In recent times, if you have been delving into the development of AI, then you may have come across the term ‘agent frameworks.’ Today, we are going to discuss one of them, the Strands Agents. This is a tool that is altering the way developers create intelligent systems. But if you are a beginner, you need not worry; we will guide you through everything in a simple way in this article.
Table of contents
What are Strands Agents?
Consider Strands Agents as the integrated operation of your AI’s brain and body. Unlike conventional chatbots that only react to your input, these agents can perform various actions. They may extract information, come up with solutions, operate tools, and link several actions to complete difficult tasks.
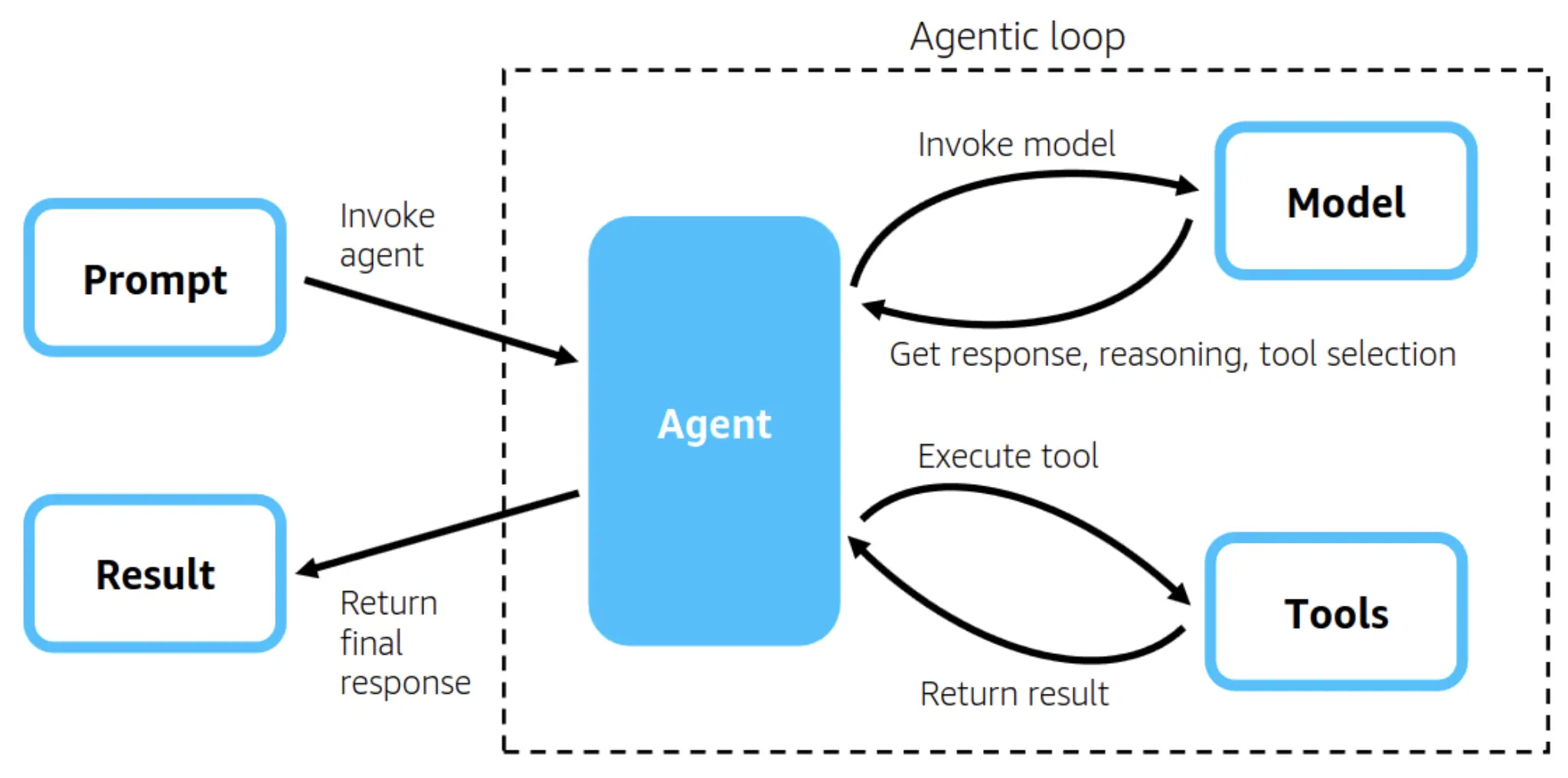
Strands is an innovative model powered by LangChain, which caters to the whole range of functionalities that come along with such complex agents. Strands’ highlights are its modularity; rather than coding long lines of standard code repetitively, one can use a creative method of connecting through ready-made parts like LEGO blocks to get the desired AI systems skillfully built.
Key Features of Strands Agents
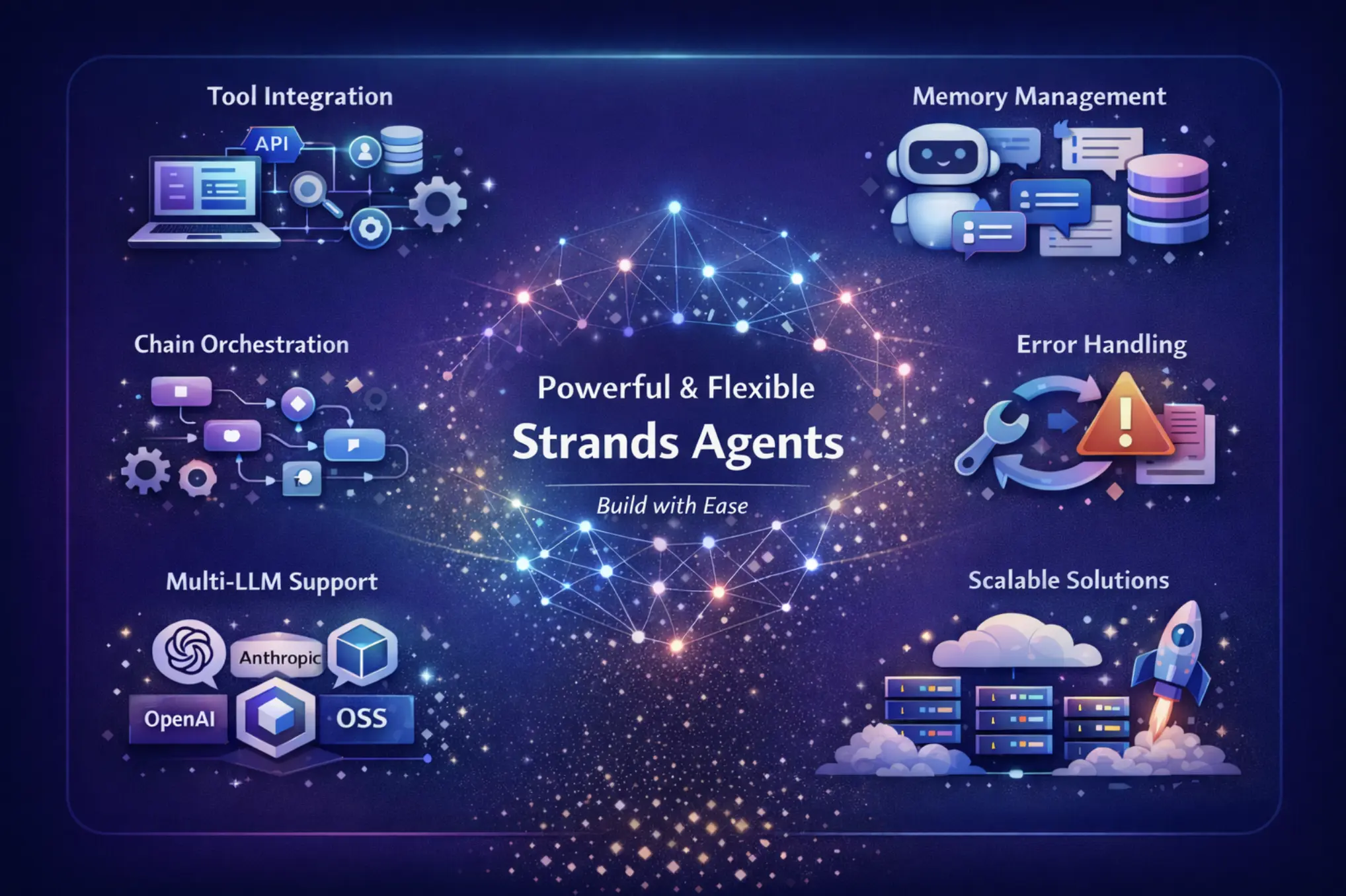
Strands give you the ability to make agents with ease and very powerful features:
- Tool Integration: Your agent easily connects to APIs, databases, search engines, and custom functions.
- Memory Management: The system stores all conversations and retains context across multiple user interactions.
- Chain Orchestration: The workflow combines different operations into one seamless process.
- Error Handling: The system automatically retries failed actions and manages failover smoothly.
- Flexibility: It is compatible with more than one LLM provider, such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and open-source models.
- Scalability: Just create simple prototypes or complex systems that are ready for production.
The framework will do the hard work for you so that you can spend your time on developing features instead of struggling with the infrastructure.
Why use Strands Agents?
Artificial intelligence has become a critical asset in every industry. AI systems that not only answer but also help to make complex decisions are the new standards in the market. Strands is an AI platform that provides this power without the usual complexity. Whether a customer service without a bot that checks the order status or a research assistant that pulls data from multiple sources, Strands would provide the architecture in both cases. The learning curve is smooth; however, the skills are vast.
Components of Strands Agents
Let’s first explain the basic concepts before getting to the practical part. A typical agent in Strands is made up of three primary parts:
- Language model: The AI’s mind that interprets requests and chooses a course of action
- Tools: Various functions your agent can perform (like searching, calculating, or interacting with databases)
- Memory: The way the agent holds on to the context of the conversation and previous interactions

In addition to that, Strands is using “chains,” a kind of operation that is predetermined when done in a specific sequence. A chain can be such that it first searches for information, then summarizes it, and finally presents the output in a formatted way.
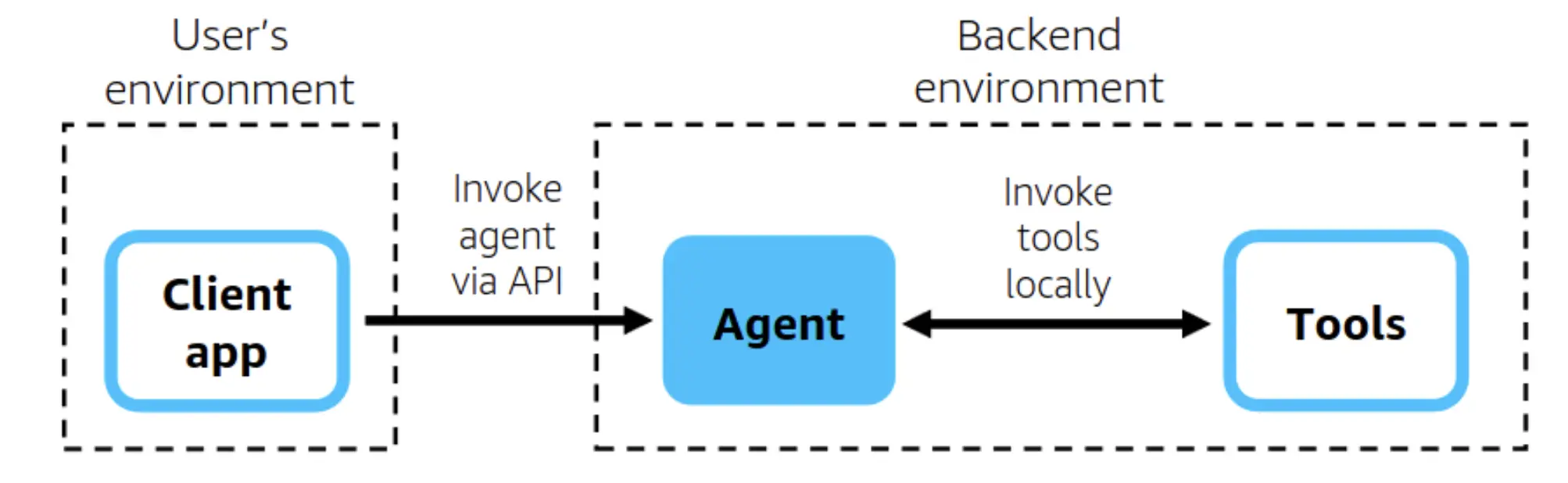
Getting Started with Strands Agent
First of all, get Python version 3.8 or a higher version installed on your computer. Creating a virtual environment is the best method to manage dependencies with this framework. It will become easier than managing them without one. The next step is to obtain an API key from a firm that provides large language models (LLMs). OpenAI, Anthropic, and Cohere are the three major firms that still allow free access to their products for academic purposes.
Hands-On Task 1: Building a Research Assistant Agent
We are going to build an agent that can search the internet and provide a summary of the results. This hands-on task will expose you to the basics of agent development.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Launch your terminal and make a new project folder:
mkdir strands-research-agent
cd strands-research-agent
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
pip install langchain langchain-openai langchain-community duckduckgo-search
Step 2: Create your Agent file
Create a file called research_agent.py with this code:
from langchain.agents import initialize_agent, Tool
from langchain.agents import AgentType
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_community.tools import DuckDuckGoSearchRun
import os
# Set your OpenAI API key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your-api-key-here"
# Initialize the search tool
search = DuckDuckGoSearchRun()
# Define tools
tools = [
Tool(
name="Web Search",
func=search.run,
description="Useful for searching the internet for current information."
)
]
# Initialize the language model
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.7, model="gpt-4o-mini")
# Create the agent
agent = initialize_agent(
tools=tools,
llm=llm,
agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
verbose=True
)
# Test your agent
if __name__ == "__main__":
query = "What are the latest developments in renewable energy?"
response = agent.run(query)
print("\n\nFinal Answer:")
print(response) Step 3: Run and Test
First, save the file and then run it with the command python research_agent.py. The agent will go through the whole process, giving you a nice overview of its activities. The verbosity = True parameter allows you to witness the agent’s reasoning, which is very interesting and informative at the same time.
Step 4: Customize Your Agent
Go ahead and make these changes to get a better insight:
- Use different questions to test different cases
- Change the temperature parameter (0 for concentrated, 1 for imaginative answers)
- Implement error handling through try-except blocks
- Change the description of the tool and observe how that influences the agent’s action
Try this out by changing the parameter levels, and observe a variety of results.
Hands-On Task 2: Agent Calculator with Memory
Now, we will create something more complex, an agent that not only performs arithmetic calculations but also remembers the past ones. What would be a better way of showing the context retention over a few interactions?
Step 1: Installing the libraries
A math package should be included in your setup:
pip install numexprStep 2: Development of the Calculator Agent
A new file named calculator_agent.py should be created:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import ChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage
import os
# Set your API key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "api-key-here"
# Initialize the language model
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4o-mini")
# Initialize chat history
chat_history = ChatMessageHistory()
def calculator_agent(user_input):
"""Calculator agent with memory"""
# Build messages with history
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="You are a helpful calculator assistant. Perform mathematical calculations and remember previous results. When the user refers to 'that result' or 'the previous answer', use the conversation history to understand what they mean.")
]
# Add chat history
messages.extend(chat_history.messages)
# Add current input
messages.append(HumanMessage(content=user_input))
# Get response
response = llm.invoke(messages)
# Save to history
chat_history.add_user_message(user_input)
chat_history.add_ai_message(response.content)
return response.content
# Interactive loop
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Calculator Agent Ready! (Type 'quit' to exit)")
print("Try asking things like:")
print("- What is 25 times 4?")
print("- Add 50 to that result")
print("- What was my first calculation?\n")
while True:
user_input = input("\nYou: ")
if user_input.lower() == 'quit':
print("Goodbye!")
break
response = calculator_agent(user_input)
print(f"\nAgent: {response}")Step 3: Test Memory Functionality
The first step is to open the command line and run the command “python calculator_agent.py.” Then test this procedure:
Question: “What is 25 times 4?”
Next, question: “Add 50 to that result.”
Last question: “What was my first calculation?”
The agent tracks and gives you access to past calculations. This is the wonderful memory effect at its most powerful.
<image>
Step 4: Understand the Components
The ConversationBufferMemory keeps all the dialogues in the previous conversation. When you say “that result,” the agent recalls and comprehends your situation. This is what naturally and human-like interactions are. Other types of memory can be tried as well.
- ConversationSummaryMemory: Provides a continuous summary for prolonged discussions
- ConversationBufferWindowMemory: Remembers just the last N interactions
- VectorStoreMemory: Stores interactions in a vector database that can be searched
Every type has a separate application depending on your requirements.
Real-World Applications
The same foundational concepts behind today’s simple agents also power the sophisticated agents of the future. Here are some applications for which we can use these agents that are implementing similar structures:
- Bots for customer support that verify the status of orders and return items
- AI helpers that take care of calendars, emails, and bookings
- Tools for research that gather data from various channels
- Financial counselors who look at the market statistics and the performance of the portfolios
- Content generation machines that search for subjects, write, and proofread articles
Think of it as an upgrading of our research agent to the level of writing complete reports, or a further development of the calculator agent to the point of performing financial planning with real-time data through APIs.
Conclusion
Strands Agents are a turning point in the development of AI as they come with a range of advanced properties that let them operate as human assistants in the most challenging cases. The era of robots that only talk is over; systems now act, remember, and even think.
The two agents that we developed for today are the building blocks. You understand the structure, see the working code, and experience the development workflow. Now simply keep on building, keep on trying out new things, and most of all, enjoy your time doing it. The future of AI is being created at this very moment, and you are one of the characters in that plot.





