Imagine building a full Android app that generates AI questions, runs on a real backend, and uses a database without writing a single line of code. Claude Code, Anthropic’s terminal-based assistant, makes it possible to ship a working product from one clear prompt.
This tutorial shows how to create an AI Study Assistant that ingests PDFs and produces exam-ready questions, MCQs, and summaries for JEE, NEET, GATE, and boards. In this article, you will see the full workflow in action.
Table of contents
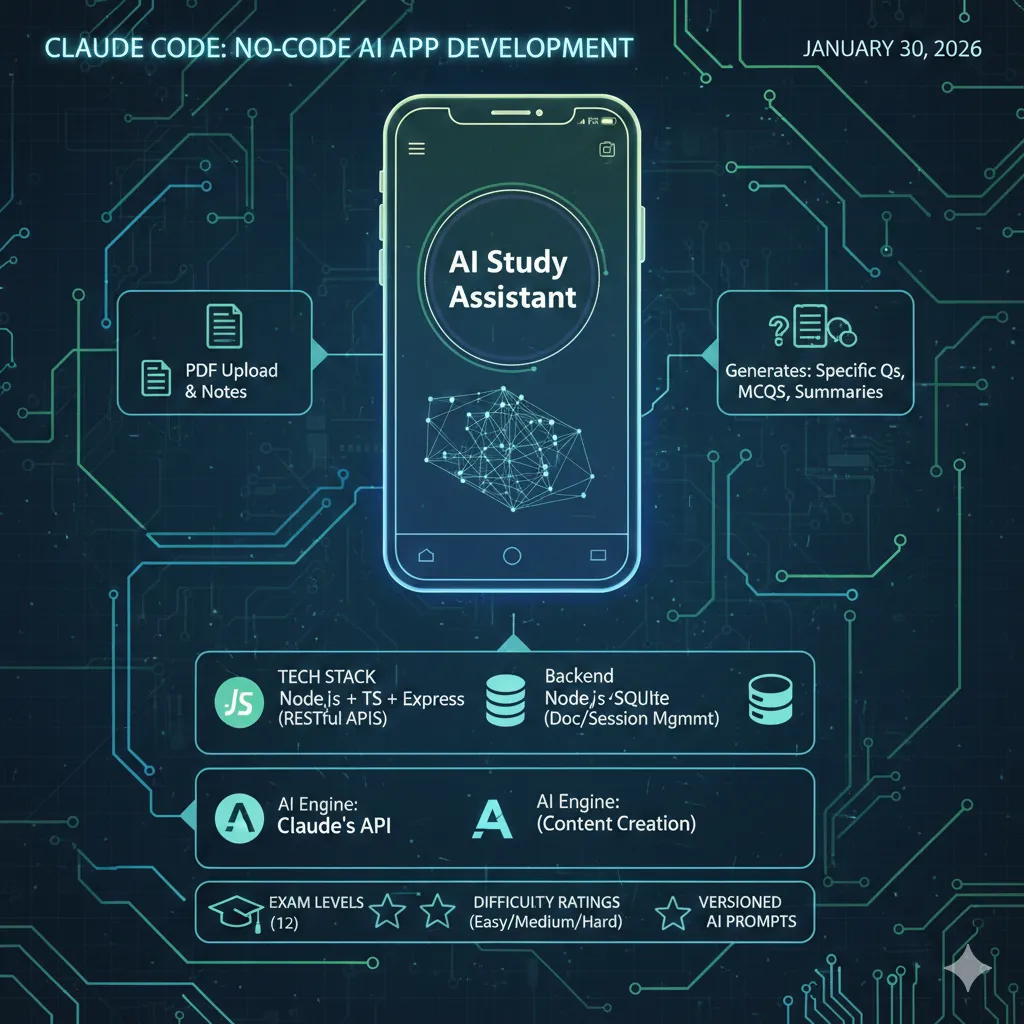
What we’ll be building:
- Backend – Node.js + Typescript + Express with RESTful API’s
- Database – SQLite for document/session management
- AI Engine – Claude’s API for intelligent content creation
- Mobile Application – Android & MVVM architected
- Additional Features – 12 exam levels, classification/ratings of question difficulty levels, Versioned AI prompts
Hands on
Without further ado, let’s jump into the process:
Step 1: Project Setup
Open your terminal and initialize the project:
cd ~/Documents/Projects
mkdir StudyAssistant
cd StudyAssistant
claude Step 2: The Magic Prompt
Write a detailed single prompt to build the AI Assistant in the command line interface of Claude code:
AI Study Assistant: Build an AI agent that converts uploaded notes or PDFs into exam-specific questions, MCQs/MSQs, and revision summaries after the user selects an exam level.
Flow: Upload → select exam → analyze notes → generate exam-aligned content.
Requirements: Questions, MCQs/MSQs (with correct answers), and summaries must match exam difficulty and stay grounded in the notes only.
/exam/select
/content/generate
/history
Goal: Deliver a clean, end-to-end, exam-focused study assistant.
Step 3: Auto-Generated Backend
Claude-Code starts working and generates this production-ready structure:

The key features of this auto-generated backend are:
- Exam Configurations: Configuration options include 12 types of examinations, including (JEE/NEET/GATE/UPSC/BOARD) with individually defined difficulty levels.
- Versioned Prompts: Prompts are stored in JSON format; therefore, when changing the system, you can update your prompts without compromising the functionality of the current version of the application.
- Clean Architecture: All of our services are designed to follow the single responsibility principle and will be easy to test and extend.
Step 4: RESTful API Endpoints
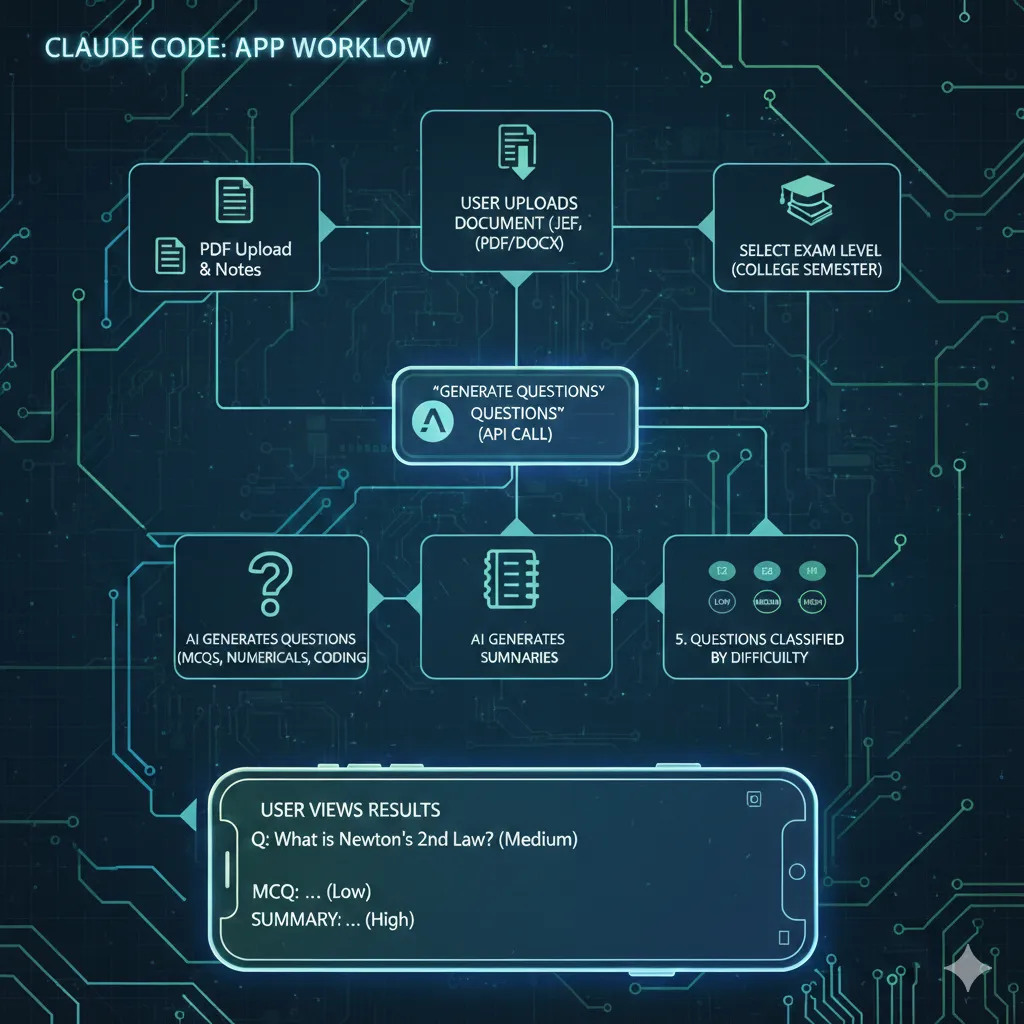
Claude code helped in creating the API endpoints as well according to our requirements. These endpoints will help in the smooth working of our app.

The workflow of the app according to the endpoints will be as follows:
- User uploads their document could be PDF or in docx format.
- Then, accordingly they’ll select the level of the examination JEE, NEET or any level of college semester.
- Click ‘Generate Question’, the endpoint calls the claude API to generate questions and summarize the notes as well.
- User can now view the generated question (MCQs, numericals, coding questions) with the different level of difficulty (low, medium, high).
Step 5: Setting up the Android App (MVVM Architecture)
Claude Code generated a separate Android folder, having all the files required to setup the android app. Following is the structure it created for the Android App:
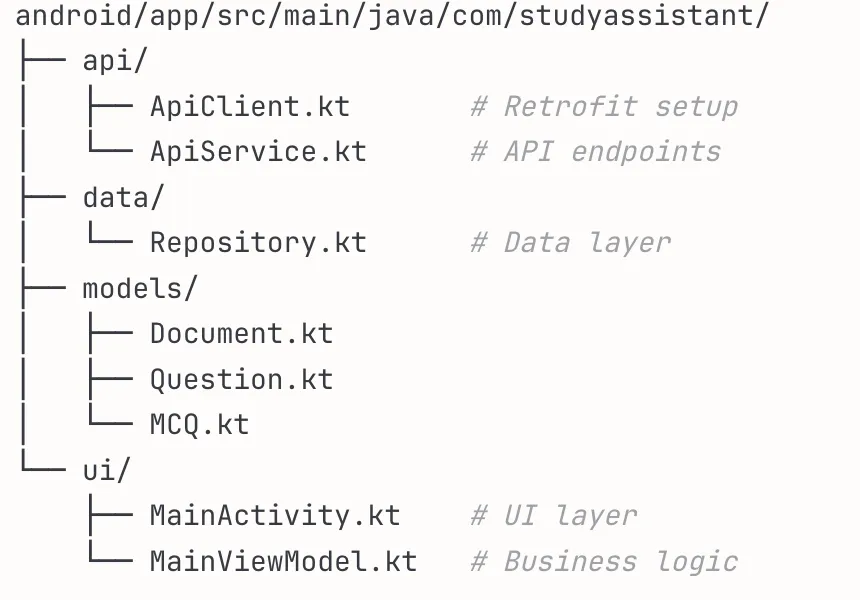
Here, the ApiClient.kt, is the main file as it provides the repository pattern which is used as a single source of truth for data.
private const val BASE_URL = "http://10.0.2.2:3000/api/" // Emulator localhost Step 6: Running the Application
The entire codebase structure of backend, databased and android app has been created, now we’ll run the backend first. You can use the following commands to initialize the backend server:
cd backend
npm install
npm run dev Output:
AI Study Assistant API running on port 3000
Environment: development
Database: ./database/study_assistant.db
Once the backend server has been setup, we’ll launch the android app now.
- Open Android Studio. Go to ‘file’ in the topbar, click on open and select your ‘Android’ folder created by Claude Code.
- Click on Gradle sync as it will sync all the code to run our app on an emulator (virtual device).
- Go to the Device manager in ‘Tools’ and select any virtual device or if you want to run the app on your own device then either you can connect your device via wifi or using a USB.
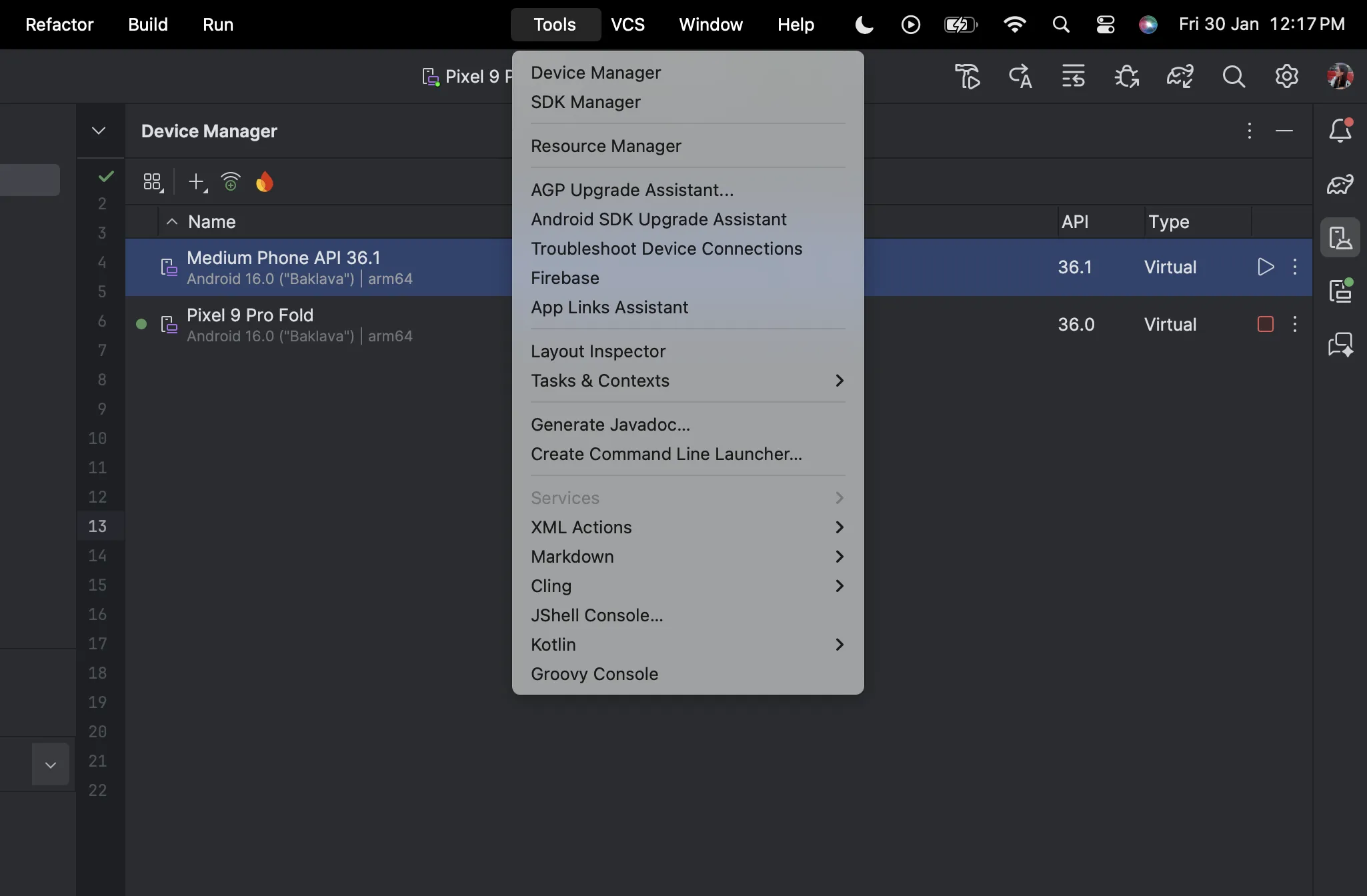
- Once the device has been connected, click on ‘Run’.
Step 7: Run the application (Demo)
You’ll see a virtual device running on the right sidebar, click on that and select your application ‘AI Study Assistant’.
How can you Customize it Further?
- Add new examination levels like CAT, SAT, JEE Advanced and so on by simply editing the backend file yourself or asking Claude Code to do it for you.
sat: {
id: 'sat',
name: 'SAT',
questionTypes: ['mcq', 'numerical'],
difficultyDistribution: { easy: 30, medium: 50, hard: 20 },
questionCount: { mcq: 30, numerical: 15 }
}- Ask the agent to make more creative questions by experimenting with the prompt, temperature and different parameters.
{
"systemPrompt": "You are an expert {{examLevel}} question setter...",
"temperature": 0.7,
"maxTokens": 2000
}- You can change the UI theme, making it more professional and advanced by editing android/app/src/main/res/values/colors.xml.
<color name="primary">#1976D2</color> <!-- Change to your brand color --> Key Takeaways: Mastering AI-Assisted Development
Here are the key aspects that we need to understand after we have built the project or for our future projects:
| Aspect | Details |
| Prompt Engineering is Critical |
Bad Prompt: “Build a study app” Good Prompt: “Build production-ready AI Study Assistant with Node.js, SQLite, Android MVVM, 12 exam levels, versioned prompts, clean architecture” |
| What Claude Code Excels At |
Boilerplate code generation Following established patterns (MVVM, REST APIs) Consistent naming conventions Modular architecture API endpoint creation Database schema design |
| What Still Needs Human Review |
Security implementations (API keys, input validation) Edge case handling Performance optimization at scale Complex business logic Production monitoring and logging |
Conclusion
The development process has become more efficient which results in complete system transformation. The barrier to entry for building sophisticated apps has dropped because existing advanced technologies enable users to create complex applications without needing programming skills. Students and entrepreneurs now have the ability to create the tools which they previously could only imagine.
The no-code revolution is here. After the AI Study Assistant, what will you build next?
Frequently Asked Questions
A. It converts uploaded PDFs into exam-specific questions, MCQs/MSQs with answers, and revision summaries based only on the notes.
A. Node.js + TypeScript + Express for backend, SQLite for storage, Claude API for generation, and an Android MVVM app for the client.
A. Add a new exam config in the backend and update the versioned prompt settings to control question types, difficulty mix, and output style.





