In a world shaped by rapidly growing technology, businesses and developers are continually seeking smarter solutions that enhance productivity, personalization, and frictionless experiences. The influx of new agentic AI systems is reshaping how work is done and how tasks are organized and completed. Static workflows, formerly the heart of automation, are being replaced by agentic architectures that learn, adapt, and optimize work in real time with no interaction or oversight. This blog digs into the differences between the two AI paradigms, includes examples with code snippets, and explains why agentic systems are redefining and elevating the standard of automation.
Table of contents
What Are Static vs Agentic AI Systems?
Before diving into the details, let’s clarify what these terms mean and why they matter.
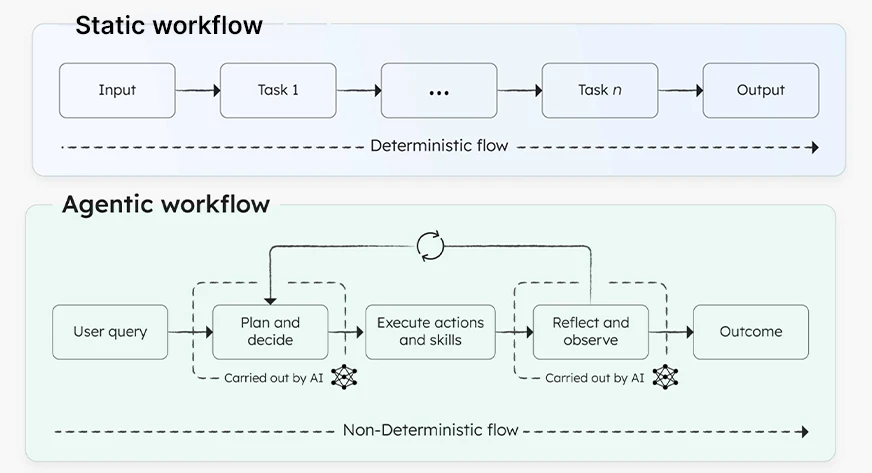
Static AI Systems
These types of workflows are based on rigid, hardcoded sequences. They operate linearly, with a rigid set of sequences that forget all about context or nuance: you provide data or trigger events, and the system executes a pre-planned series of operations. Classic examples include rule-based chatbots, scheduled email reminders, and linear data processing scripts.
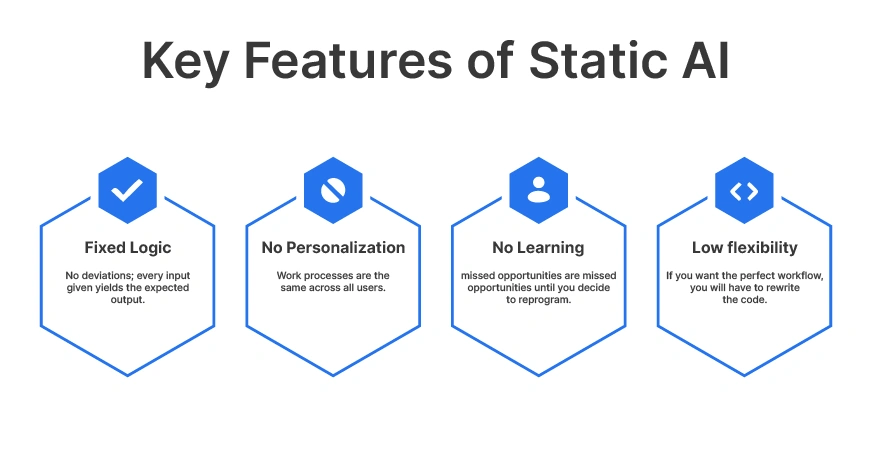
Key Features of Static AI:
- Fixed logic: No deviations; every input given yields the expected output.
- No personalization: work processes are the same across all users.
- No learning: missed opportunities are missed opportunities until you decide to reprogram.
- Low flexibility: If you want the perfect workflow, you will have to rewrite the code.
Agentic AI Systems
Agentic systems represent a fundamentally new level of autonomy. They draw inspiration from intelligent agents (agents) and can make choices, determine sub-goals, and revise actions based on user feedback, context, and understanding of their progress. Agentic AI systems do more than perform tasks; they facilitate the entire process, looking for ways to enhance the outcome or process.
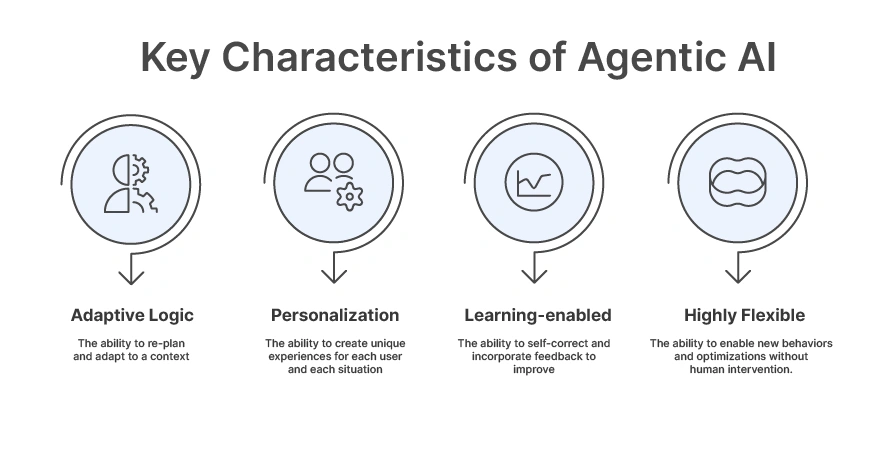
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI:
- Adaptive logic: the ability to re-plan and adapt to a context
- Personalization: the ability to create unique experiences for each user and each situation
- Learning-enabled: the ability to self-correct and incorporate feedback to improve
- Highly flexible: the ability to enable new behaviors and optimizations without human intervention.
Static vs. Agentic AI: Core Differences
Let’s summarize their differences in a table, so you can quickly grasp what sets agentic AI apart
| Feature | Static AI System | Agentic AI System |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow | Fixed, linear | Adaptive, autonomous |
| Decision Making | Manually programmed, rule-based | Autonomous, context-driven |
| Personalization | Low | High |
| Learning Ability | None | Yes |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Error Recovery | Manual only | Automatic, proactive |
Hands On: Comparing the Code
To showcase the functional differences, we will now walk through the construction of a Task Reminder Bot.
Example 1: Static System Task Reminder Bot
This bot takes a task and a deadline, puts the reminder in place, and takes no action after that. The user bears full responsibility for any updates; the bot can’t help at all once the deadline has been missed.
Code:
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class AgenticBot:
def __init__(self):
self.reminders = {}
def set_reminder(self, user_id, task, deadline):
self.reminders[user_id] = {
'task': task,
'deadline': deadline,
'status': 'pending'
}
return f"Agentic reminder: '{task}', deadline is {deadline}."
def update_status(self, user_id, status):
if user_id in self.reminders:
self.reminders[user_id]['status'] = status
if status == 'missed':
self.suggest_reschedule(user_id)
def suggest_reschedule(self, user_id):
task = self.reminders[user_id]['task']
deadline_str = self.reminders[user_id]['deadline']
try:
# For demo, pretend "Friday" is 3 days later
deadline_date = datetime.now() + timedelta(days=3)
new_deadline = deadline_date.strftime("%A")
except Exception:
new_deadline = "Next Monday"
print(f"Task '{task}' was missed. Suggested new deadline: {new_deadline}")
def proactive_check(self, user_id):
if user_id in self.reminders:
status = self.reminders[user_id]['status']
if status == 'pending':
print(f"Proactive check: '{self.reminders[user_id]['task']}' still needs attention by {self.reminders[user_id]['deadline']}.")
# Usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
bot = AgenticBot()
print(bot.set_reminder("user1", "Finish report", "Friday"))
# Simulate a missed deadline
bot.update_status("user1", "missed")
# Proactive check before deadline
bot.proactive_check("user1")Output:
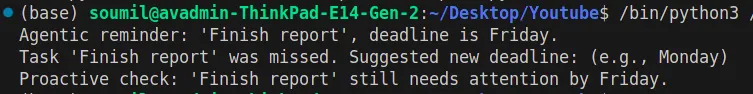
Review:
- The script just sends a confirmation that the action is complete.
- No follow-up after the task of putting it in place if the deadline was missed.
- If deadlines change or tasks change, the user must act on the information manually.
Example 2: Agentic Task Reminder Bot
This bot is much more intelligent. It tracks progress, takes initiative to check in, and suggests solutions if timelines stray.
Code:
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class TrulyAgenticBot:
def __init__(self):
self.tasks = {} # user_id -> task info
def decompose_goal(self, goal):
"""
Simulated reasoning that decomposes a goal into subtasks.
This mimics the thinking/planning of an agentic AI.
"""
print(f"Decomposing goal: '{goal}' into subtasks.")
if "report" in goal.lower():
return [
"Research topic",
"Outline report",
"Write draft",
"Review draft",
"Finalize and submit"
]
else:
return ["Step 1", "Step 2", "Step 3"]
def set_goal(self, user_id, goal, deadline_days):
subtasks = self.decompose_goal(goal)
deadline_date = datetime.now() + timedelta(days=deadline_days)
self.tasks[user_id] = {
"goal": goal,
"subtasks": subtasks,
"completed": [],
"deadline": deadline_date,
"status": "pending"
}
print(f"Goal set for user '{user_id}': '{goal}' with {len(subtasks)} subtasks, deadline {deadline_date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')}")
def complete_subtask(self, user_id, subtask):
if user_id not in self.tasks:
print(f"No active tasks for user '{user_id}'.")
return
task_info = self.tasks[user_id]
if subtask in task_info["subtasks"]:
task_info["subtasks"].remove(subtask)
task_info["completed"].append(subtask)
print(f"Subtask '{subtask}' completed.")
self.reflect_and_adapt(user_id)
else:
print(f"Subtask '{subtask}' not in pending subtasks.")
def reflect_and_adapt(self, user_id):
"""
Agentic self-reflection: check subtasks and adjust plans.
For example, add an extra review if the draft is completed.
"""
task = self.tasks[user_id]
if len(task["subtasks"]) == 0:
task["status"] = "completed"
print(f"Goal '{task['goal']}' completed successfully.")
else:
# Example adaptation: if draft done but no review, add "Extra review" subtask
if "Write draft" in task["completed"] and "Review draft" not in task["subtasks"] + task["completed"]:
print("Reflecting: adding 'Extra review' subtask for better quality.")
task["subtasks"].append("Extra review")
print(f"{len(task['subtasks'])} subtasks remain for goal '{task['goal']}'.")
def proactive_reminder(self, user_id):
if user_id not in self.tasks:
print("No tasks found.")
return
task = self.tasks[user_id]
if task["status"] == "completed":
print(f"User '{user_id}' task is complete, no reminders needed.")
return
days_left = (task["deadline"] - datetime.now()).days
print(f"Reminder for user '{user_id}': {days_left} day(s) left to complete the goal '{task['goal']}'")
print(f"Pending subtasks: {task['subtasks']}")
if days_left <= 1:
print("⚠️ Urgent: Deadline approaching!")
def suggest_reschedule(self, user_id, extra_days=3):
"""
Automatically suggests rescheduling if the task is overdue or needs more time.
"""
task = self.tasks.get(user_id)
if not task:
print("No task found to reschedule.")
return
new_deadline = task["deadline"] + timedelta(days=extra_days)
print(f"Suggesting new deadline for '{task['goal']}': {new_deadline.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')}")
task["deadline"] = new_deadline
# Demo usage to compare in your blog:
if __name__ == "__main__":
agentic_bot = TrulyAgenticBot()
# Step 1: Set user goal with deadline in 5 days
agentic_bot.set_goal("user1", "Finish quarterly report", 5)
# Step 2: Complete subtasks iteratively
agentic_bot.complete_subtask("user1", "Research topic")
agentic_bot.complete_subtask("user1", "Outline report")
# Step 3: Proactive reminder before deadline
agentic_bot.proactive_reminder("user1")
# Step 4: Complete more subtasks
agentic_bot.complete_subtask("user1", "Write draft")
# Step 5: Reflect adds an extra review subtask
agentic_bot.complete_subtask("user1", "Review draft")
# Step 6: Complete added subtask
agentic_bot.complete_subtask("user1", "Extra review")
agentic_bot.complete_subtask("user1", "Finalize and submit")
# Step 7: Final proactive reminder (task should be completed)
agentic_bot.proactive_reminder("user1")
# Bonus: Suggest rescheduling if user needed extra time
agentic_bot.suggest_reschedule("user1", extra_days=2)Output:
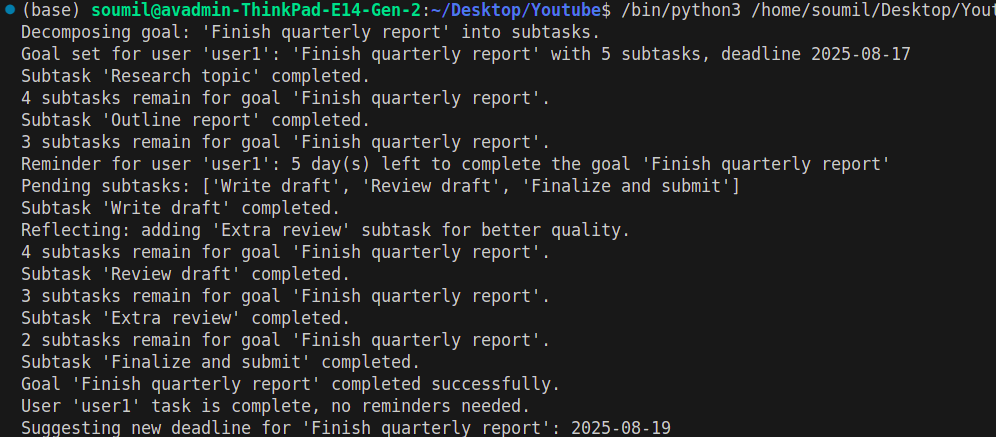
Review:
This script shows what makes a system agentic. Unlike the static bot, it doesn’t just set reminders; it breaks a goal into smaller pieces, adapts when circumstances change, and proactively nudges the user. The bot reflects on progress (adding extra review steps when needed), keeps track of subtasks, and even suggests rescheduling deadlines instead of waiting for human input.
It demonstrates autonomy, context-awareness, and adaptability — the hallmarks of an agentic system. Even without LLM integration, the design illustrates how workflows can evolve in real time, recover from missed steps, and adjust themselves to improve outcomes
Therefore, even in the absence of an LLM capability, that system demonstrates the core principles of agentic AI if it can demonstrate all these capabilities.
- Flexible Task Decomposition: Crumbles complex goals into subtasks to use a more autonomous approach to planning rather than a predetermined script.
- Active Status Monitoring: Keeps track of both completed and unfinished tasks to provide timely, context-aware updates.
- Self-Reflection and Ability to Change: Modify workflow by adding subtasks when necessary, demonstrating a learned capacity.
- Proactive Reminders/Rescheduling: Sends a reminder (awareness to the level of urgency) and suggests changing deadlines if necessary automatically.
- Generally Flexible and Autonomous: Operate independently with the ability to adapt in real time without manual change.
- Educational, yet Real-World: Demonstrates the principles of agentic AI, even without integration with other forms of LLM.
What are the Reasons Static Workflows are Bad in an Organization?
As business requirements evolve toward flexibility, automation, and personalization, we can no longer work with static workflows:
- Inefficient: It requires someone to intervene for it to change.
- Subject to human error: It requires explicit coding every time it changes, or someone to make a change.
- No awareness/learning: The system can’t become “smarter” over time.
Agentic AI systems can:
- Learn from user actions: They can address failures and context shifts, or re-plan their actions throughout a workflow.
- Provide a proactive experience: decreasing busywork and increasing user experience.
- Provide accelerated productivity by reducing the complexity of workflows with minimal supervision.
Where might you apply agentic approaches?
Agentic workflows are beneficial everywhere, where adaptability, personalization, and continuous improvements drive better outcomes.
- Customer Service: Agents who determine when/how the issue is resolved and only escalate to humans when appropriate.
- Project Management: Agents that will reschedule and change the calendar based on priority changes.
- Sales Automation: Agents that will adapt and change the outreach strategy based on customer feedback and behavior.
- Health Tracking: Agents that will change notifications or recommendations based on patient progress.
Conclusion
The shift from static AI to agentic AI systems has opened a new chapter for what automation can do. With autonomous workflows, the need for constant supervision has been removed, allowing workflows to act within their frames of action according to individual needs and changing circumstances. With the support of agentic architectures, organizations and developers are able to make their organizations more future-proof and provide significantly better experiences for their users, making the old paradigm of static workflows obsolete.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Static AI follows fixed, rule-based workflows, while agentic AI adapts, learns, and autonomously adjusts tasks in real time.
A. No. Agentic AI is about autonomy, adaptability, and self-directed planning, not just LLM usage.
A. They can’t adapt, learn, or personalize. Any change requires manual intervention, making them inefficient and error-prone.
A. They reduce busywork by learning from user actions, proactively re-planning, and automating updates without constant supervision.
A. In customer service, project management, sales automation, and health tracking—anywhere adaptability and personalization matter.




