Instagram uses artificial intelligence (AI) extensively for filtering and content moderation to maintain a safe and positive user experience. The AI-powered systems automatically detect and remove content that violates Instagram’s Community Standards, such as hate speech, bullying, nudity, violence, and spam, before such posts are reported by users. This process involves a combination of machine learning models, natural language processing, and computer vision technologies like convolutional neural networks. This article would attempt to shed some light on what goes on under the hood while Instagram maintains a positive and friendly user experience on its platform.
Table of contents
AI Content Moderation on Instagram
Instagram’s AI systems automatically detect and remove content that violates its community guidelines, including hate speech, bullying, nudity, graphic violence, and spam, often before any user reports it.
1. Image/Video Analysis:
Instagram uses deep CNN classifiers to spot prohibited visuals. For example, it trains convolutional nets (often ResNet-style backbones) on large, labeled datasets of “inappropriate vs safe images”. It also uses object detection models (one-stage detectors like YOLO or two-stage detectors like Faster R-CNN) to localize explicit content. Instagram’s parent company, Meta, notes that it can use YOLO for fast, real-time video scanning and Faster R-CNN, for example, with ResNet or ShuffleNet backbones when accuracy is paramount. In effect, CNN will flag an image if its pixels match patterns of nudity, weapons, graphic, and graphic violence.
2. Optical Character Recognition (Rosetta):
Many posts embed text like memes, screenshots, and images with captions, so Instagram uses a specialized OCR pipeline (Meta’s Rosetta system) to extract overlaid text. Then, Rosetta runs a Two-staged vision model, first a Faster R-CNN variant, which detects rectangular text regions, then a CNN based on Resnet-18 with CTC (sequences) loss, reads each word.
For example, a meme saying “1 like = 1 prayer” would be detected and transcribed. This text is fed into the moderation engine. Rosetta’s CNN+LSTM recognizer was trained on synthetic and real multilingual data, enabling Instagram to catch hate speech or spam hidden in the images.
3. Language Understanding (NLP):
Captions, comments, and messages are processed by natural-language models. Instagram applies algorithms, typically transformer-based text classifiers and RNNs, to score content against Community Guidelines.
For instance, comments are vectorized with learned embeddings or BERT-like models and fed to a spam/hate classifier. Abusive language, harassment, profanity, or hate is identified through learned patterns in text. While exact internal models are proprietary, Meta has shown it uses state-of-the-art NLP architecture to moderate dozens of languages at scale. In practice, posts flagged by either vision or NLP subsystem are either auto-blocked or sent to human review, depending on confidence.
This hybrid AI-human approach combines the speed and scale of AI with the nuanced decision-making of people, and feedback from human moderators is then used to retrain models, making the system smarter over time.
Personalization and User Experience Enhancement
Instagram’s feed, Explore tab, and Reels rely on ML ranking models to personalize each user’s experience. The system is a multi-stage recommender:
First, it retrieves a large pool of candidate posts from followed accounts, trending tags, similar users’ posts, etc. Then it ranks them via deep learning. In retrieval, Instagram uses a Two-tower neural network, one “tower” processes user features like demographics, history, interests, and the other processes media features like post metadata, content embeddings.
Each tower is typically a feedforward network, often starting from Word2Vec-like embeddings of IDs, that learns compact user/item vectors. The training objective is to make the user and item embeddings close when the user interacts with the item. At serving time, the users’ tower and an approximate nearest neighbors (ANN) index (ex, using FAISS) produce thousands of candidate posts for ranking. This Two-Tower approach is highly cacheable and allows real-time retrieval from billions of items.
Once candidates are retrieved, Instagram applies a two-stage deep ranking model. The first stage ranker is a lightweight neural network that scores thousands of posts per user (often distilling knowledge from a heavier model. The second stage is a heavier multi-task multi-label neural network (MTML) that takes the top 100 candidates and predicts detailed engagement probabilities (click, like, comment, watch, etc.). This MTML model is a feedforward deep net trained via backprop that ingests rich features like user interests, post content vectors, past interaction metrics, etc., and multiple probabilities simultaneously. In short, a deep neural network handles both retrieval and final ranking of posts, allowing Instagram to sort feeds according to each user’s preferences. This personalization keeps engagement high by surfacing the most relevant content for each user.
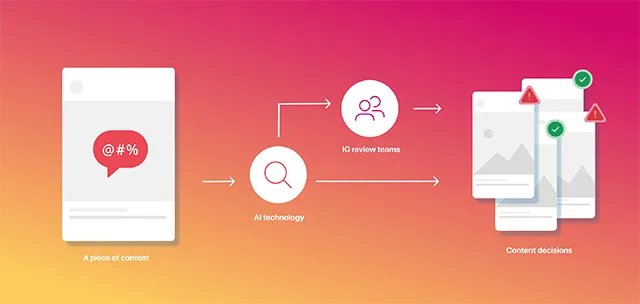
AI Against Cyberbullying and Spam
Beyond content and ranking, Instagram applies AI to fight spam bots and harassment. For example,
- Spam Detection: Accounts sending mass DMs or comments (like phishing scams) are flagged by pattern-learning models. Instagram can train binary classifiers like ensemble models or neural nets on features like posting frequency, message similarity, click rates, and account metadata. Any unnatural patterns like automated DMs, repeated links, or “like or like” schemes trigger anti-spam filters. Rosetta’s OCR also helps here; it can read spammy text in images/memes. Once flagged, accounts may be limited or removed.
- Cyberbullying & harassment: NLP models watch conversation tone. Transformers or recurrent nets analyze the sentiment and context of comments or DMs. The system attempts to differentiate nasty content from benign banter, often using contextual embeddings. When a comment sounds abusive, it can be auto-filtered. Instagram has features like restricting or hiding words to use AI in preventing bullying. These language filters run continuously to block hate speech and harassment.
- Community Integrity: ML also prunes the recommendation graph: posts with many user reports or a history of violations may be downranked by content integrity signals. For example, during retrieval, Instagram applies business rules to drop objectionable posts from candidates. In proactive mode, after the main ranking score is computed, the system applies a final reranking filter, removing or demoting posts flagged by integrity checks.
By combining automated filters with human appeals, Instagram’s AI maintains safety and authenticity. It can nudge users to “Are you sure?” if a comment looks offensive. Collectively, these systems block millions of spammy or hateful interactions per day, protecting users and keeping the platform healthy.
Summary of Techniques Used by Instagram
| Model / Technique | Description / Purpose | Examples / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CNN Image Classifiers | Used for binary or multi-class image classification (e.g., “safe” vs “nudity” vs “violence”). | Architectures like ResNet, Inception, and EfficientNet, fine-tuned on Instagram-specific datasets. |
| Object Detection | Identifies disallowed objects or text in images/videos. | Models like Faster R-CNN, YOLO, and DETR for fast or detailed detection. |
| Optical Character Recognition (OCR) | Extracts and reads text in memes or screenshots for moderation. | Rosetta: Faster R-CNN for detection + CNN+LSTM for multilingual recognition. |
| Transformers for NLP | Analyzes captions and comments for hate speech and spam. | Models like BERT, RoBERTa, and XLM for multilingual moderation. |
| Two-Tower Neural Networks | Powers large-scale retrieval in feed and Explore recommendations. | Uses FAISS for fast approximate nearest neighbor search. |
| Multi-task Deep Networks | Predicts likes, comments, and watch time for personalized ranking. | Large MLPs serve as second-stage rankers in Instagram’s pipeline. |
| Self-supervised Learning (SEER) | Learns visual representations from billions of unlabeled images. | SEER: Meta’s 1B+ parameter model for large-scale visual learning. |
What are the Benefits of AI Moderations
Manual content moderation is not feasible for platforms with millions or billions of users who generate vast amounts of content every day. But with AI, it is possible to
- Scales moderation to billions of posts daily.
- Removes harmful content fast, often before anyone reports it.
- Improves safety, creating a more supportive community.
- Personalizes experience and keeps content relevant and engaging.
These systems allow Instagram to handle a content volume that would be impossible for humans alone, improving both user and platform quality.
Challenges and Limitations of AI Moderations
Even the most advanced AI systems aren’t perfect. Instagram’s moderation faces a few challenges, like:
- False Positives: Artistic or educational nudity mistakenly flagged as a violation.
- False Negatives: Harmful content slipping through due to context or deliberate evasion, for example, using altered spellings or distorted images.
- Bias and Fairness: Models can reflect human labeling biases, leading to uneven moderation across languages, cultures, or communities.
- Transparency: Users often don’t fully understand how moderation decisions are made, leading to frustration around “shadow bans” or post removals.
Conclusion
Instagram’s AI is a comprehensive mix of computer vision, natural language processing, and large-scale recommendation models. State-of-the-art CNNs with architectures like ResNet, EfficientNet, YOLO, and faster R-CNN handle image/video content. Advanced OCR (Rosetta) extracts text from memes to flag hidden violations. Concurrently, deep NLP models parse user text to catch hate speech or spam. On the other hand, neural recommender systems for the Two Tower retrieval and multi-tasking ranking networks continuously learn from user behavior to tailor each feed. This powerful AI-driven approach enables Instagram to moderate and personalize on a global scale. While issues like bias and explainability remain, these models are central to keeping Instagram safe, engaging, and relevant for its billions of users.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Instagram uses AI models like CNNs, OCR (Rosetta), and NLP transformers to detect and remove hate speech, nudity, violence, and spam before users report it. These systems automatically flag, block, or send content for human review.
A. Instagram’s feed and Explore tab rely on Two-Tower neural networks for retrieval and multi-task deep networks for ranking. These models personalize each user’s feed based on their behavior, interests, and engagement patterns.
A. Key issues include false positives, bias across languages or cultures, and limited transparency around moderation decisions, leading to user frustration and occasional “shadow ban” complaints.





