This blog consists of various topics of SQL and their explanation with answers. There are 12 theoretical questions that are frequently asked in interviews for freshers level and below, there are 15 MCQs related to SQL Questions for practice.
This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Table of contents
- What is Database?
- What is DBMS?
- What is RDBMS, and how does it differ from a Database Management System (DBMS)?
- What are the Applications of SQL?
- Difference between SQL Vs DBMS?
- What is Subquery in SQL?
- 7 What is the SELECT Statement Role in SQL?
- What are the Subsets of SQL?
- Explain any 2 Subsets in SQL with their Definition
- What is JOINT in SQL and Explain any 2 Types?
- What is a Primary Key in SQL?
- What is a Foreign Key?
- SQL Questions (MCQ)
- Take away from these SQL Questions
What is Database?
A database is a system that stores, retrieves, and manipulates data. Databases are of various types small, medium, and large. Design and modeling approaches, often complex, are employed in creating various databases. Typically, a database is managed by a database management system (DBMS).
Common databases are structured with rows and columns, resembling a table, similar to Excel data. There are various types of databases:
- Relational databases
- Object-Oriented Databases
- Distributed databases
- Data warehouses
- NoSQL databases
- Graph databases
What is DBMS?
DBMS stands for Database Management System. The DBMS responsibility is to store, create, update and manage the databases. DBMS ensures well-organized data, free of loopholes, easily accessible to developers. It ensures a connection between databases and the end-users of applications or products.
What is RDBMS, and how does it differ from a Database Management System (DBMS)?
| RDBMS | DBMS |
| RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. | DBMS stands for Database Management System. |
| It stores the data in the rows & col in table format. | It stores the data in the format of files. |
| It is designed to handle large amounts of data. | It is designed to handle a small amount of data. |
| Multiple data elements are accessible together. | Individual access to data elements is possible. |
| RDBMS support multiple users. | DBMS doesn’t support multiple users. |
| A distributed database is supported. | A distributed database is not supported. |
| In RDBMS normalization is not achievable. | In DBMS normalization is achievable. |
What are the Applications of SQL?
- Writing data integration scripts by the developers and database administrator.
- Setting and running analytical queries on the regular basis and making new datasets from the original data.
- Retrieving subsets of information within an original database for analytics and visualization purposes
- Most common use is Adding, updating, and deleting rows and columns of data in a database
Difference between SQL Vs DBMS?
| SQL | DBMS |
| SQL stands for Structured Query Language. | DBMS stands for Database Management System. |
| It is a query language. | It is a database. |
| SQL is designed for managing the database | DBMS is designed for providing the security to database. |
| It allows the user to create a view of data. | It contains automatic backup and database recovery. |
| SQL consist of various types of Languages such as DDL, and DML. | It reduced the complexity of the relationship between the data. |
| For example:. SQL, SQL Server. | For example:, MySQL, Oracle |
What is Subquery in SQL?
What is the SELECT Statement Role in SQL?
The SELECT command is used to display the rows from the database based on the query. The SELECT command is a data manipulation language (DML) command
For example:. We have a student database for a school and we have multiple columns some are StuID, and StuName, and the query is to display the student name.
Query: SELECT * from student;
What are the Subsets of SQL?
- Data definition language (DDL): DDL consists of SQL commands which can be used for defining database schema. DDL deals with the description of the database, update, and delete of the database where it consists of commands like CREATE, ALTER, TRUNCATE, and COMMENT.
- Data manipulation language (DML): DML is used to manipulate the existing data in the database. The DML commands are SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, etc.
- Data control language (DCL): DCL controls the access to the data stored in the database and the DCL commands are GRANT and REVOKE.
- Transaction Control Language (TCL): TCL is used to deal with the transaction operations in the database. The TCL commands are COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SET TRANSACTION, SAVEPOINT, etc.

Explain any 2 Subsets in SQL with their Definition
There are 5 subsets in SQL:
1. Data Definition Language
DDL stands for Data Definition Language where the commands are used to define the database schema. DDL is mostly used to describe the database schema to developers and to create, and modify the overall structure of the database.
The examples of DDL commands are:
- CREATE – Using the create command we can create the database or its objects such as a table, index, function, and views.
- DROP – Using the drop command we can delete objects from the database.
- ALTER – Using the alter command we can change the structure of the database.
- TRUNCATE – Using the truncate command we can remove all the records from a table, including all spaces allocated for the records are removed.
- COMMENT – Using the comment command we can add comments to the data dictionary.
- RENAME – Using the rename command we can rename an object which exists in the database.
2. Data Manipulation Language
DML stands for Data Manipulation Language where the commands are used for manipulating the data in the database.
The examples of DML commands are:
- SELECT – Using the select command to retrieve data from the database.
- INSERT– Using the insert command to insert data into a table.
- UPDATE– Using the update command to update existing data within a table.
- DELETE– Using the delete command to delete records from a database table.
What is JOINT in SQL and Explain any 2 Types?
A JOIN clause is used to combine rows from more than one table based on the same column from both tables. The two tables are merged and we will retrieve new data from that.
Inner Join: Most of the common types of SQL is Inner Join. Inner Join will return all the rows from multiple tables when the condition is satisfied.
Syntax Inner Join:
SELECT * FROM Table_A JOIN Table_B; SELECT * FROM Table_A INNER JOIN Table_B;
Left Join: In Left Join of SQL only rows from the left table are returned and the union of left and right table where the condition is satisfied.
Syntax Left Join:
SELECT * FROM Table_A A LEFT JOIN Table_B B ON A.col = B.col;
Right Join: In Right Join of SQL all the rows from the right table are returned but only the matching rows from the left table where the join condition is fulfilled.
Syntax right Join:
SELECT * FROM Table_A A RIGHT JOIN Table_B B ON A.col = B.col;
Full Join: In Full join of SQL all the records are returned when there is a match in any of the tables. Therefore, it returns all the rows from the left-hand side table and all the rows from the right-hand side table.
Syntax Full Join:
SELECT * FROM Table_A A FULL JOIN Table_B B ON A.col = B.col;
There are a plethora of types of joins, as you can refer to below. Below is a cheat sheet for various types of JOINT in SQL.

What is a Primary Key in SQL?
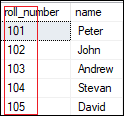
We can define a primary key in a student table as follows:
CREATE TABLE Student ( roll_number INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(45), );
What is a Foreign Key?
The foreign key is also known as the referencing key. We use a foreign key to link one or more tables together from the database.
A foreign key is often specified as a key that is related to the primary key of another table in simple terms it means that the foreign key field in one table refers to the primary key field of another table. It maintains referential integrity. ACID properties are maintained by the primary key-foreign key relationship. Foreign key also prevents actions that would destroy links between the child and parent tables from the database.
For example, we have student data of a university or college where the columns are roll number and name and we want to display the unique kids having their roll number. Here, the ROLL Number can be treated as the primary key for a student.
We can define a foreign key in a student table as follows:
CREATE TABLE Students ( roll_number INT NOT NULL name VARCHAR(255) LibraryID INT PRIMARY KEY (roll_number) FOREIGN KEY (Library_ID) REFERENCES Library(LibraryID) );
SQL Questions (MCQ)
Let’s explore some questions for SQL in theoretical and practical. There are 15 questions for SQL in the form of MCQ.
1. What are some commonly used RDBMS among the options provided?
C. HeidiSQL
D. All of the above
ANSWER: D (All of the above)
2. What is the full form of SQL?
A. Structured Query Language
B. Structured Query List
C. Sample Query Language
D. None of these.
ANSWER: A (Structured Query Language)
3. What command do we use to create a new table in SQL?
C. INSERT TABLE
D. SELECT TABLE
ANSWER: B (CREATE TABLE)
Explanation: CREATE TABLE function is used to create the table in SQL database.
4.Among the choices provided, which one does not qualify as a valid SQL type?
A. FLOAT
B. NUMERIC
C. DECIMAL
D. CHARACTER
ANSWER: C (DECIMAL)
Explanation: DECIMAL is not a valid SQL type because in SQL it is a numeric type.
5. What command from the options below is capable of deleting all rows from a table?
C. DROP
D. ALTER
ANSWER: B (TRUNCATE)
Explanation: TRUNCATE command is used to delete all the rows without removing the individual rows from the table. TRUNCATE statement is similar to the DELETE statement in SQL just without the WHERE clause in the query.
6. From the option which command is a part of Data Control Language?
C. Both
D. None of this
ANSWER: C (Both)
Explanation: REVOKE and GRANT are the commands for the Data control language.
7. What SQL function compares the similarities of two strings and returns the result as a 4-character code?
C. COCNAT
D. FIND
ANSWER: B(SOUNDEX)
8. Primary key can not be?
B. Not Null
C. Both Null and Not Null
D. Null
ANSWER: D(Null)
Explanation: A primary key is a field or the combination of fields that uniquely identify each record in the table. The primary key is a unique key as the table can have only one primary key and it can not be null.
9. How Many Primary keys can have in a table?
C. Depends on the Columns
D. Depends on the situation
ANSWER: A (Only 1)
Explanation: A primary key is a field or the combination of fields that uniquely identify each record in the table. The primary key is a unique key as the table can have only one primary key and it can not be null.
10. What are Rows of Relation Known as?
C. Entity
D. None of this
ANSWER: A(Tuple)
Explanation: The collection of rows & columns is called the table, whereas a table is known as the relation in the SQL therefore in a relation rows are called the tuples.
11. What does DDL stand for?
C. Data definition language
D. Detailed data language
ANSWER: C(Data definition language)
12. Identify the TCL commands among the options provided below.
A. COMMIT and ROLLBACK
B. UPDATE and INSERT
C. SELECT and INSERT
D. GRANT and COMMIT
ANSWER: A (COMMI and ROLLBACK)
13. In the command if we are not specifying ASC or DESC after a SQL ORDER BY clause, the result is displayed in which order?
A. DESC
B. ASC
C. NOT DEFINED FORMAT
ANSWER: B (ASC)
Explanation: In the command, if we are not specifying ASC or DESC after a SQL ORDER BY clause, the result is displayed in which order.
14. Which data manipulation command is used to combine the rows from one or more tables?
C. PRODUCT
D. MULTIPLY
ANSWER: A (JOIN)
15.Identify the command not included in SQL from the given options below.
C. CHECK
D. B and C
ANSWER: B (UNION)
Conclusion on SQL Questions
This blog has lots of questions about things like databases, SQL (Structure Query Language), and different types of joints. Begin by providing a definition, illustrate with an example, and conclude by presenting your answer using SQL syntax. This will show the interviewer that you really know your stuff.
Takeaway from these SQL Questions
I’ll present some intermediate-level questions frequently asked by interviewers, along with their answers. In the next series, there will be numerous questions based on coding for SQL.
So stay updated!








Hi, Is the below statement correct wrt to a RDBMS? "In RDBMS normalization is not achievable."
Hey Prashant, Thanks for pointing that out. The normalization terms got switched between the difference. RDBMS: RDBMS support normalization.. DBMS: DBMS does not support normalization.