can read more about txtai here.
Usage Example
Here’s how simple it is to run a RAG query in txtai using the built-in pipeline:
from txtai import Embeddings, LLM, RAG
# 1. Initialize txtai components
embeddings = Embeddings() # uses a local FAISS+SQLite by default
embeddings.index([{"id": "doc1", "text": "RAG stands for retrieval-augmented generation."}])
llm = LLM("text-davinci-003") # or any model
# 2. Create a RAG pipeline
prompt = "Answer the question using only the context below.\n\nQuestion: {question}\nContext: {context}"
rag = RAG(embeddings, llm, template=prompt)
# 3. Run the RAG query
result = rag("What does RAG mean?", maxlength=512)
print(result["answer"])This code snippet takes a single document and runs a RAG pipeline. The RAG helper manages the retrieval for relevant passages from the vector index and fill {context} in the prompt template. It will allow you to wrap your RAG pipeline code in a good layer of structure with APIs and no-code UI. Cognita does use LangChain/LlamaIndex modules under the hood, but organizes them with structure: data loaders, parsers, embedders, retrievers, and metric modules. For more, check the repository here.
6. LLMWare
LLMWare is a complete RAG framework that has a strong deviation towards “smaller” specialized model inference that is secure and faster. Most frameworks use a large cloud LLM. LLMWare runs desktop RAG pipelines with the necessary computing power on a desktop or local server. It limits the risk of data exposure while still utilizing secure LLMs for large-scale pilot studies and various applications.
LLMWare has no-code wizards and templates for the usual RAG functionality, including the functionality of document parsing and indexing. It also has tooling for various document formats (Office and PDF) that are useful first steps for the cognitive AI functionality to document analysis.
- Open source product (Apache-2.0, 14K+ stars) for enterprise RAG
- An approach that focuses on “smaller” LLMs (Ex: Llama 7B variants) and inference runs on a device while offering RAG functionalities even on ARM devices
- Tooling: offering CLI and REST APIs, interactive UIs, and pipeline templates
- Distinctive Characteristics: preconfigured pipelines, built-in capabilities for fact-checking, and plugin features for vector search and Q&As.
- Examples: enterprises pursuing RAG but cannot send data to the cloud, e.g. financial services, healthcare, or builders of mobile/edge AI applications.
Usage Example
LLMWare’s API is designed to be easy. Here’s a basic example based on their docs:
from llmware.prompts import Prompt
from llmware.models import ModelCatalog
# 1. Load a model for prompting
prompter = Prompt().load_model("llmware/bling-tiny-llama-v0")
# 2. (Optionally) index a document to use as context
prompter.add_source_document("./data", "doc.pdf", query="What is RAG?")
# 3. Run the query with context
response = prompter.prompt_with_source("What is RAG?")
print(response)This code uses an LLMWare Prompt object. We first specify a model (for example, a small Llama model from Hugging Face). We then add a folder that contains source documents. LLMWare parses “doc.pdf” into chunks and filters based on relevance to the user’s question. The prompt_with_source function then makes a request, passing the relevant context from the source. This returns a text answer and metadata response. For more, check the repository here.
7. Cognita
Cognita by TrueFoundary is a production-ready RAG framework built for scalability and collaboration. It is primarily about making it easy to go from a notebook or experiment to deployment/service. It supports incremental indexing and has a web UI for non-developers to try uploading documents, picking models, and querying them in real time.
- This is open source (Apache-2.0)
- Architecture: Fully API-based and containerized, it can run fully locally through Docker Compose (including the UI).
- Components: Reusable libraries for parsers, loaders, embedders, retrievers, and more. Everything can be customized and scaled.
- UI – Extensibility: A web frontend is provided for experimentation and a “model gateway” to manage the LLM/embedder configurations. This helps when both the developer and the analyst work together to build out RAG pipeline components.
Usage Example
Cognita is primarily accessed through its command-line interface and internal API, but this is a conceptual pseudo snipped using its Python API:
from cognita.pipeline import Pipeline
from cognita.schema import Document
# Initialize a new RAG pipeline
pipeline = Pipeline.create("rag")
# Add documents (with text content)
docs = [Document(id="1", text="RAG stands for retrieval-augmented generation.")]
pipeline.index_documents(docs)
# Query the pipeline
result = pipeline.query("What does RAG mean?")
print(result['answer'])In a real implementation, you would use YAML to configure Cognita or use its CLI instead to load the data and kick off a service. The previous snippet describes the flow: you create a pipeline, index your data, then ask questions. Cognita documentation has more details. For more, check the complete documentation here. This returns a text answer and metadata response. For more, check the repository here.
Conclusion
These open-source GitHub repositories for RAG systems offer extensive toolkits for developers, researchers, and hobbyists.
- LangChain and LlamaIndex offer flexible APIs for constructing customized pipelines and indexing solutions.
- Haystack offers NLP pipelines that are tested in production with respect to the scalability of data ingestion.
- RAGFlow and LLMWare address enterprise needs, with LLMWare somewhat limited to on-device models and security.
- In contrast, txtai offers a lightweight, simple, all-in-one local RAG solution, while Cognita takes care of everything with an easy, modular, UI driven platform.
All of the GitHub repositories meant for RAG systems above are maintained and come with examples to help you run easily. They collectively demonstrate that RAG is no longer on the cutting edge of academic research, but is now available to everyone who wants to build an AI application. In practice, the “best option” is dependent upon your needs and priorities.





