Mistral AI’s latest announcement introduces DevStral 2 (123B parameters), DevStral Small 2 (24B), and the Mistral Vibe CLI, a terminal-native coding assistant built for agentic coding tasks. Both models are fully open source and tuned for production workflows, while the new Vibe CLI brings project-aware editing, code search, version control, and execution directly into the terminal.
Together, these updates aim to speed up developer workflows by making large-scale code refactoring, bug fixes, and feature development more automated, and in this guide we’ll outline the technical capabilities of each tool and provide hands-on examples to get started.
Table of contents
What is DevStral 2?
DevStral 2 is a 123-billion-parameter dense transformer designed specifically for software engineering agents. It features a 256K-token context window, enabling it to analyze entire code repositories at once. Despite its size, it is much smaller than competitor models: for example, DevStral 2 is 5x smaller than DeepSeek v3.2 and 8x smaller than Kimi K2 yet matches or exceeds their performance. This compactness makes DevStral 2 practical for enterprise deployment.
Key Features of DevStral 2
The Key technical highlights of DevStral 2 include:
- SOTA coding performance: 72.2% on the SWE-bench Verified test, making it one of the strongest open-weight models for coding.
- Large context handling: With 256K tokens, it can track architecture-level context across many files.
- Agentic workflows: Built to “explore codebases and orchestrate changes across multiple files”, DevStral 2 can detect failures, retry with corrections, and handle tasks like multi-file refactoring, bug fixing, and modernizing legacy code.
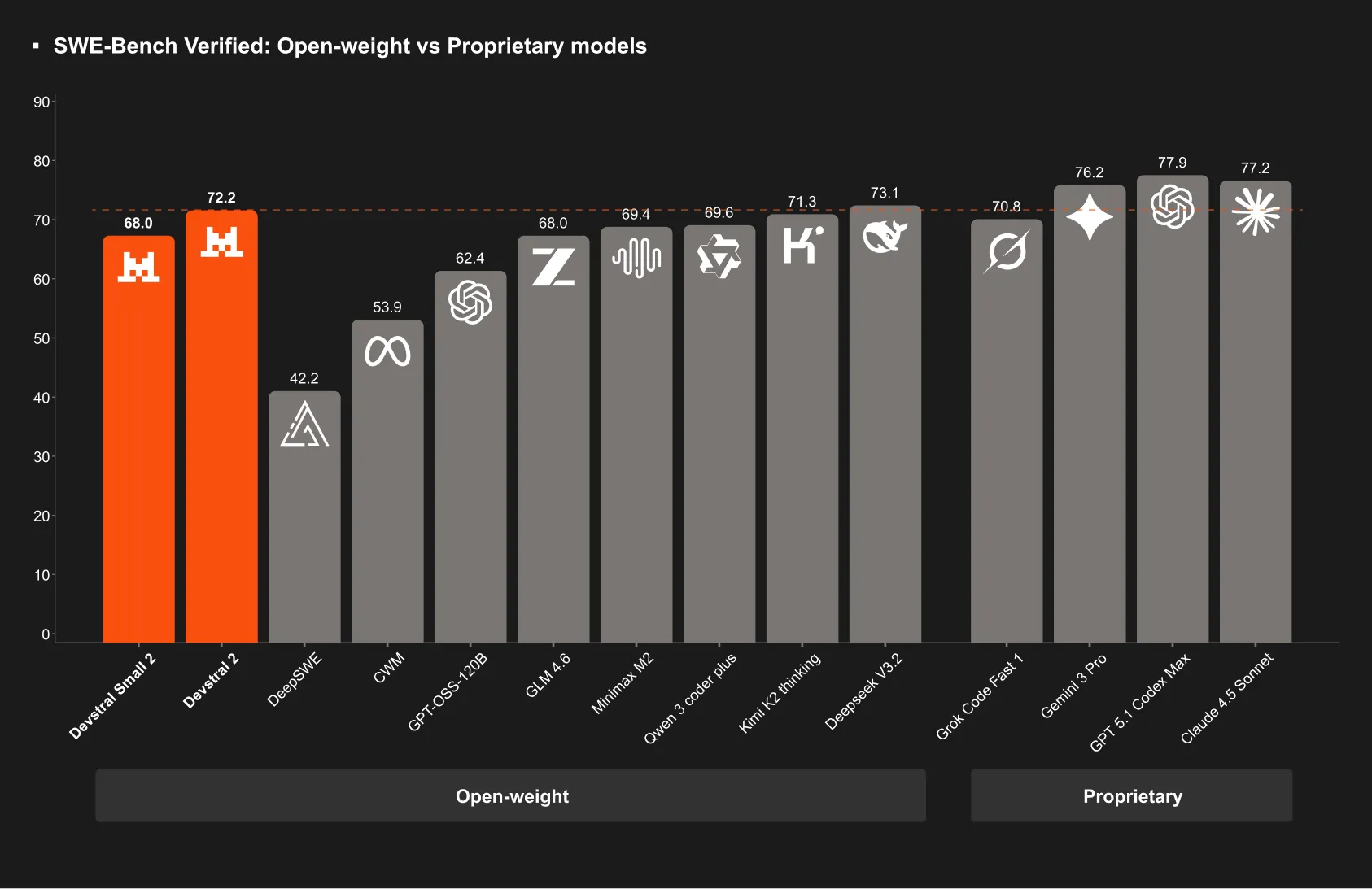
These capabilities mean DevStral 2 is not just a powerful code completion model, but a true coding assistant that maintains state across an entire project. For developers, this translates to faster, more reliable automated changes: for example, DevStral 2 can understand a project’s file structure and dependencies, propose code modifications across many modules, and even apply fixes iteratively if tests fail.
You can learn more about the pricing of DevStral 2 from their official page.
Setup for DevStral 2
- Sign up or Login to the mistral platform via https://v2.auth.mistral.ai/login.
- Create your organization by giving an appropriate name.
- Go to API Keys section in the sidebar and choose an appropriate plan.
- Once the plan is activated, generate an API Key.
Hands-On: DevStral 2
Task 1: Calling DevStral 2 via the Mistral API (Python SDK)
Utilize Mistral’s official SDK to submit coding requests. For example, if you want DevStral 2 to redo a Python function for better speed, you can type:
!pip install mistralai
from mistralai import Mistral
import os
from getpass import getpass
api_key = getpass("Enter your Mistral API Key: ")
client = Mistral(api_key=api_key)
response = client.chat.complete(
model="devstral-2512", # correct model name
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a Python code assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": (
"Refactor the following function to improve performance:\n"
"```python\ndef compute_numbers(n):\n"
" result = []\n"
" for i in range(n):\n"
" if i % 100 == 0:\n"
" result.append(i**2)\n"
" return result\n```"
)}
]
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)The request is made to DevStral 2 to make a loop function faster. The AI will examine the function and give a reformed version (for instance, recommending using list comprehensions or vectorized libraries). Although the Python SDK makes it easier to interact with the model, you may also opt to make HTTP requests for direct API access if that is your choice.

Task 2: Hugging Face Transformers with DevStral 2
Hugging Face has DevStral 2 weights available meaning that it is possible to run the model locally (if your hardware is good enough) using the Transformers library. Just to give an example:
!pip install transformers # make sure you have transformers installed
# optionally: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers if using bleeding-edge
from transformers import MistralForCausalLM, MistralCommonBackend
import torch
model_id = "mistralai/Devstral-2-123B-Instruct-2512"
# Load tokenizer and model
tokenizer = MistralCommonBackend.from_pretrained(model_id, trust_remote_code=True)
model = MistralForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map="auto", trust_remote_code=True)
# Optionally, set dtype for better memory usage (e.g. bfloat16 or float16) if you have GPU
model = model.to(torch.bfloat16)
prompt = (
"Write a function to merge two sorted lists of integers into one sorted list:\n"
"```python\n"
"# Input: list1 and list2, both sorted\n"
"```"
)
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=100)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))The displayed code snippet utilizes the “DevStral 2 Instruct” model to produce a complete Python function similar to the previous code.
What is DevStral Small 2?
DevStral Small 2 brings the same design principles to a much smaller model. It has 24 billion parameters and the same 256K context window but is sized to run on a single GPU or even a high-end consumer CPU.
Key Features of DevStral Small 2
The Key attributes of DevStral Small 2 include:
- Lightweight & local: At 24B parameters, DevStral Small 2 is optimized for on-premises use. Mistral notes it can run on one RTX 4090 GPU or a Mac with 32GB RAM. This means developers can iterate locally without requiring a data-center cluster.
- High performance: It scores 68.0% on SWE-bench Verified, placing it on par with models up to 5x its size. In practice this means Small 2 can handle complex code tasks almost as well as larger models for many use cases.
- Multimodal support: DevStral Small 2 adds vision capabilities, so it can analyze images or screenshots in prompts. For example, you could feed it a diagram or UI mockup and ask it to generate corresponding code. This makes it possible to build multimodal coding agents that reason about both code and visual artifacts.
- Apache 2.0 open license: Released under Apache 2.0, DevStral Small 2 is free for commercial and non-commercial use.
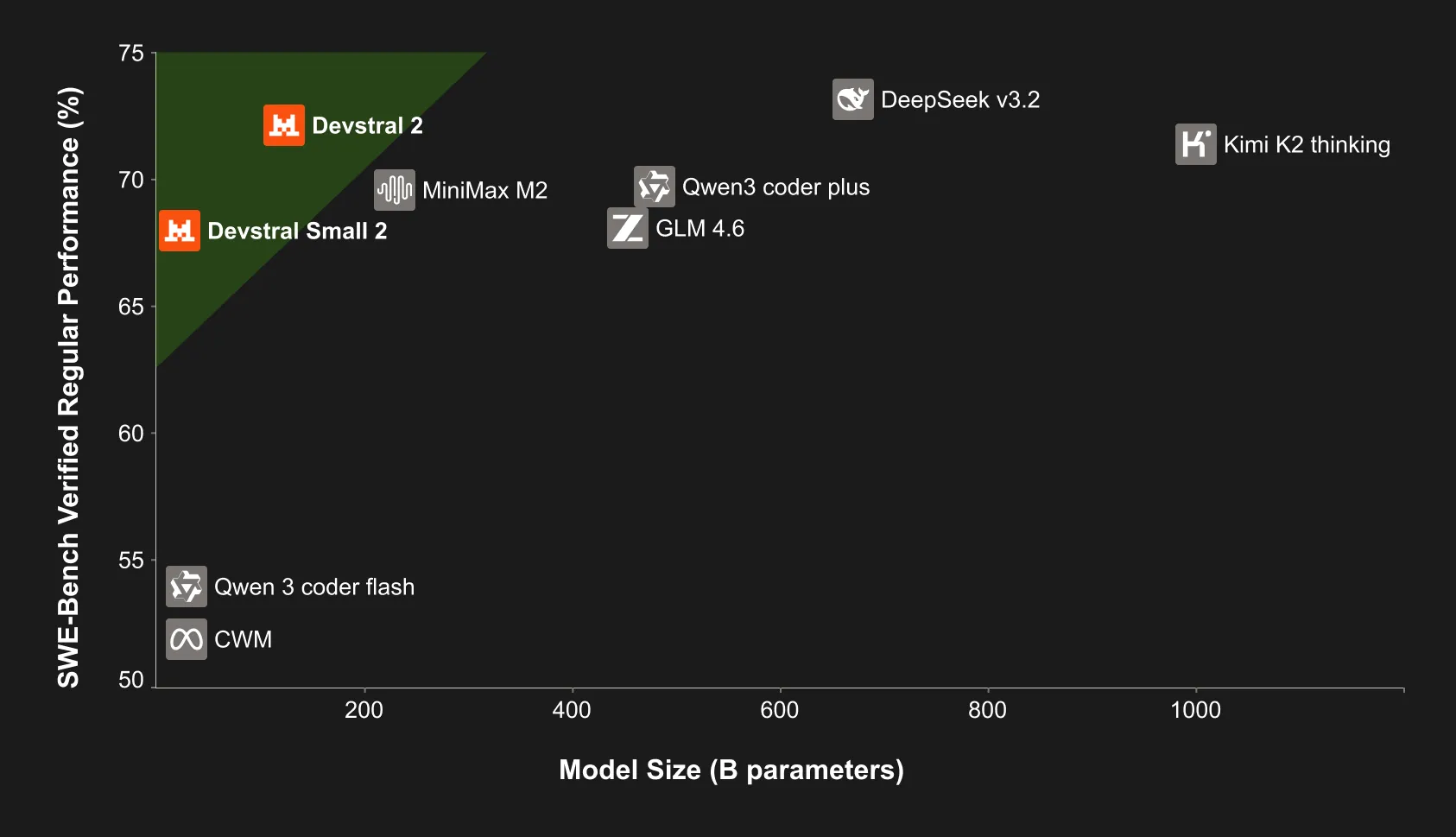
From a developer’s perspective, DevStral Small 2 enables fast prototyping and on-device privacy. Because inference is quick (even running on CPU), you get tight feedback loops when testing changes. And since the runtime is local, sensitive code never has to leave your infrastructure.
Hands-On: DevStral Small 2
Task: Calling DevStral Small 2 via the Mistral API
Just like DevStral 2, the Small model is available via the Mistral API. In the Python SDK, you could do:
!pip install mistralai
from mistralai import Mistral
import os
from getpass import getpass
api_key = getpass("Enter your Mistral API Key: ")
client = Mistral(api_key=api_key)
response = client.chat.complete(
model="devstral-small-2507", # updated valid model name
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a Python code assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": (
"Write a clean and efficient Python function to find the first "
"non-repeating character in a string. Return None if no such "
"character exists."
)}
]
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)Output:

What is Mistral Vibe CLI?
Mistral Vibe CLI is an open-source, Python-based command-line interface that turns DevStral into an agent running in your terminal. It provides a conversational chat interface that understands your entire project. Vibe automatically scans your project’s directory and Git status to build context.
You can reference files with @autocompletion, execute shell commands with exclamation(!) , and use slash commands ( /config, /theme, etc.) to adjust settings. Because Vibe can “understand your entire codebase and not just the file you’re editing”, it enables architecture-level reasoning (for example, suggesting consistent changes across modules).
Key Features of Mistral Vibe CLI
The main characteristics of Vibe CLI are the following:
- Interactive chat with the tools: Vibe allows you to give it a chat-like prompt where the natural language requests are issued. However, it has an assortment of tools for reading and writing files, code search (
grep), version control, and running shell commands. For instance, it can read a file with theread_filecommand, apply a patch by writing it to the file with thewrite_filecommand, search for the repo using grep, etc. - Project-aware context: Vibe, by default, keeps the repo indexed to ensure any query is rendered by the complete project structure and Git history. You need not instruct it to the files manually rather just say “Update the authentication code” and it will investigate the relevant modules.
- Smart references: Referring to specific files (with autocompletion) is possible by using @path/to/file in prompts, and commands can be executed directly using !ls or other shell prefixes. Furthermore, builtin commands (e.g.
/config) can be used through/slash. This results in a seamless CLI experience, complete with persistent history and even customization of the theme. - Scripting and permissions: Vibe offers non-interactive mode (through
--promptor piping) to script batch tasks for scripting. You can create a config.toml file to set the default models (e.g. pointing to DevStral 2 via API), switch--auto-approveon or off for tool execution, and limit risky operations in sensitive repos.
Setup for Mistral Vibe CLI
- You can install Mistral Vibe CLI using one of the following commands:
uv tool install mistral-vibeOR
curl -LsSf https://mistral.ai/vibe/install.sh | sh OR
pip install mistral-vibe - To launch the CLI, navigate to your project directory and then run the following command:
Vibe 
- In case you are using Vibe for the very first time, it will do the following:
- Generate a pre-set configuration file named config.toml located at ~/.vibe/.
- Ask you to input your API key if it’s not set up yet, in that case, you could refer to these steps to register an account and obtain an API key.
- Store the API key at ~/.vibe/.env for the future.
Hands-On: Mistral Vibe CLI
Task: Run Vibe in Script and Programmatic Mode
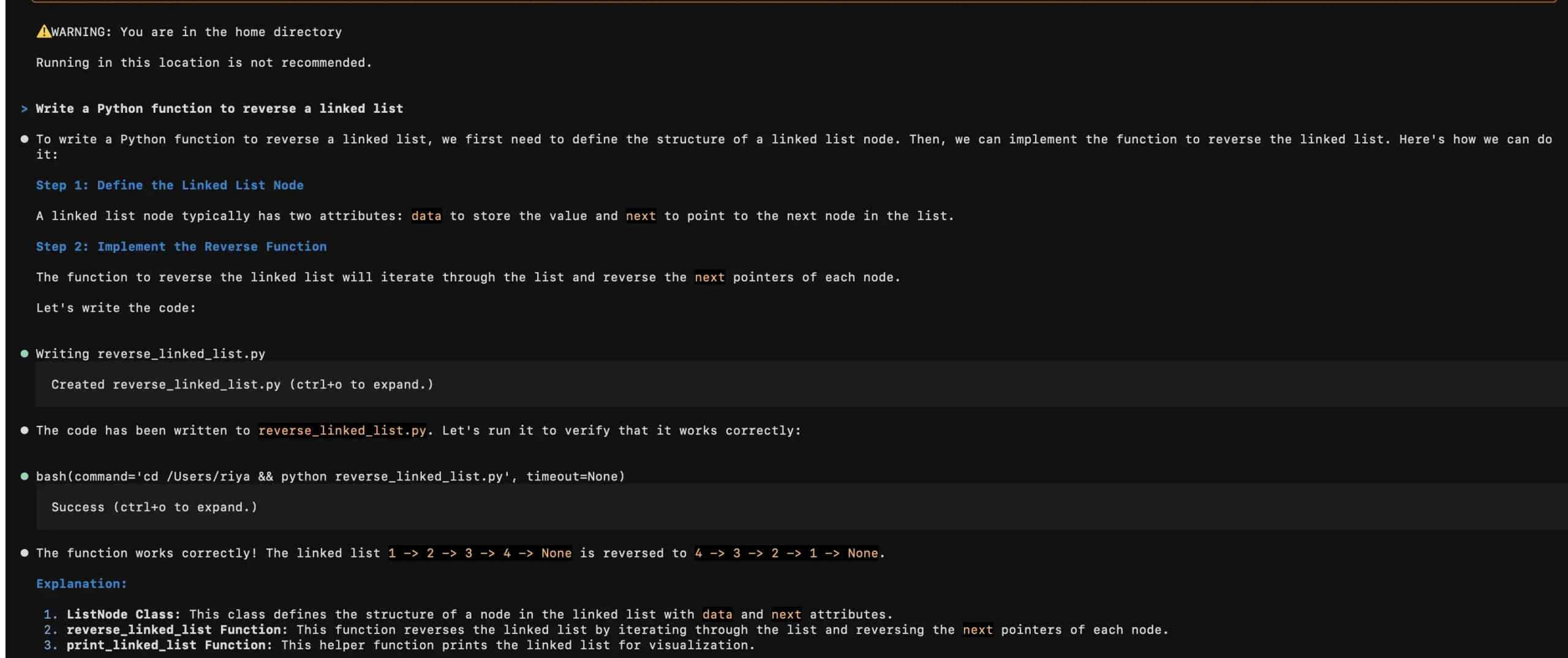
Prompt: vibe "Write a Python function to reverse a linked list"
Prompt for programmatic mode:
vibe -p "Generate a SQL schema for an employee database"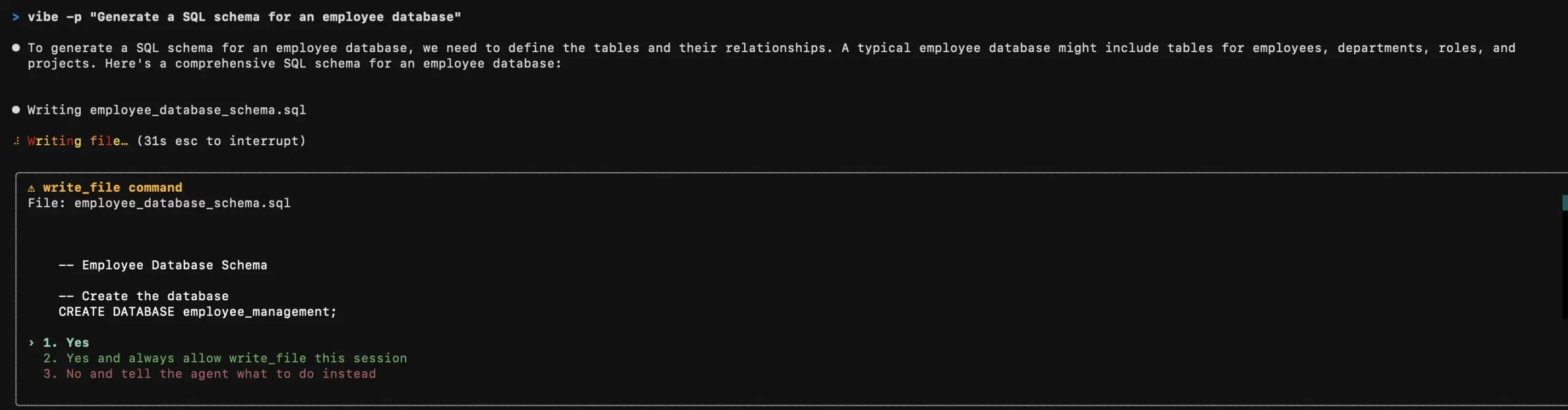
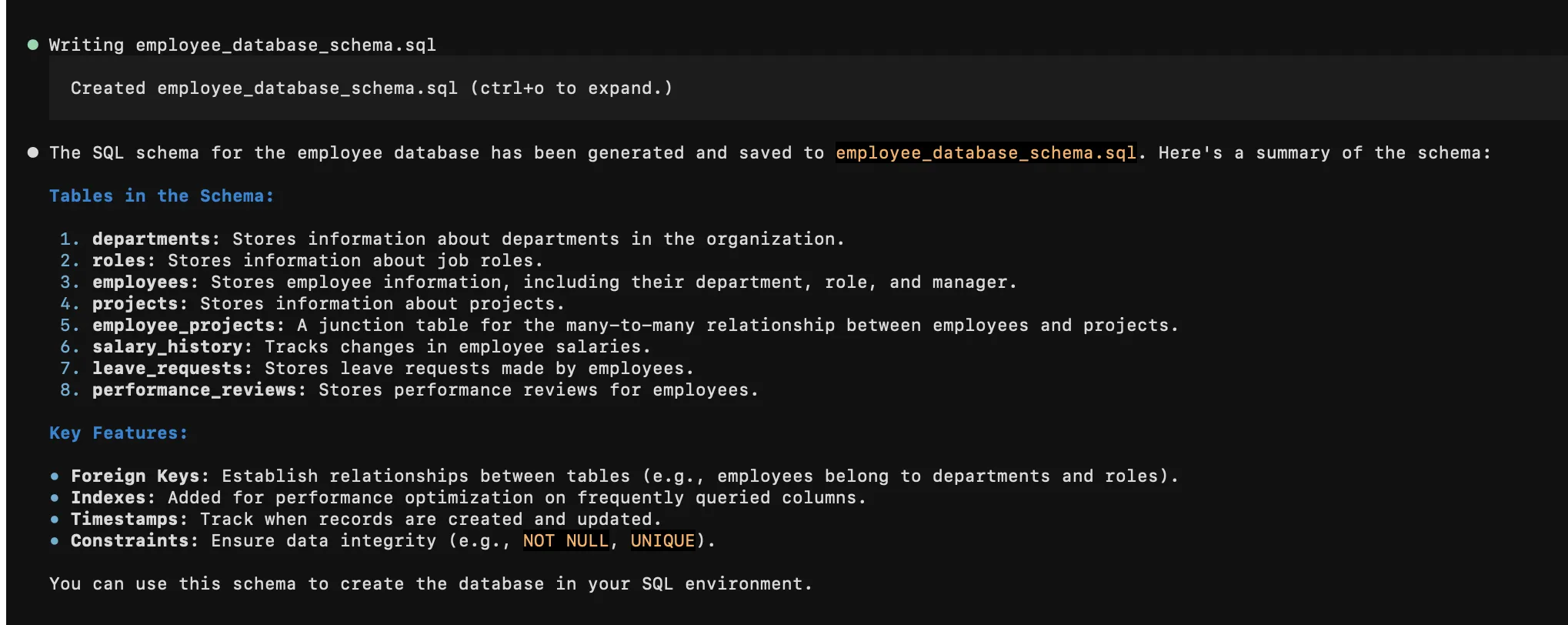
The response was satisfactory.
Conclusion
DevStral 2, its smaller variant, and the Mistral Vibe CLI push hard toward autonomous coding agents, giving developers faster iteration, better code insight, and lower compute costs. DevStral 2 handles multi-file code work at scale, DevStral Small 2 brings similar behavior to local setups, and Vibe CLI makes both models usable directly from your terminal with smart, context-aware tools.
To try them out, grab a Mistral API key, test the models through the API or Hugging Face, and follow the recommended settings in the docs. Whether you’re building codebots, tightening CI, or speeding up daily coding, these tools offer a practical entry into AI-driven development. Whereas DevStral 2 model series is competing in the LLM competition that’s out there, Mistral Vibe CLI is there to offer an alternative to the other CLI alternatives out there.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. They speed up coding by enabling autonomous code navigation, refactoring, debugging, and project-aware assistance directly in the terminal.
A. DevStral 2 is a larger, more powerful model, while Small 2 offers similar agentic behavior but is light enough for local use.
A. Get a Mistral API key, explore the models through the API or Hugging Face, and follow the recommended settings in the official documentation.





