A lot of teams drown in scattered PDFs, scans, and odd-looking documents, trying to pull out the bits of information they actually need. LlamaExtract is here to their rescue. You upload your files, tell it what structure you want, and it hands back neat JSON that fits your schema. It works through a web app, Python SDK, or REST API, all powered by the Llama Cloud service inside the LlamaIndex ecosystem. In this article, we’ll walk through how LlamaExtract works, why it’s useful, and how you can use it to turn messy documents into clean, structured data with almost no manual effort.
Table of contents
Why this is useful
Companies have spent a great amount of time extracting information related to their contracts, invoices, forms, and financial reports. Manual data entry or reliance on fragile regex scripts is often used by people, and it fails at the first instance that a document appears differently. Most of this work is eliminated with LlamaExtract. It supports documents of different format and layout both including tables and text in more than one column even without having to do a special parsing of each new file. It converts sloppy documents into neat JSON which can be directly inserted into databases, APIs or machine learning piping.
Major Functions
Here are the main standout features of LlamaExtract tool:
- Flexible schema setup: Select the fields you prefer to extract. The same can be described using a Pydantic model or a JSON schema. A tool is also capable of proposing a schema based on sample documents. The fields may be modified either in the interface or in the code. It is now easy to optimize the structure until the results appear to be correct.
- Smart extraction: The documents are read by a system that has models which comprehend the context and structure of documents. It is able to work with tables, mixed format, scanned pages, and uncommon formatting. It pulls the right values even when it has a different document style with each file. You do not have to deal with any of the model calls yourself.
- Built-in OCR: Scans of PDFs and images do not require additional measures. The device has OCR, thus as a user, you do not require an independent service. It accepts PDF, pictures and private text files.
Hands-On: Data Extraction across any Document
This tutorial uses the new Python SDK exactly as described in the reference you shared. You can copy every cell into Google Colab and run it step by step.
Step 1. Install dependencies
!pip install llama-cloud-services python-dotenv pydanticStep 2. Set your API key
In Colab, we set it directly in the environment (you don’t need a .env file unless you want one).
import os
os.environ["LLAMA_CLOUD_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY_HERE" # Replace with your real keyIf you prefer a .env file, you can upload it to Colab and use:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()Step 3. Initialize the client
from llama_cloud_services import LlamaExtract
extractor = LlamaExtract() # reads LLAMA_CLOUD_API_KEY automaticallyStep 4. Define your schema with Pydantic
This describes the invoice fields we want to extract.
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class InvoiceSchema(BaseModel):
invoice_number: str = Field(description="Invoice number")
invoice_date: str = Field(description="Date of the invoice")
vendor_name: str = Field(description="Vendor or supplier name")
total_amount: float = Field(description="Total amount due")Step 5. Create an extraction agent
Agent store schemas and extraction settings in the cloud.
agent = extractor.create_agent(
name="invoice-parser",
data_schema=InvoiceSchema
)Step 6. Upload invoice files to Colab
Upload your PDFs on the left sidebar of Colab and put them in the list below (based off their filename):
files = [
"/content/sample-invoice.pdf",
"/content/invoice-0-4.pdf",
"/content/invoice-1-3.pdf",
"/content/invoice-2-1.pdf",
"/content/invoice-3-0.pdf",
"/content/invoice-7-0.pdf"
]Step 7. Run extraction on your invoice files
results = [agent.extract(f) for f in files] 
Step 8. View the extracted results
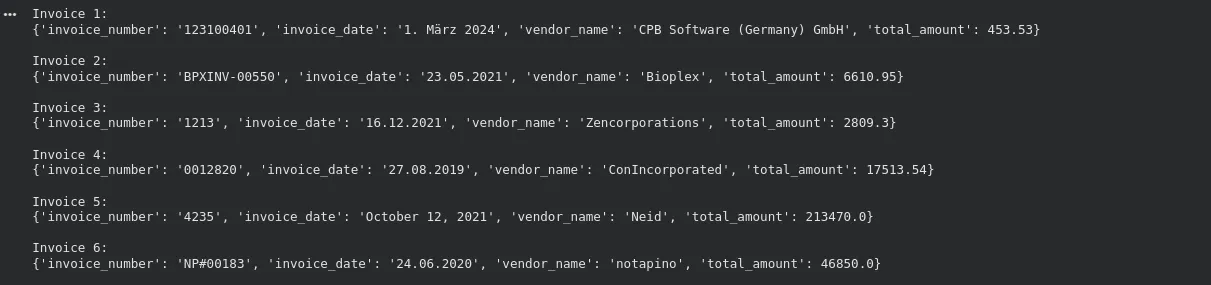
for i, res in enumerate(results):
print(f"Invoice {i+1}:")
print(res.data)
print()Output:
DataFrame
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame([res.data for res in results])
df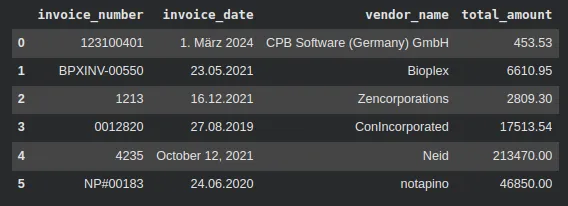
How LlamaExtract works with LLMs
Here’s how LlamaExtract works with LLMs:
- Schema inference: To extract a schema, you put your sample documents into LlamaExtract (which sends the sample documents to a language model). The model seeks common occurrences which may be dates, totals, names or 3 or 4-digit IDs. Using those patterns, it generates field names and types of a JSON schema. This allows you to develop the initial structure without having to type everything out.
- Field extraction: By doing an extraction job, the service reads every document and fills fields in your schema using a language model. The model is aware of context, difference of words and layout. It has the ability to extract values of text, tablet or scanned reading. There is no need to write prompts and no need to work with any model output.
- Different model backends: The model providers are quite numerous in LlamaIndex. The cloud service probably selects a powerful model by default in order to performance good accuracy. Some modes can be changed or faster or cheaper model settings can be used. What is important is that it is extracted using a large language model, rather than by rule-based parsing.
Simply put, LlamaExtract is an API that encodes the powerful language models. You have the advantage of higher level document comprehension without having to communicate with the models themselves.
Restrictions and limitations
With all the functionality that’s on offer using LlamaExtract, there are a few limitations as well:
- Cloud based: Everything is processed on LlamaCloud. You have to upload your documents i.e. you will need access to the internet. These may increase privacy or compliance on the event that the files are sensitive. Ensure that you are using the service in line with your data policies.
- Cost at scale: Training big models would become costly. Pricing is usage based. When making large volumes, first of all, estimate the cost before processing a huge volume. Large tasks can be required to be batched and long documents can also be time consuming.
- Very large documents: The tool process works with long files although very large or complicated documents can strain capacity. A technical manual which is very long and full of tables or figures may have to be divided. Look and see whether the file is bulkier than usual.
- Accuracy is not perfect: OCR can fail on blurry scans. The system can misread certain fields, especially when the layout is unusual. Use confidence scores to decide when manual review is needed. Spot-check results early to catch patterns or repeated mistakes.
- Repeating tables and nested data: The tool supports nested schemas and lists, such as line items in an invoice. Still, repeating rows in tables can be tricky. Test this carefully because some lines may be skipped or merged on difficult scans. Defining a clean sub-model for each item helps.
Keeping these points in mind helps you plan better and avoids surprises. With the right checks in place, the tool can save significant time and give structured data from documents that would be slow to process by hand.
Conclusion
Llama Extract makes it much easier to deal with all the scattered, messy documents that usually slow teams down. Instead of writing brittle scripts or pulling information out by hand, you upload your files, define the structure you want, and the tool takes care of the rest. It reads text, tables, and even scanned pages, then returns clean and consistent JSON you can use right away.
There are still things to keep in mind, like cloud usage, cost, and the occasional OCR mistake on bad scans. But with a bit of planning, it can save a huge amount of time and cut down on repetitive work. For most teams handling invoices, reports, or forms, it offers a simple and reliable way to turn unstructured documents into useful data.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. It reads PDFs, scans, or images with OCR and a language model, interprets the layout, and outputs clean JSON that follows the schema you defined. No regex or prompt engineering needed.
A. You can. You can also let the tool infer a schema from sample documents, then tweak fields in the UI or code until the extraction looks right.
A. Cloud processing, cost, latency, and OCR errors on low-quality scans. Large or complex documents may need batching. Confidence scores help decide when manual review is needed.





