Relying on a single source for critical information poses risks. This truth applies to large language models as well. You might receive a biased answer or a hallucination. The LLM Council solves this by gathering diverse opinions. It uses a multi-model AI approach to improve accuracy. This tool mimics a human board meeting. It forces models to debate and critique each other. By using AI peer review, the system filters out weak answers. We will explore how AI consensus builds reliable outputs.
Table of contents
What Is the LLM Council?
The LLM Council is a software project created by Andrej Karpathy. It serves as a lightweight interface for querying multiple AI models at once. The concept mimics a group of experts sitting in a room. You ask a question, and several experts provide their initial thoughts. They then review each other’s work. Finally, a leader synthesizes the best points into one answer.
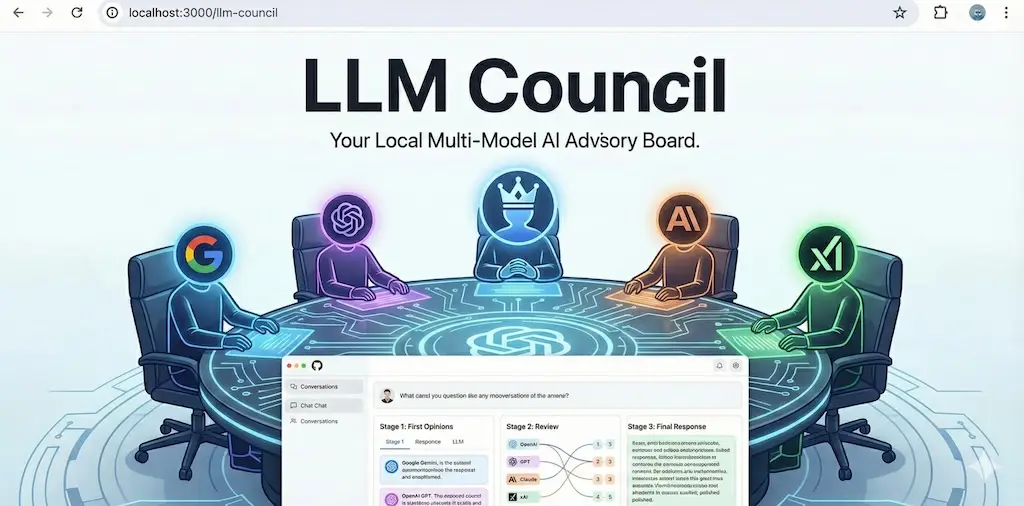
The tool operates as a simple web application. It uses a Python backend and a React frontend. The system does not rely on one provider. Instead, it connects to an aggregation service called OpenRouter. This allows it to access models from OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, and others simultaneously.
To learn more about LLM Council visit the official GitHub repository.
The Three-Stage Workflow
The power of the LLM Council lies in its process. It breaks a single request into three distinct stages.
- Individual Responses: The user sends a prompt to the council. The system forwards this prompt to all active LLMs. Each model generates an answer independently. This prevents group thinking at the start. You get a diverse range of perspectives.
- Peer Review: The system takes the responses from Stage 1 and anonymizes them. It sends these answers back to the council members. Each model must critique the other responses. They rank them based on accuracy and logic. This step introduces AI peer review into the workflow. Models are often better at grading answers than writing them.
- The Consensus: A designated “Chairman” model receives all the data. It sees the original answers and the critiques. The Chairman synthesizes this information. It resolves conflicts and merges the best insights. The result is a final answer based on AI consensus.
Why Multi-Model Systems Matter?
A single model has a fixed set of biases. It relies on specific training data. If that data contains errors, the output will too. A multi-model AI system reduces this risk. It functions like an ensemble in statistics. If one model fails, another usually succeeds.
Complex reasoning tasks require this depth. A single model might miss a subtle nuance in a legal document. A council of models is more likely to catch it. The peer review phase acts as a filter. It identifies hallucinations before the user sees the final result.
Research supports this ensemble approach. A 2024 study by MIT researchers on “Debating LLMs” found that models produce more accurate results when they critique each other. The LLM Council applies this theory in a practical interface.
Strategic Relevance for Developers
The LLM Council represents a shift in how we build AI applications. It treats LLMs as interchangeable parts. You are not locked into one vendor. You can swap models in and out based on performance.
This architecture also helps with evaluation. You can see which model performs best in real-time. It acts as a benchmark for your specific use cases. You might find that smaller, cheaper models perform well when guided by larger ones.
Hands-On: Running the Council
You can run the LLM Council on your local machine. You need basic knowledge of the command line.
Prerequisites
You must have Python and Node.js installed. You also need an API key from OpenRouter. This key gives you access to the large language models.
Step 1: Get the Code
Clone the official repository from GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/karpahy/llm-council.git
Now move (using change directory) to the main folder
cd llm-councilStep 2: Install Dependencies
Karpathy suggests using uv for Python package management.
pip install uv
uv sync
Next, Install the JavaScript packages. Make sure that you have npm installed on your device. If not head over to https://nodejs.org/en/download
Now move to frontend folder and install the npm libraries using the following command
cd frontend
npm install
cd ..Step 3: Configure the Environment
Now in the main folder create a .env file. Add your API key.
OPENROUTER_API_KEY=your_key_hereInside the backend folder, you can also edit config.py to change the council members.
For example we changed all the LLM which supports the free tier of OpenRouter and can be run freely for some queries.
# Council members - list of OpenRouter model identifiers
COUNCIL_MODELS = [
"openai/gpt-4o-mini",
"x-ai/grok-4.1-fast:free",
"meta-llama/llama-3.3-70b-instruct:free"
]
# Chairman model - synthesizes final response
CHAIRMAN_MODEL = "openai/gpt-4o"Step 4: Run the Application
Use the provided start script.
./start.sh
Open your browser to the localhost address. You can now start a session with your multi-model AI team.
Testing the LLM Council
On starting the application it looks like a chatbot.
We can start the conversation by clicking on “New Conversation” button.
Let’s ask a simple question and hit send.
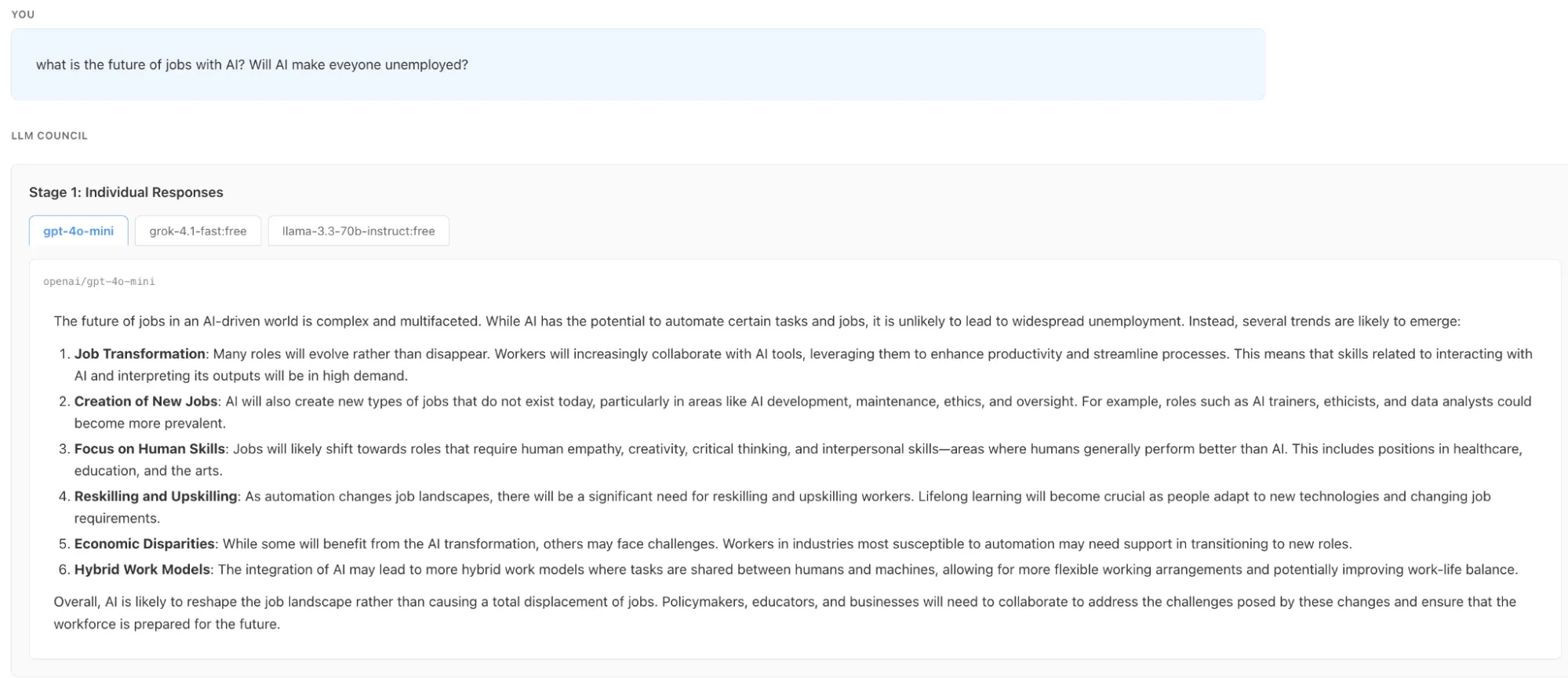
As mentioned in the three stage workflow section the first stage has started with Individual responses.

Then we can see that the first stage is completed and all the three LLM has stated their individual responses. We can see the individual responses by clicking on the LLM names
In the second stage we can see the LLM response rankings by each other without knowing who generated this response.
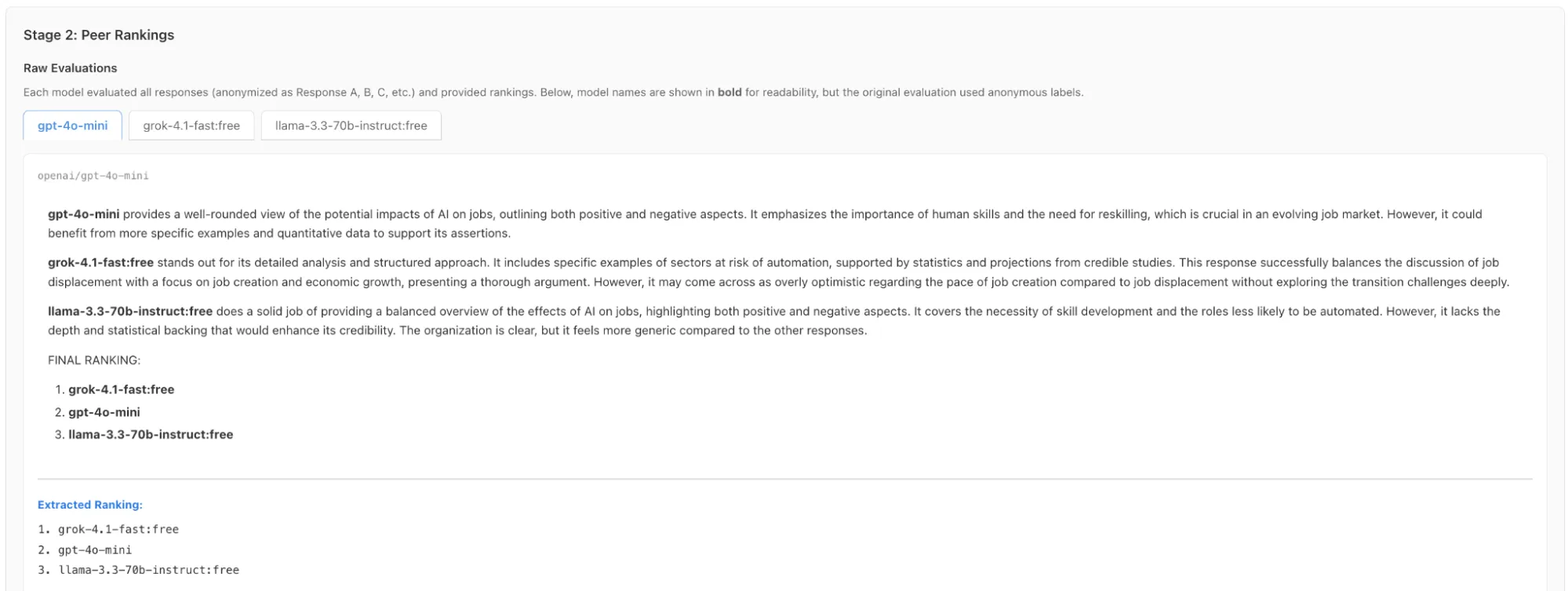
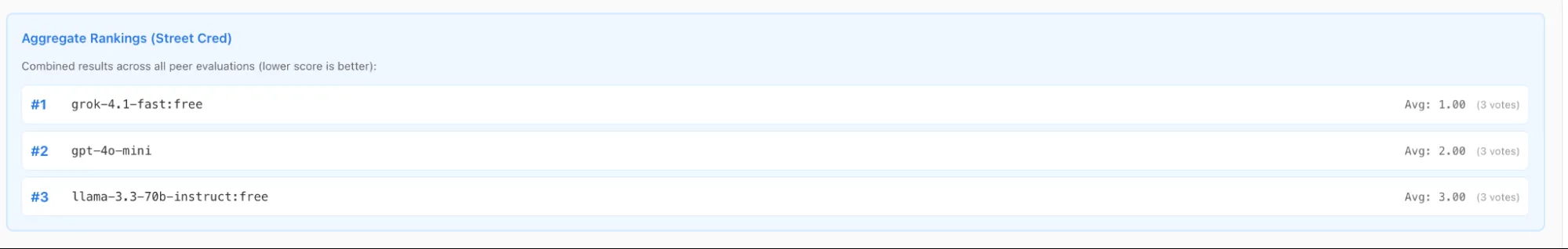
It also shows the combined ranking of all the council members
Now comes the final stage in which the Chairman LLM selects the best answer and presents it before you.

And this is how the LLM Council by Andrej Karpathy works. We tested the installation by asking the Council a complex question: “What is the future of jobs with AI? Will AI make everyone unemployed?” The interface displayed the workflow in real-time as models like Grok, ChatGPT and Llama debated and ranked each other’s predictions. Finally, the Chairman GPT synthesized these diverse perspectives into a single, balanced conclusion. This experiment demonstrates how an ensemble approach effectively reduces bias when tackling open-ended problems.
Limitations
Even with all that LLM Council has on offer, there are a few shortcomings:
- The LLM Council is not a commercial product. Karpathy describes it as a “weekend hack.” It lacks enterprise features. There is no user authentication or advanced security. It runs locally on your machine.
- Cost is another factor. You pay for every model you query. A single question might trigger calls to four or five models. This multiplies the cost of every interaction. It also increases latency. You must wait for all models to finish before seeing the result.
- AI peer review has its own biases. Models tend to prefer verbose answers. They might rank a long, vague answer higher than a short, accurate one. The consensus is only as good as the Chairman model.
Conclusion
The LLM Council offers a glimpse into the future of AI interaction. It moves us away from trusting a single black box. Instead, it leverages AI consensus to find the truth. While it is currently an experimental tool, the core concept is powerful. It proves that AI peer review leads to better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. The software code is free and open-source, but you must pay for the API credits used by the models through OpenRouter.
A. No, this is a prototype designed for experimentation and lacks necessary security protocols for enterprise production use.
A. You can include any model available on OpenRouter, such as GPT-4, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Gemini Pro, or Llama 3.





