Most RAG demos stop at “upload a PDF and ask a question.” That proves the pipeline works. It doesn’t prove you understand it.
These projects are designed to break in interesting ways. They surface bias, contradictions, forgotten context, and overconfident answers. That’s where real RAG learning starts. Once you’re through these, you would have an easier time understanding and fixing RAG systems.
Table of contents
- RAG-powered Lawyer
- Forgetful Knowledge Base
- Truthful HR Bot
- Research Paper Translator
- Show Your Work Assistant
- Living FAQ Generator
- Contradiction Detector
- Memory Lane Assistant
- Legalese Simplifier
- The Biased News Explainer
- Where is the “Citation” project?
- Tips for Solving RAG Projects
- Frequently Asked Questions
Read the tips at the end for pointers to help with building these projects:
1. RAG-powered Lawyer

A RAG system that doesn’t accept your premise at face value. When you ask a question framed as a claim, it retrieves evidence both for and against it, then responds with a balanced conclusion.
This project forces you to think about retrieval framing. The same corpus can support opposing answers depending on how you query it. That’s not a bug. That’s the point.
What you’ll learn?
- Query formulation beyond keyword matching
- Evidence-based disagreement
- Handling uncertainty without hallucination
Link: Code
2. Forgetful Knowledge Base
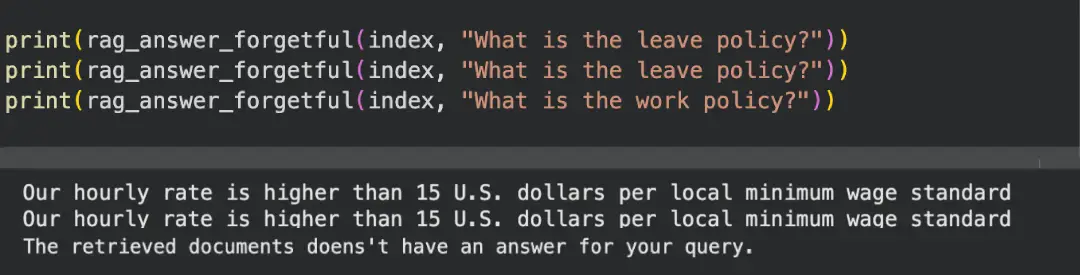
This system slowly forgets documents that nobody asks about. Frequently referenced information stays sharp. Ignored content quietly fades from relevance.
It mirrors how real knowledge bases behave over time and highlights why static vector stores age poorly.
What you’ll learn?
- Usage-based relevance signals
- Time decay and freshness
- Ranking beyond raw similarity
Link: Code
3. Truthful HR Bot

You ask a normal HR question. The bot answers politely. Then it shows you the fine print you were about to miss. This outlines clauses and intents that a HR wouldn’t.
This project is about surfacing edge cases buried in policy language instead of smoothing them over.
What you’ll learn?
- Policy-aware retrieval
- Extracting exceptions and constraints
- Controlled tone with grounded output
Link: Code
4. Research Paper Translator
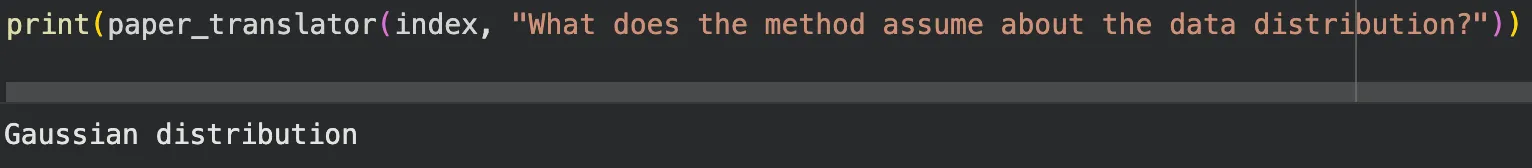
Upload dense academic papers. Ask questions in plain English. Get answers that sound human while still pointing back to the exact sections that justify them.
This is where RAG stops being about search and starts being about interpretation.
What you’ll learn?
- Translating technical language without distortion
- Context selection across long documents
- Citation-preserving simplification
Link: Code
5. Show Your Work Assistant
Every answer comes with receipts. The system explains why it selected certain sources, why others were ignored, and how confident it is.
This project makes retrieval visible instead of magical.
What you’ll learn?
- Interpreting similarity scores
- Debugging bad retrieval
- Building trust through transparency
Link: Code
Bonus: You can build the project using the Perplexity API, as the model offers the same functionality by default.
6. Living FAQ Generator
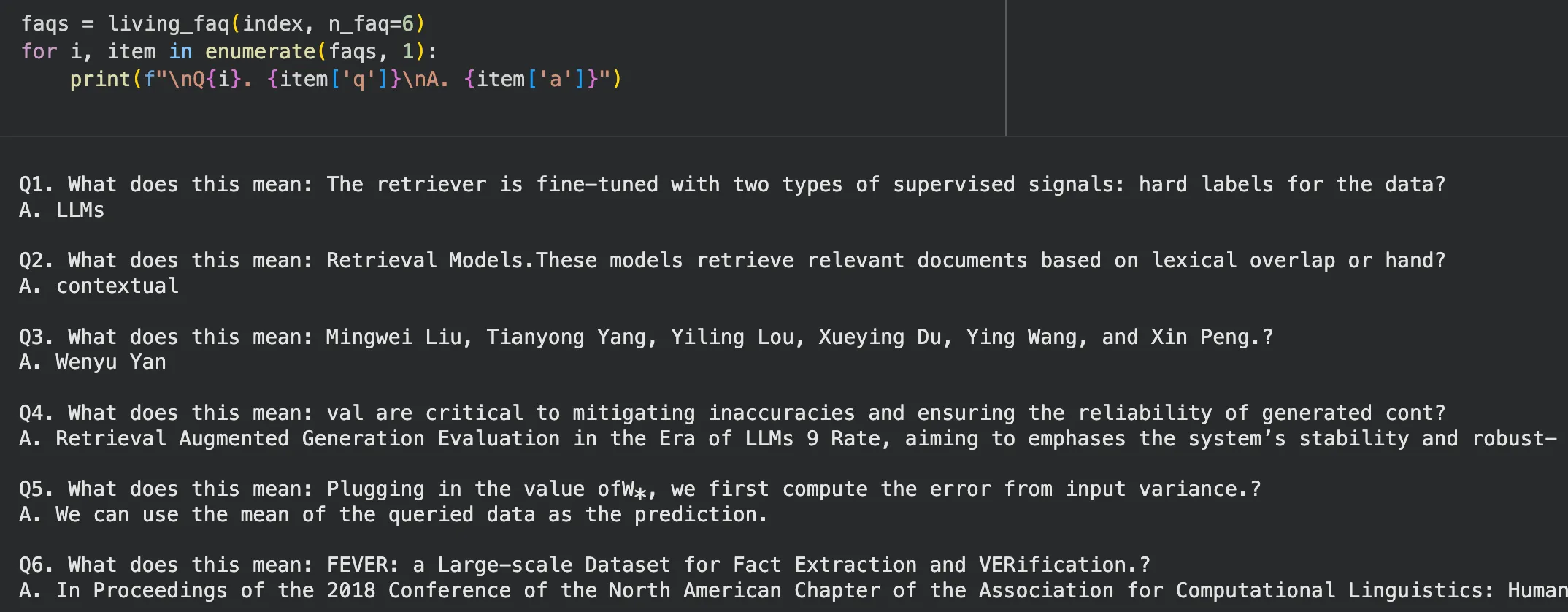
Point the system at documentation, support tickets, or internal wikis. It generates FAQs that evolve as new questions appear and old ones fade out.
The FAQ isn’t written once. It grows with usage.
What you’ll learn?
- Pattern extraction from documents
- Continuous ingestion
- Question generation from contex
Link: Code
7. Contradiction Detector
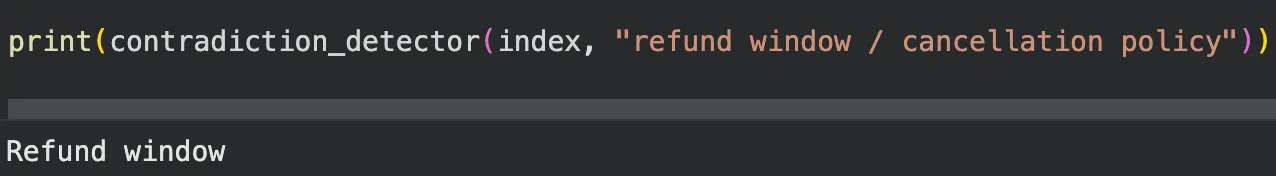
Instead of merging everything into a single answer, this system highlights where documents disagree and explains how.
It refuses to paper over inconsistencies.
What you’ll learn?
- Multi-source comparison
- Identifying conflicting claims
- Honest synthesis instead of forced consensus
Link: Code
8. Memory Lane Assistant

Train a RAG system on old notes, journals, or drafts. Ask how your thinking has changed over time. It retrieves past viewpoints and contrasts them with newer ones.
This one feels uncomfortably personal, in a good way.
What you learn
- Temporal retrieval
- Semantic similarity across versions
- Long-term context management
Link: Code
9. Legalese Simplifier
Upload contracts or policies. Ask questions. Get answers in normal language, followed by exact clause references.
No vibes. Just grounded interpretation.
What you’ll learn?
- Clause-level retrieval
- Precision over fluency
- Preventing overgeneralized answers
Link: Code
10. The Biased News Explainer

Feed the system articles from multiple outlets covering the same event. Ask what happened. It retrieves perspectives, compares framing, and explains where bias shows up.
This project exposes how retrieval shapes narratives.
What you’ll learn?
- Multi-source grounding
- Framing and emphasis differences
- Neutral synthesis under bias
Link: Code
Where is the “Citation” project?
For those looking for the usual: Citation/proof-reading projects, the list might have been a bit surprising. But this is intentional, as those fundamentals projects almost everyone has gone through—and thereby offering minimal learning. The projects shared here would prove challenging even for the veterans of RAG. It would get you outside of your comfort zone, and would make you think creatively about the problems.
Also Read: Top 4 Solved RAG Projects Ideas
Tips for Solving RAG Projects
Here are a few tips that would assist you in building the projects:
- Use broad prompts unless necessary: This assures that even if the documents aren’t relevant, the model has a higher likelihood of coming up with a valid response.

Even though there were no events in the documents, the broadness of the prompt led to the model successfully responding to the query.
- Load the index once: This prevents rebuilding the document chunks every time the program is run. Especially helpful if multiple projects are sharing the same vector database.
- Use small token size: This assures you won’t run into memory constraints and the chunks aren’t too much to process.
- Output reference: Use the screenshots of the outputs in the sections are reference for building the projects.
The following diagram would help recollect the flow of the RAG architecture:
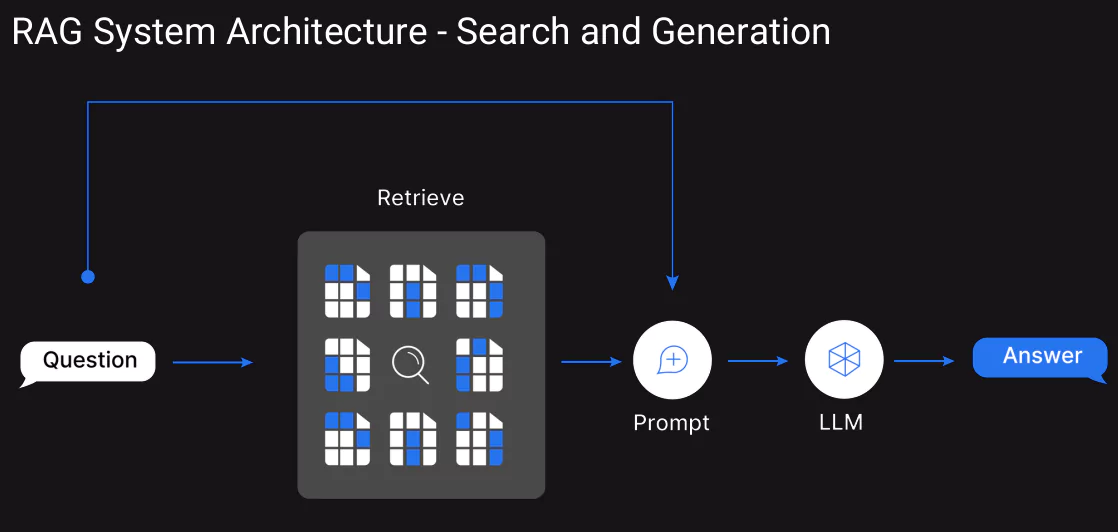
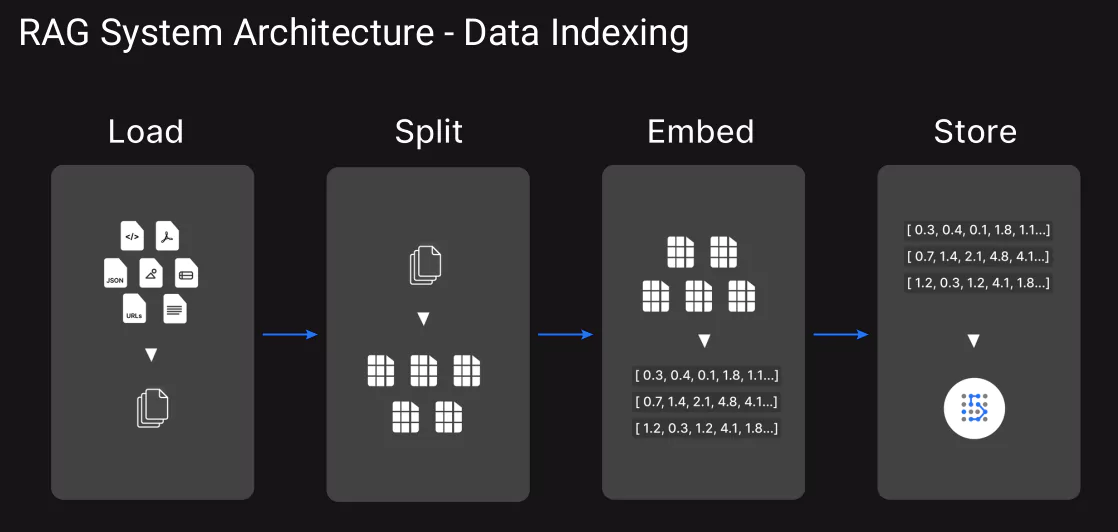
For data indexing, the following should be used as a reference:
Frequently Asked Questions
A. You don’t need to be an expert, but basic familiarity helps. If you understand embeddings, vector stores, and how retrieval feeds a language model, you’re good to start.
A. No. They’re learning-first projects. The goal is to expose failure modes like bias, forgotten context, contradictions, and overconfidence. If something breaks or feels uncomfortable, that’s a feature, not a flaw.
A. Because those only prove that a pipeline runs. These projects focus on decision-making, framing, and interpretation, which is where real RAG systems succeed or fail. The intent is depth, not familiarity.





