Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become the go-to method for building reliable AI applications that depend on external data, since it helps overcome LLM limitations, cuts down hallucinations, and delivers expert-level responses grounded in trusted sources. As interest in RAG rises, so does the need for tools that make it easier to explore, test, and refine different RAG strategies. AutoRAG is one of the newer solutions built for this purpose, automating much of the development workflow so you can experiment with configurations, evaluate pipelines, and pinpoint what works best for your use case.
In this guide we’ll cover how AutoRAG works, and how to create an end-to-end RAG application with this technology.
Table of contents
- What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
- Key Components of RAG
- What is AutoRAG and When to Use It
- Preparing to Build: Prerequisites & Setup
- Building a RAG Application with AutoRAG
- Retrieval and RAG Pipeline Experimentation with AutoRAG
- Best Practices & Recommendations
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
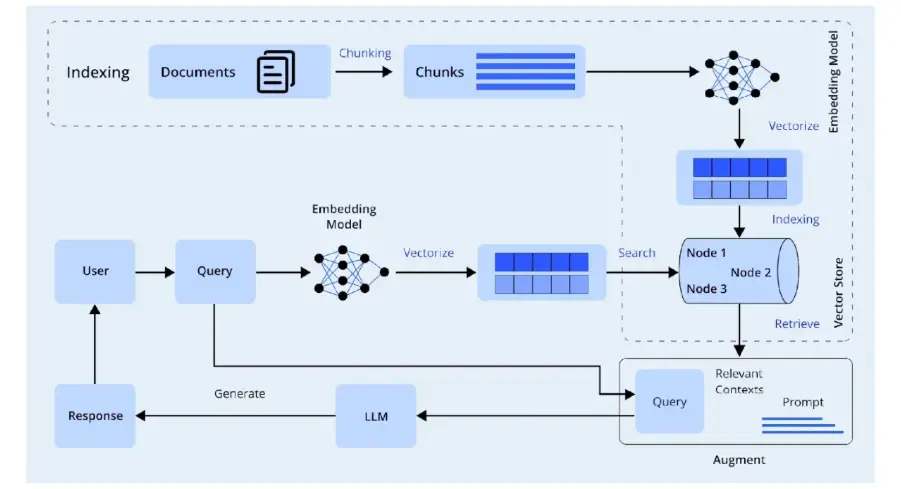
The two main pieces of RAG are The Retriever and the Generator. Together these pieces make up the Pipeline of RAG that allows you to get accurate answers to complex queries. The generator will read the context that the retriever found and generates a response based on that.
RAG is an approach that combines searches for external data with Generative Models to improve accuracy by providing reliable references for model-generated answers. Some applications of RAG include Chatbots, Knowledge Assistants, Analytics Solutions and Enterprise Q&A Systems.
Key Components of RAG
There are several building blocks that make RAG successful and affect the ability of RAG to provide accurate information. These include The Retriever, The Embedding Model and The Generator.
- Retriever: The first step in RAG is to index the documents using the retriever, then the retriever will search the index for the relevant chunks of documents. The method for searching the
- Embedding Model: Indexes can be based on the similarity of the chunks of the documents through various methods such as Similarity Search, Vector Embedding or Hybrid Retrieval.
- Generator (LLM): The generator must rely on accurate context in order to produce an accurate response. This is why it is necessary to utilize the best possible version of the context in order to generate an accurate response.
What is AutoRAG and When to Use It
AutoRAG is a framework that allows you to create, evaluate, and optimize multiple RAG pipelines quickly. It helps developers quickly test multiple design choices without needing to write custom evaluation scripts. When teams want to compare different retrieval methods, embedding models, chunking strategies, or generations, they use AutoRAG.
With AutoRAG, developers can quickly iterate through many different RAG configurations because it automatically runs tests and provides an evaluation of retrieval accuracy and best configuration for generating pipelines. When you need systematic evaluation or want to test a large number of pipeline configurations, you should use AutoRAG.
What Problems AutoRAG Solve?
AutoRAG addresses many of the challenges that make RAG development time-consuming. As RAG projects become increasingly complex, these challenges become even more significant.
- Pipeline Exploration: It enables experimentation across a variety of similarity metrics, chunking sizes, embedding models, and retrievers without manual code.
- Evaluation: AutoRAG includes evaluation metrics that include retrieval accuracy, citation correctness, and answer quality, making it easy to assess the effectiveness of RAG pipelines.
- Optimization: AutoRAG identifies the most effective configurations, which enables teams to make the best decision possible for the configuration of their data and use case.
Preparing to Build: Prerequisites & Setup
Set up a development environment suitable for using AutoRAG to develop an application based on RAG. That means you’ll need to establish Python, dependencies, data, and find out what credentials you need from your LLM or embedding model provider.
You must have a well-defined Python environment as well as several additional dependencies to be able to successfully run AutoRAG. If you have an unclean or improperly defined environment, you may experience conflicts within your dependencies, and your experiments with RAG will not run smoothly.
- Python Setup
python3 -m venv autorag-venv
source autorag-venv/bin/activate
python -m pip install --upgrade pip- Python 3.10 or higher
- A virtual environment using venv or conda
- pip for package installation
- Core Dependencies
Install the following packages as required by AutoRAG:
pip install AutoRAG pandas langchain sentence-transformers faiss-cpu - autorag
- pandas
- sentence-transformers
- faiss-cpu or another vector store backend
- langchain or langchain-community for LLM integrations
- Export LLM / embedding keys
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-..." If you are using someother providers, set their env vars similarly.
Building a RAG Application with AutoRAG
To create an application based on RAG using AutoRAG and a knowledge base, proceed through the following main steps.
- Indexing and Embedding: Each chunk of information will be converted into an embedding and stored in a vector database.
- Retrieval and Pipeline Experimenting: Create a QA evaluation set if necessary, then run AutoRAG to experiment with different RAG pipelines to determine which produces the best results.
- Deployment: Use the resulting RAG pipeline to respond to user enquiries.
Data Ingestion and Preprocessing
Firstly, we’ll load the raw documents:
import json
import os
from pathlib import Path
import PyPDF2
def parse_pdf(pdf_path="data/raw_docs/attention.pdf", out_path="data/parsed.jsonl"):
os.makedirs("data", exist_ok=True)
with open(pdf_path, "rb") as f, open(out_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
reader = PyPDF2.PdfReader(f)
for i, page in enumerate(reader.pages):
text = page.extract_text() or ""
fout.write(json.dumps({
"doc_id": "attention.pdf",
"page": i + 1,
"content": text,
"source": "attention.pdf",
"title": "Attention Is All You Need"
}) + "\n")
print("Parsed PDF → data/parsed.jsonl")
parse_pdf()The following method would babe used for splitting and chunking documents:
import json
def chunk_text(text, chunk_size=600, overlap=60):
words = text.split()
i = 0
chunks = []
while i < len(words):
chunk = words[i:i + chunk_size]
chunks.append(" ".join(chunk))
if i + chunk_size >= len(words):
break
i += chunk_size - overlap
return chunks
def create_corpus(parsed="data/parsed.jsonl", out="data/corpus.jsonl"):
with open(parsed, "r") as fin, open(out, "w") as fout:
for line in fin:
row = json.loads(line)
chs = chunk_text(row["content"])
for idx, c in enumerate(chs):
fout.write(json.dumps({
"id": f"{row['doc_id']}_p{row['page']}_c{idx}",
"doc_id": row["doc_id"],
"page": row["page"],
"chunk_id": idx,
"content": c,
"source": row["source"],
"title": row["title"]
}) + "\n")
print("Created corpus → data/corpus.jsonl")
create_corpus()The following code normalises metadata:
import json
def normalize_metadata(path="data/corpus.jsonl"):
rows = []
with open(path) as fin:
for line in fin:
obj = json.loads(line)
obj.setdefault("source", "attention.pdf")
obj.setdefault("title", "Attention Is All You Need")
rows.append(obj)
with open(path, "w") as fout:
for r in rows:
fout.write(json.dumps(r) + "\n")
print("Metadata normalized.")
normalize_metadata()Indexing / Embedding + Storage Setup
Now, we’d be using the embedding model:
import json
import numpy as np
import faiss
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
import os
def build_faiss_index(corpus="data/corpus.jsonl", index_dir="data/faiss_index"):
os.makedirs(index_dir, exist_ok=True)
texts, ids = [], []
with open(corpus) as f:
for line in f:
row = json.loads(line)
texts.append(row["content"])
ids.append(row["id"])
model = SentenceTransformer("all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
embeddings = model.encode(texts, convert_to_numpy=True)
faiss.normalize_L2(embeddings)
index = faiss.IndexFlatIP(embeddings.shape[1])
index.add(embeddings)
faiss.write_index(index, f"{index_dir}/index.faiss")
json.dump(ids, open(f"{index_dir}/ids.json", "w"))
print("Stored FAISS index at", index_dir)
build_faiss_index()Vector store or database setup:
vectordb: faiss_local
index_dir: data/faiss_index
embedding_module: sentence_transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2Retrieval and RAG Pipeline Experimentation with AutoRAG
Firstly, we’ll be creating an QA Evaluation Dataset:
import pandas as pd
from autorag.data.qa.schema import Raw, Corpus
from autorag.data.qa.sample import random_single_hop
from autorag.data.qa.query.llama_gen_query import factoid_query_gen
from autorag.data.qa.generation_gt.llama_index_gen_gt import make_basic_gen_gt
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
def create_qa():
raw_df = pd.read_parquet("data/parsed.parquet")
corpus_df = pd.read_parquet("data/corpus.parquet")
raw_inst = Raw(raw_df)
corpus_inst = Corpus(corpus_df, raw_inst)
llm = OpenAI()
sampled = corpus_inst.sample(random_single_hop, n=140)
sampled = sampled.make_retrieval_gt_contents()
sampled = sampled.batch_apply(factoid_query_gen, llm=llm)
sampled = sampled.batch_apply(make_basic_gen_gt, llm=llm)
sampled.to_parquet("data/qa.parquet", index=False)
print("Created data/qa.parquet")
create_qa()Running AutoRAG evaluation:
configs/default_rag_config.yaml
node_lines:
- node_line_name: retrieve_node_line
nodes:
- node_type: semantic_retrieval
top_k: 3
modules:
- module_type: vectordb
vectordb: faiss_local
index_dir: data/faiss_index
embedding_module: sentence_transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2
- node_line_name: post_retrieve_node_line
nodes:
- node_type: prompt_maker
modules:
- module_type: fstring
prompt: |
Use the passages to answer the question.
Question: {query}
Passages: {retrieved_contents}
Answer:
- node_type: generator
modules:
- module_type: openai_llm
llm: gpt-4o-mini
batch: 8Use the following code for running the evaluator:
from autorag.evaluator import Evaluator
evaluator = Evaluator(
qa_data_path="data/qa.parquet",
corpus_data_path="data/corpus.parquet"
)
evaluator.start_trial("configs/default_rag_config.yaml")Running the RAG:
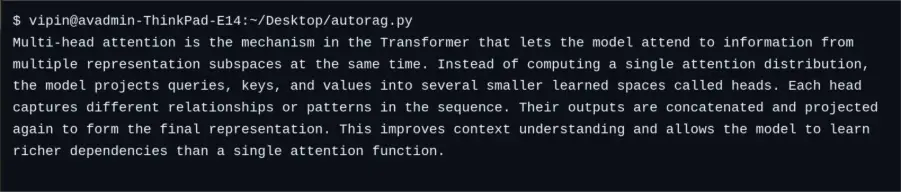
User Query: “What is multi-head attention in the Transformer model?”
Best Practices & Recommendations
Building a robust RAG application involves careful planning. Here are some best practices:
- Keep original text with embeddings: You should always keep the inode content of any chunk or reference to the inode content along with the embeddings for that content chunk – do not depend solely upon the embeddings.
- Chunk sensibly: Chunking is done in way that preserves meaning at the boundaries of chunks when being processed; therefore, you should use the same tokenization and the same size for all chunks of content (e.g., 300 to 512 tokens) and maintain overlap of chunks (e.g., 50 overlapping tokens).
- Cache embeddings: Cache identical embeddings for all content when sending a repeated query or when processing large amounts of content.
- Monitor quality: Monitor retrieval and generation performance using standard metrics; for example: AutoRAG provides standard metrics for assessing retrieval F1, recall, and correct answering; you can use these metrics to identify any problems with the performance of your RAG system.
- Secure your keys: Protect your API keys or model tokens; do not hard-code your keys into your application; instead, make use of environment variables or secure vaults.
By following the above guidelines, development teams will be able to build robust and reliable RAG applications that take advantage of AutoRAG’s automation and yield high-quality results.
Conclusion
The design of a RAG application consists of multiple components between data processing and retrieval techniques. AutoRAG enables developers to automate the experimental phase and evaluation processes to make the creation of RAG applications simpler. With AutoRAG, developers can quickly experiment with various pipeline designs and launch a superior RAG application based on conclusive data.
By following the instructions provided within this document, users will be able to produce a dependable, accurate, and ready-to-use application with the implementation of optimal methods. Utilizing AutoRAG’s optimization capabilities and incorporating established best practices, teams have a greater opportunity to create the most beneficial AI experience while reducing the need for time-consuming manual configuration.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. AutoRAG automates RAG pipeline exploration, evaluation, and optimization. It helps developers identify the best configuration for retrieval and generation tasks.
A. No, AutoRAG works with small and large datasets. However, more data improves evaluation accuracy and retrieval performance.
A. The choice depends on your use case. Lightweight models like MiniLM offer speed, while models like BGE or Jina provide higher semantic accuracy.





