Machine learning is about learning from experience. Algorithms study data, spot patterns, and get better over time. When trained on things like purchase history, these models can anticipate what people might want next. It’s practical, adaptive, and already part of how many everyday decisions are made.
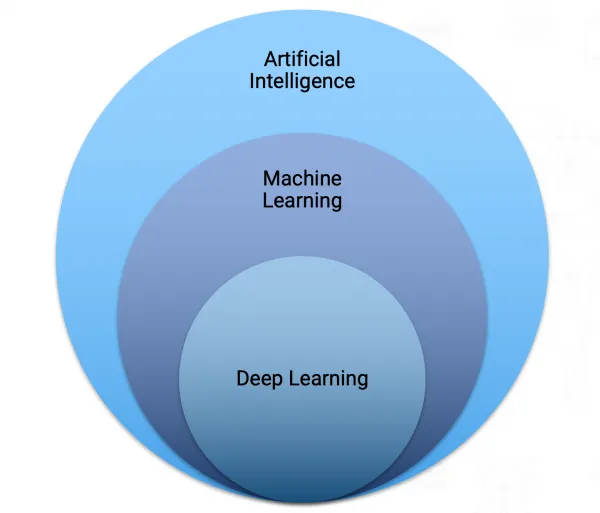
Artificial intelligence is no longer a distant idea. It’s shaping real conversations across industries, from healthcare to finance. But when it comes to decisions, machine learning and deep learning often get blurred together. Both learn from data, yet serve different goals. In this article, we’ll unpack that difference and what it means for smarter, growth-aligned choices.
Table of contents
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is often described as the “workhorse” of AI. This is the technique that uses most of the everyday apps in businesses. From recommended systems and fraud detection to future analytics in marketing. At its core, ML includes algorithms that analyze the data, recognize patterns, and make predictions. These models “learn” from previous data to improve their performance over time. For example, an ML model trained on the user’s purchase history can predict which product a customer can buy.
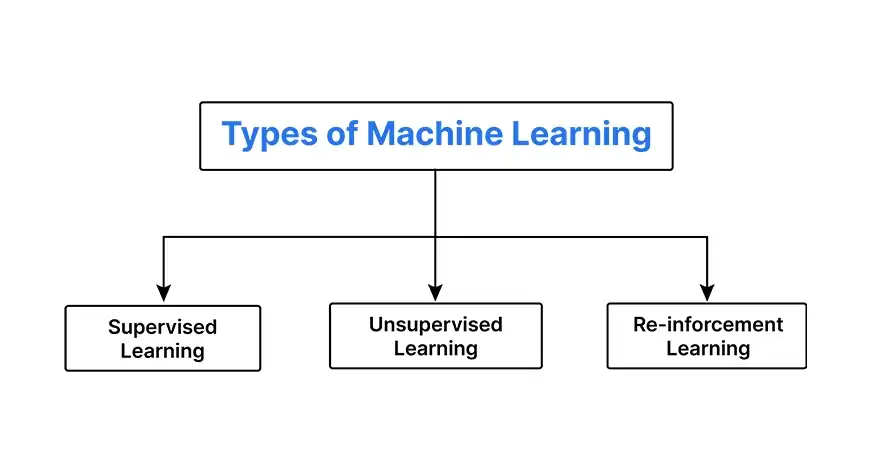
For businesses, the appeal of ML lies in its ability to simplify decision-making and improve efficiency.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning is a more advanced form of ML, and it has attracted significant attention. It uses an artificial neural network with several layers to process the human brain mimic data. Unlike ML, which often needs data scientists to define features manually, deep learning automatically removes these features from raw data. This makes DL particularly powerful when working with unnecessary data such as images, texts, and voice. However, deep education requires large-scale data and computational resources. This means that it is not always practical for every business use. But when applied correctly, its forecasting power and automation capabilities are unique.
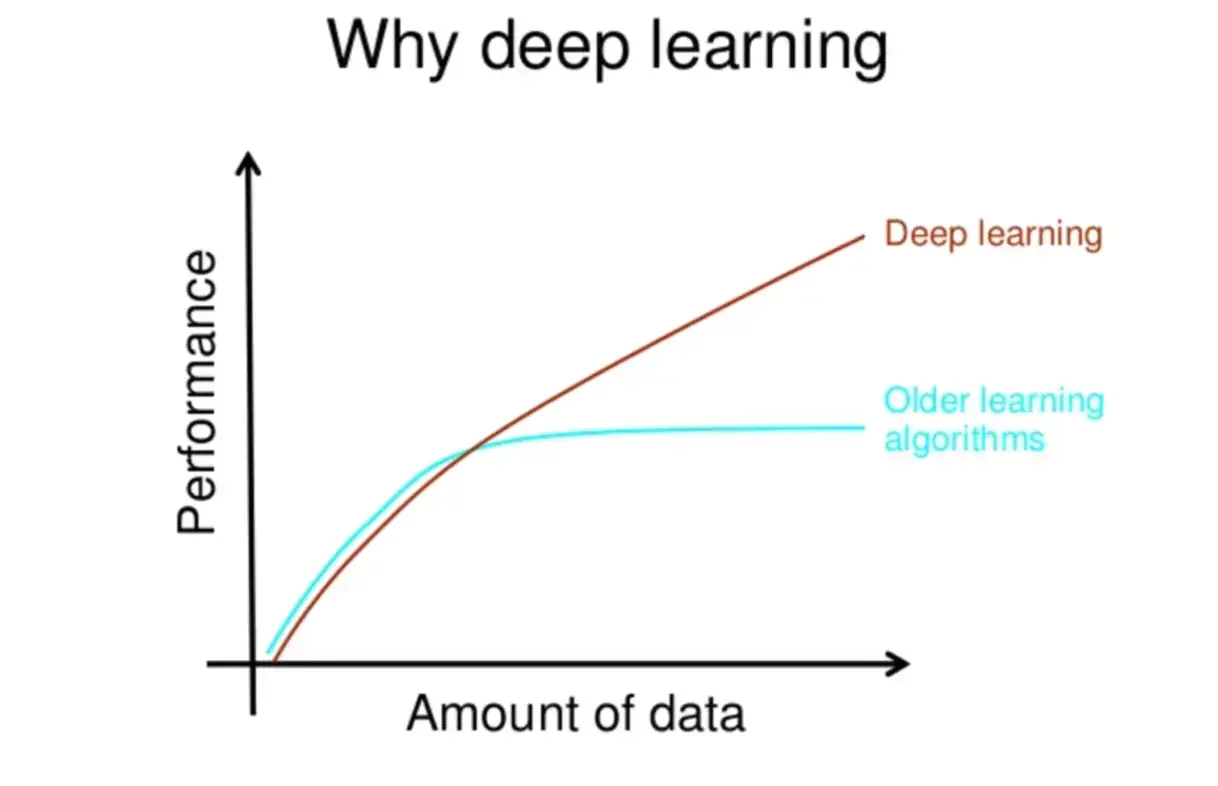
With the high performance on offer by Deep learning models, its the ideal choice for tech businesses.
Key Differences to Know in Deep Learning vs. Machine Learning
Let’s look at the contrasts from a business lens.
Data and Complexity
The machine learning works best with small, structured datasets. Think about customer procurement history, demographic details, or transaction records. If your business is currently starting its AI journey, ML development services are a more cost-effective and efficient option. While deep learning thrives on a large scale, on unnecessary data such as images, audio, or lessons. This makes DL a preferred approach to cases of advanced use. Such as speech recognition, medical imaging, or individual virtual aids.
Connect it to Control, Speed, and Ownership
One of the main differences is how each approach handles feature extraction.
- Machine Learning requires humans (data scientists, analysts) to identify which data features matter most. For example, in predicting creditworthiness, features like income level, employment status, and credit history are engineered into the model. This makes ML models easier to interpret but more labor-intensive.
- Deep Learning, however, automates this process. The neural network identifies relevant features itself. This makes DL more scalable and powerful but requires greater computational resources.
Make the Business Consequence Transparent
- Machine Learning models are transparent. A decision tree or logistic regression model can be explained and audited. This makes ML suitable for industries where compliance and accountability are critical. Such as finance, insurance, or healthcare.
- Deep Learning models, with their layered neural networks, are often described as “black boxes.” They provide outstanding accuracy but little explanation of how the decision was reached. It makes them better suited for R&D-heavy functions where predictive power outweighs transparency. As per McKinsey Global Survey, 56% of businesses already use AI in at least one function.
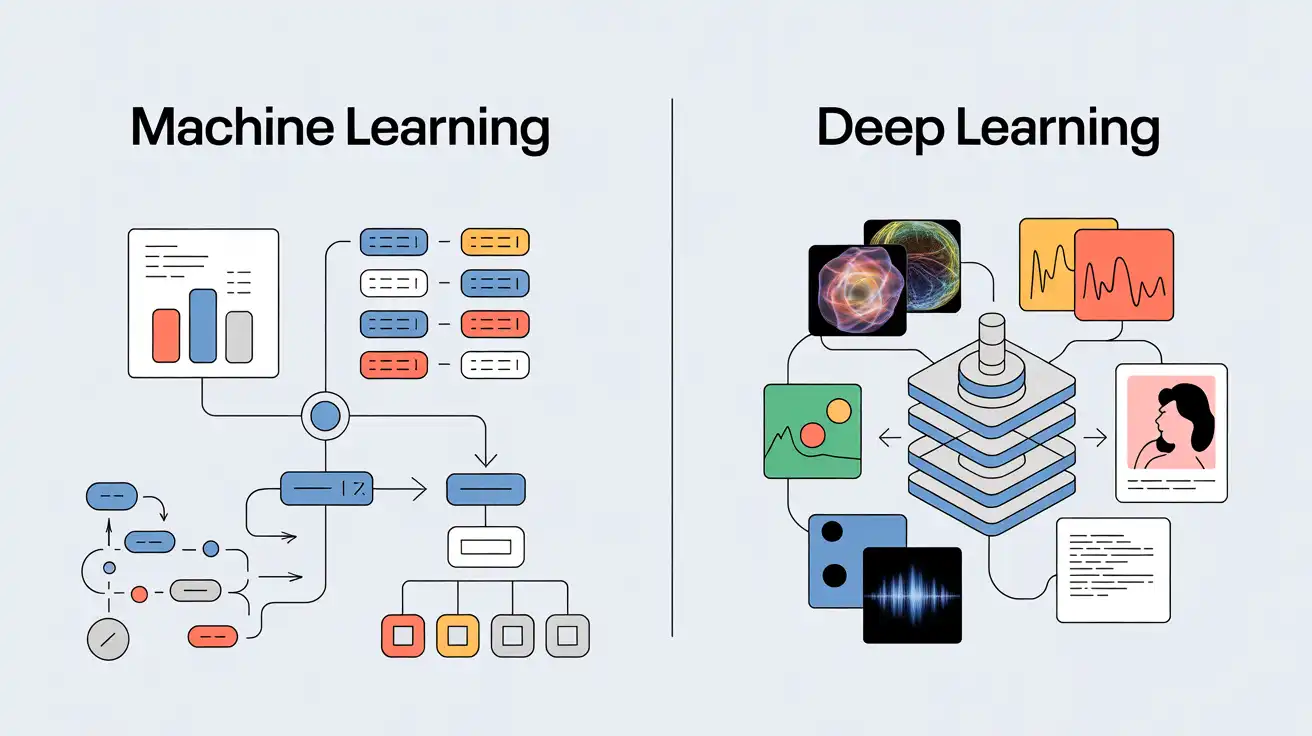
From a business perspective, the choice between ML and DL often comes down to whether accuracy, explainability, speed, or regulatory safety is the top priority.
Business Applications
Machine Learning Use business cases include:
- Personalized e-commerce recommendations
- Fraud detection in banking
- Predictive maintenance in manufacturing
- Targeted marketing campaigns
Deep Learning Use Cases:
- Self-driving vehicles
- Medical diagnostics from imaging data
- Voice assistants like Alexa and Siri
- Real-time translation tools
Why Machine Learning and Deep Learning Matter for Businesses?
Machine learning and deep learning are transforming how businesses operate by automating time-consuming manual tasks, delivering personalized customer experiences at scale, and strengthening data-driven decision-making. They also enhance cybersecurity by detecting anomalies and potential threats early, while improving overall operational efficiency and reducing costs. As AI adoption accelerates, it’s clear that by 2025, nearly every enterprise will rely on these technologies in some capacity. This further highlights just how essential they’ve become for sustainable growth and competitiveness.
Real-Life Business Examples
- Amazon’s Recommendation System: Uses machine learning to suggest products based on browsing and purchase behavior. This level of personalization not only drives higher sales but also strengthens customer loyalty by making shopping experiences more relevant.
- Slack’s Workflow Automation: Leverages AI to automatically route customer queries to the right teams, reducing response times and improving support efficiency. Faster resolutions lead to smoother operations and happier customers.
- Shopify’s Chat Support: Employs AI-powered chat assistance to engage customers in real time during checkout. By being available at the exact moment of decision-making it helps boost conversion rates and overall customer satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Business
The decision between ML and DL is not about which is better. It’s about aligning technology with your business needs, data availability, and resources.
Choose Machine Learning if:
- You work with structured datasets
- Interpretability and compliance are essential
- Resources are limited, but you want quick wins
Choose Deep Learning if:
- You manage massive unstructured datasets
- Predictive accuracy is a priority
- You’re investing in innovation-heavy areas like R&D or automation
Conclusion
Machine learning and deep learning aren’t rivals; they work best together. Machine learning handles structured data for faster, smarter decisions, while deep learning extracts insights from complex data like images or speech. Combined, they help businesses automate, predict, and grow more intelligently. The real question isn’t whether to use AI, but how quickly you can make it part of your strategy. Those who move first will lead the game.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Machine Learning relies on human-defined features and works well with structured data. Deep Learning uses neural networks to automatically extract features from unstructured data like images or text, requiring more data and computing power.
A. Choose ML when you have structured data, limited resources, or need transparency for compliance. It’s ideal for quick, interpretable insights like fraud detection or customer segmentation.
A. They automate tasks, personalize customer experiences, improve decision-making, detect threats early, and reduce costs—making them essential for growth and competitiveness in data-driven industries.




