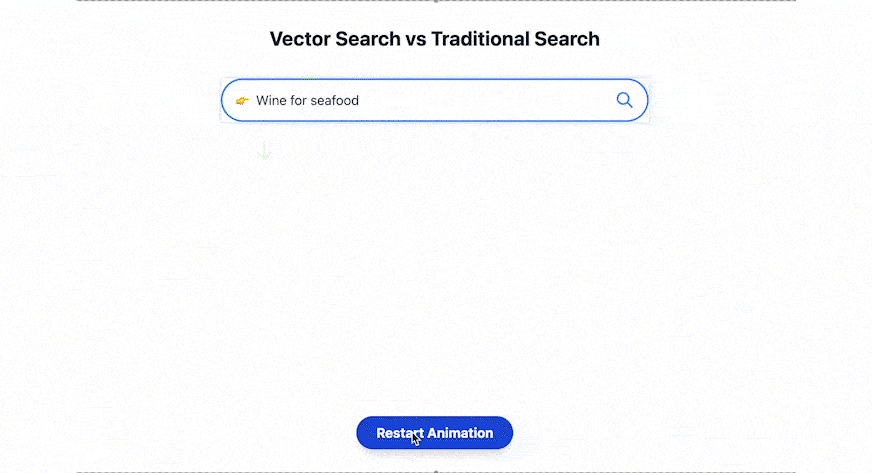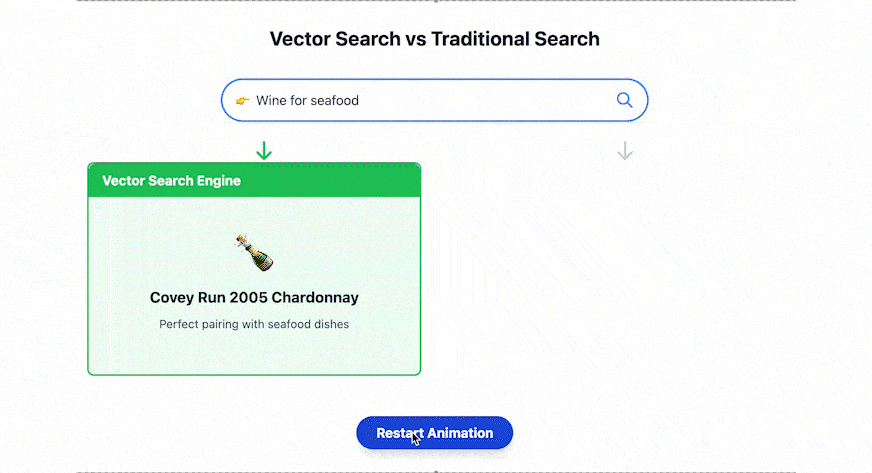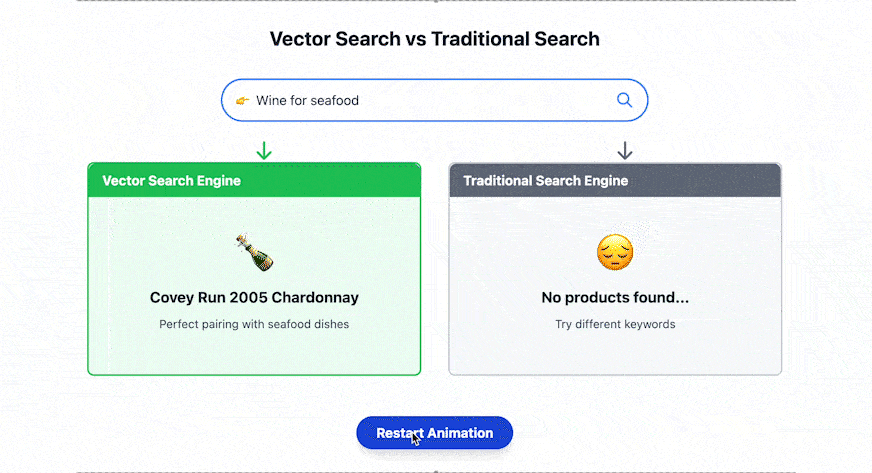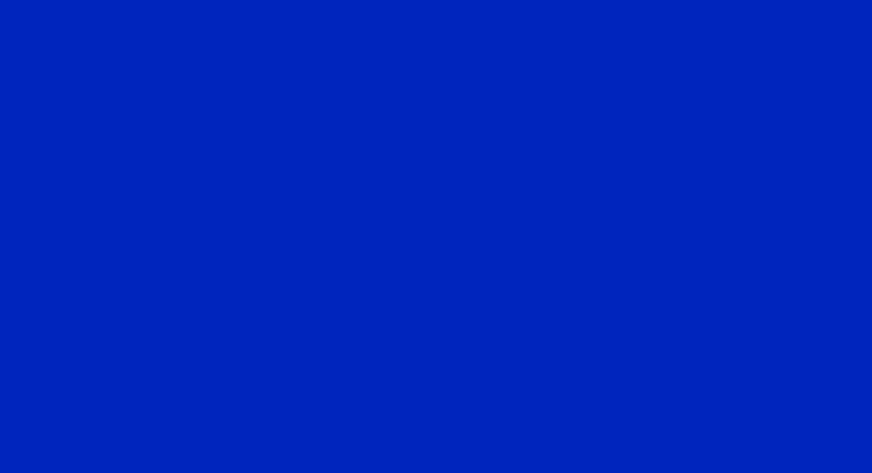
The way we search and relate to data is changing. Instead of returning results that contain “cozy” and “nook,” you can search for “cozy reading nooks” and see images of a soft chair by a fireplace. This approach focuses on semantic search or searching for the meaning, rather than relying on rigid keyword-based searches. This is a critical segue, as unstructured data (images, text, videos) has exploded, and traditional databases are increasingly impractical for the level of demand of AI.
This is exactly where Weaviate comes in and separates itself as a leader in the category of vector databases. With its unique functionality and capabilities, Weaviate is changing how companies consume AI-based insights and data. In this article, we will explore why Weaviate is a game changer through code examples and real-life applications.
Table of contents
- What is Weaviate?
- Core Principles and Architecture of Weaviate
- Getting started with Weaviate: A Hands-on Guide
- Prerequisites
- Step 1: Deploy Weaviate
- Step 2: Install Python Dependencies
- Step 3: Set Environment Variables
- Step 4: Connect to Weaviate
- Step 5: Define Schema with Embedding & Generative Support
- Step 6: Insert Example Data in Batch
- Step 7: Semantic Search using nearText
- Step 8: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Key Features of Weaviate
- Weaviate vs Competitors
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Weaviate?
Weaviate is an open-source vector database specifically designed to store and handle high-dimensional data, such as text, images, or video, represented as vectors. Weaviate allows businesses to do semantic search, create recommendation engines, and build AI models easily.
Instead of relying on a traditional database that retrieves exact data based on columns stored in each row, Weaviate focuses on intelligent data retrieval. It uses machine learning-based vector embeddings to find relationships between data points based on their semantics, rather than searching for exact data matches.
Weaviate provides an easy way to build applications that run AI models that require quick and efficient processing of very large amounts of data to build models. Storage and retrieval of vector embeddings in Weaviate make it the ideal function for companies involved with unstructured data.
Core Principles and Architecture of Weaviate

At its core, Weaviate is built on principles of working with high-dimensional data and making use of efficient and scalable vector searches. Let’s take a look at the building blocks and principles behind its architecture:
- AI-Native and modular: Weaviate is designed to integrate machine learning models into the architecture from the onset, giving it first-class support for producing embeddings (vectors) of varying data types out of the box. The modularity of the design allows for many possibilities, ensuring that if you wanted to build on top of Weaviate or add any custom features, or connections/calls to external systems, you can.
- Distributed system: The database is designed to be able to grow horizontally. Weaviate is distributed and leaderless, meaning there are no single points of failure. Redundancy for high availability across nodes means that in the event of a failure, the data will be replicated and produced from a number of connected nodes. It is eventually consistent, making it suitable for cloud-native as well as other environments.
- Graph-Based: Weaviate model is a graph-based data model. The objects (vectors) are connected by their relationship, making it easy to store and query data with complex relationships, which is highly important in applications like recommendation systems.
- Vector storage: Weaviate is designed to store your data as vectors (numerical representations of objects). This is ideal for AI-enabled searches, recommendation engines, and all other artificial intelligence/machine learning-related use cases.
Getting started with Weaviate: A Hands-on Guide
It does not matter if you are building a semantic search engine, a chatbot, or a recommendation system. This quickstart will show you how to connect to Weaviate, ingest vectorised content, and provide intelligent search capabilities, ultimately generating context-aware answers through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with OpenAI models.
Prerequisites
Ensure the latest version of Python is installed. If not, install using the following command:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip -yCreate and activate a virtual environment:
python3 -m venv weaviate-env
Source weaviate-env/bin/activateWith the above code, your shell prompt will now be prefixed with your new env, i.e, weaviate-env indicating that your environment is active.
Step 1: Deploy Weaviate
So there are two ways to deploy Weaviate:
Option 1: Use Weaviate Cloud Service
One way to deploy Weaviate is using its cloud service:
- First, go to https://console.weaviate.cloud/.
- Then, sign up and create a cluster by selecting OpenAI modules.
Also take note of your WEAVIATE_URL (similar to https://xyz.weaviate.network) and WEAVIATE_API_KEY.
Option 2: Run Locally with Docker Compose
Create a docker-compose.yml:
version: '3.4'
services:
weaviate:
image: semitechnologies/weaviate:latest
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
QUERY_DEFAULTS_LIMIT: 25
AUTHENTICATION_ANONYMOUS_ACCESS_ENABLED: 'true'
PERSISTENCE_DATA_PATH: './data'
DEFAULT_VECTORIZER_MODULE: 'text2vec-openai'
ENABLE_MODULES: 'text2vec-openai,generative-openai'
OPENAI_APIKEY: 'your-openai-key-here'Configures Weaviate container with OpenAI modules and anonymous access.
Launch it using the following command:
docker-compose up -dThis starts Weaviate server in detached mode (runs in the background).
Step 2: Install Python Dependencies
To install all the dependencies required for the program, run the following command in the command line of your operating system:
pip install weaviate-client openaiThis installs the Weaviate Python client and OpenAI library.
Step 3: Set Environment Variables
export WEAVIATE_URL="https://<your-instance>.weaviate.network"
export WEAVIATE_API_KEY="<your-weaviate-key>"
export OPENAI_API_KEY="<your-openai-key>"For local deployments, WEAVIATE_API_KEY is not needed (no auth).
Step 4: Connect to Weaviate
import os
import weaviate
from weaviate.classes.init import Auth
client = weaviate.connect_to_weaviate_cloud(
cluster_url=os.getenv("WEAVIATE_URL"),
auth_credentials=Auth.api_key(os.getenv("WEAVIATE_API_KEY")),
headers={"X-OpenAI-Api-Key": os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")}
)
assert client.is_ready(), " Weaviate not ready"
print(" Connected to Weaviate")The previous code connects your Weaviate cloud instance using credentials and confirms that the server is up and reachable.
For local instances, use:
client = weaviate.Client("http://localhost:8080")This connects to a local Weaviate instance.
Step 5: Define Schema with Embedding & Generative Support
schema = {
"classes": [
{
"class": "Question",
"description": "QA dataset",
"properties": [
{"name": "question", "dataType": ["text"]},
{"name": "answer", "dataType": ["text"]},
{"name": "category", "dataType": ["string"]}
],
"vectorizer": "text2vec-openai",
"generative": {"module": "generative-openai"}
}
]
}Defines a schema called Question with properties and OpenAI-based vector and generative modules.
client.schema.delete_all() # Clear previous schema (if any)
client.schema.create(schema)
print(" Schema defined")Output:

The preceding statements upload the schema to Weaviate and confirm success.
Step 6: Insert Example Data in Batch
data = [
{"question":"Only mammal in Proboscidea order?","answer":"Elephant","category":"ANIMALS"},
{"question":"Organ that stores glycogen?","answer":"Liver","category":"SCIENCE"}
]Creates a small QA dataset:
with client.batch as batch:
batch.batch_size = 20
for obj in data:
batch.add_data_object(obj, "Question")Inserts data in batch mode for efficiency:
print(f"Indexed {len(data)} items")Output:
Confirms how many items were indexed.
Step 7: Semantic Search using nearText
res = (
client.query.get("Question", ["question", "answer", "_additional {certainty}"])
.with_near_text({"concepts": ["largest elephant"], "certainty": 0.7})
.with_limit(2)
.do()
)Runs semantic search using text vectors for concepts like “largest elephant”. Only returns results with certainty ≥ 0.7 and max 2 results.
print(" Semantic search results:")
for item in res["data"]["Get"]["Question"]:
q, a, c = item["question"], item["answer"], item["_additional"]["certainty"]
print(f"- Q: {q} → A: {a} (certainty {c:.2f})")Output:

Displays results with certainty scores.
Step 8: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
rag = (
client.query.get("Question", ["question", "answer"])
.with_near_text({"concepts": ["animal that weighs a ton"]})
.with_limit(1)
.with_generate(single_result=True)
.do()
)Searches semantically and also asks Weaviate to generate a response using OpenAI (via generate).
generated = rag["data"]["Get"]["Question"][0]["generate"]["singleResult"]
print(" RAG answer:", generated)Output:

Prints the generated answer based on the nearest match in your Weaviate DB.
Key Features of Weaviate

Weaviate has many special features that give it a flexible and strong edge for most vector-based data management tasks.
- Vector search: Weaviate can store and query data as vector embeddings, allowing it to conduct semantic search; it improves accuracy as similar data points are found based on meaning rather than simply matching keywords.
- Hybrid search: By bringing together vector search and traditional keyword-based search, Weaviate offers more pertinent and contextual results while providing greater flexibility for varied use cases.
- Scalable infrastructure: Weaviate is able to operate with single-node and distributed deployment models; it can horizontally scale to support very large data sets and ensure that performance is not affected.
- AI-native architecture: Weaviate was designed to work with machine learning models out of the gate, supporting direct generation of embeddings without needing to go through an additional platform or external tool.
- Open-source: Being open-source, Weaviate allows for a level of customisation, integration, and even user contribution in continuing its development.
- Extensibility: Weaviate supports extensibility through modules and plugins that enable users to integrate from a variety of machine learning models and external data sources.
Weaviate vs Competitors
The following table highlights the key differentiators between Weaviate and some of its competitors in the vector database space.
| Feature | Weaviate | Pinecone | Milvus | Qdrant |
| Open Source | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Hybrid Search | Yes (Vector + Keyword Search) | No | Yes (Vector + Metadata Search) | Yes (Vector + Metadata Search) |
| Distributed Architecture | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Pre-built AI Model Support | Yes (Built-in ML model integration) | No | No | No |
| Cloud-Native Integration | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Data Replication | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
As shown in the previous table, Weaviate is the only vector database that provides a hybrid search that can do both vector search and keyword-based search. Thus, there are more search options available. Weaviate is also open-source, unlike Pinecone, which is proprietary. The open-source advantages and transparent libraries in Weaviate provide customization options benefiting the user.
Especially, Weaviate’s integration of machine learning for embeddings in the database significantly distinguishes its solution from those of its competitors.
Conclusion
Weaviate is a leading-edge vector-based database with a revolutionary architecture that is AI-native and designed to deal with higher-dimensional data while also incorporating machine learning models. The hybrid data and search capabilities of Weaviate and its open-source nature provide a robust solution for AI-enabled applications in every conceivable industry. Weaviate’s scalability and high performance make it well-positioned to continue as a leading solution for unstructured data. From recommendation engines and chatbots to semantic search engines, Weaviate unlocks the full potential of its advanced features to help developers enhance their AI applications. The demand for AI solutions is only set to grow; thus, Weaviate’s significance in the field of vector databases will become increasingly relevant and will fundamentally influence the future of the field through its ability to work with complex datasets.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Weaviate is an open-source vector database, and is designed for high-dimensional data, such as text, image, or video’s that are leveraged to enable semantic search and AI-driven applications.
A. Unlike traditional databases that retrieve exact data, Weaviate retrieves structured data using machine learning based vector embeddings to retrieve based on meaning and relations.
A. Hybrid search in Weaviate combines the concepts of vector search and traditional search based on keywords to provide relevant and contextual results for more diverse use cases.




